
(a)
Interpretation:
The alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogen and the Noble gases in the periodic table need to be labeled.
Concept introduction:
Element is the basic unit of any substance which can combine with same or different elements to form molecules and compounds. Elements are composed of the same type of atoms therefore they exhibit unique physical and chemical properties.
The
(a)
Answer to Problem 3E
Explanation of Solution
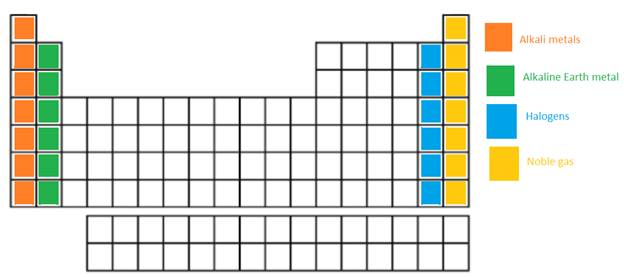
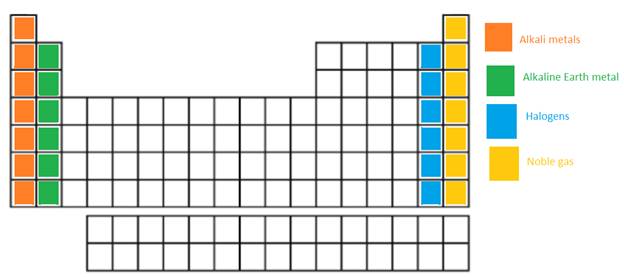
In the long form of periodic table; alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogen and the Noble gases are name of certain groups. In periodic table, the vertical columns are called as groups.
Alkali metal = The IA or 1st group is named as alkali metals as these metallic elements form alkaline oxides and hydroxides.
Alkaline earth metals = The IIA or 2nd group is named as Alkaline earth metals as these metallic elements form alkaline compounds and are also found in Earth crust.
Halogens = It is VIIA or 17th group of the periodic table. They are non-metallic elements.
Noble gases = These elements are placed in group 18th or also called as zero group. They are non-reactive and monoatomic gases.
The position of these elements in the periodic table is as follows:
(b)
Interpretation:
The main group elements, transition metal, Lanthanide and actinide needs to be shown in the periodic table.
Concept introduction:
Element is the basic unit of any substance which can combine with same or different elements to form molecules and compounds. Elements are composed of same type of atoms therefore they exhibit unique physical and chemical properties.
The chemical reaction of two or more elements leads to the formation of new molecules and compounds.
(b)
Answer to Problem 3E
Explanation of Solution
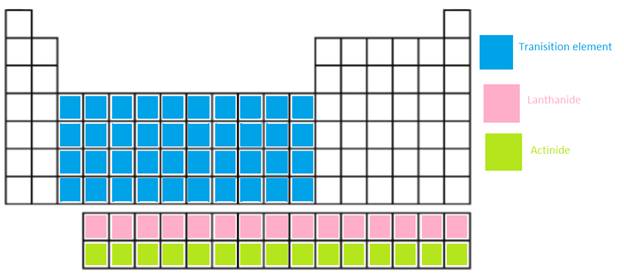
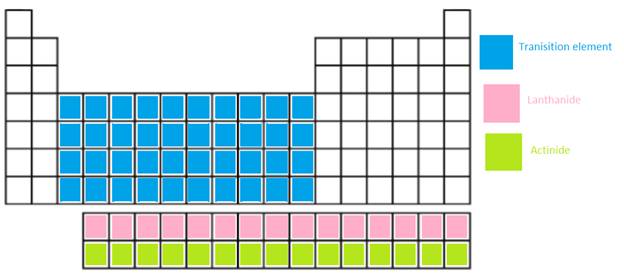
In periodic table, the vertical columns are called as groups and horizontal rows are period.
Transition metal =
Lanthanide = These are the f-block elements which are placed at the bottom of main body. It is a series of 14 elements where electrons are filled in 4f orbitals.
Actinide = These are the f-block elements which are placed at the bottom of main body. It is series of 14 elements where electrons are filled in 5f orbitals.
The position of these elements in the periodic table is given below:
Chapter U1 Solutions
Living by Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
- 2. Calculate the branching ratio of the reaction of the methyl peroxy radical with either HO, NO 298K) (note: rate constant can be found in the tropospheric chemistry ppt CH,O,+NO-HCHO+HO, + NO, CH₂O+HO, CH₂00H +0₂ when the concentration of hydroperoxyl radical is DH01-1.5 x 10 molecules and the nitrogen oxide maxing ratio of 10 ppb when the concentration of hydroperoxyl radicalis [H0] +1.5x10 molecules cm" and the nitrogen oxide mixing ratio of 30 p Under which condition do you expect more formaldehyde to be produced and whyarrow_forwardIndicate the product of the reaction of benzene with 1-chloro-2,2-dimethylpropane in the presence of AlCl3.arrow_forwardIn what position will N-(4-methylphenyl)acetamide be nitrated and what will the compound be called.arrow_forward
- DATA: Standard Concentration (caffeine) mg/L Absorbance Reading 10 0.322 20 0.697 40 1.535 60 2.520 80 3.100arrow_forwardIn what position will p-Toluidine be nitrated and what will the compound be called.arrow_forwardIn what position will 4-methylbenzonitrile be nitrated and what will the compound be called.arrow_forward
- In what position will benzenesulfonic acid be nitrated?arrow_forwardIf compound A reacts with an excess of methyl iodide and then heated with aqueous Ag₂O, indicate only the major products obtained. Draw their formulas. A Harrow_forwardExplanation Check 1:01AM Done 110 Functional Groups Identifying and drawing hemiacetals and acetals In the drawing area below, create a hemiacetal with 1 ethoxy group, 1 propoxy group, and a total of 9 carbon atoms. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ✓ $ 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Sarrow_forward
- Write the systematic name of each organic molecule: CI structure CI CI Explanation CI ठ CI Check B ☐ 188 F1 80 name F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 60 F7 2arrow_forwardWrite the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure i HO OH Explanation Check name ☐ ☐arrow_forwardX 5 Check the box under each molecule that has a total of five ẞ hydrogens. If none of the molecules fit this description, check the box underneath the table. CI Br Br Br 0 None of these molecules have a total of five ẞ hydrogens. Explanation Check esc F1 F2 tab caps lock fn Q @2 A W # 3 OH O OH HO © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility IK F7 F7 F8 TA F9 F10 & 6 28 * ( > 7 8 9 0 80 F3 O F4 KKO F5 F6 S 64 $ D % 25 R T Y U பட F G H O J K L Z X C V B N M H control option command P H F11 F12 + || { [ command optionarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





