
A hot liquid flows along a V-groove in a solid whose top and side surfaces are well insulated and whose bottom surface is in contact with a coolant.
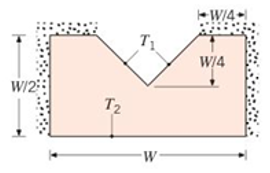
Accordingly. the V-groove surface is at a temperature
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Heating Ventilating and Air Conditioning: Analysis and Design
DeGarmo's Materials and Processes in Manufacturing
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (3rd Edition)
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
- In secondsarrow_forwardIn a gas manufacturing plants, they presented a horizontal tube in which a gas assumed to be ideal is flowing steadily. It was identified that no heat and work interaction was done. Also, there is a significant changes in the pipe diameter as well as velocity. If in case we select N2 as the flowing gas at 761.67 R at a velocity of 5.6 m/h, Calculate the temperature where the velocity us 180 km/h? Assume cp=7/2 R.arrow_forwardThe diagram shows a schematic for a thermometer based on the expansion of some fluid. There is a spherical reservoir of the fluid, with radius R, which is connected via a tube to a vertical section, with a circular cross section, radius r. a. assuming r << R, show that the change in fluid level in the tube is given by: 4 BR³ AT AL = 3 p² Where AT is the change in temperature and is the volumetric expansion coefficient of the fluid b. what properties should the system have to be most sensitive?arrow_forward
- 3- Consider the flow of fluid between two large parallel isothermal plates separated by a distance L. The upper plate is moving at a constant velocity of V and maintained at temperature T, .The lower plate is stationary and a constant heat flux ( q") is being applied from lower plate to fluid. By simplifying and solving the continuity, momentum and energy equations, obtain relations for temperature and velocity of fluid according to location. (Frictional heating due to viscous dissipation is negligible.) To L Fluid q"arrow_forwardA chromel–constantan thermocouple measuring the temperature of a fluid is connected by mistake with copper–constantan extension leads (such that the two constantan wires are connected together and the copper extension lead wire is connected to the chromel thermocouple wire). If the fluid temperature was actually 250 C and the junction between the thermocouple and extension leads was at 90 C, what e.m.f. would be measured at the open ends of the extension leads if the reference junction is maintained at 0 C? What fluid temperature would be deduced from this (assuming that the connection error was not known)?arrow_forwardPROBLEM: VB-17 BOOK: ENGINEERING THERMOFLUIDS, M. MASSOUDarrow_forward
- 1- Consider single-phase fluid flow in a 1-D horizontal reservoir.The reservoir is discretized using four blocks in the x-direction. A well located in block 3 produces at a rate of 400STB/D. All grid blocks have Ax-250ft, w-900ft, h-100 ft, and kx-270md. The FVF and the viscosity of the flowing fluid are 1.0 RB/STB and 2cP, respectively. Identify the interior and boundary blocks in this reservoir. Write the flow equation for block 3 and give the physical meaning of each term in the equation.arrow_forwardAssume that T0 = 1800 K is the temperature of fluid iron(which is roughly its melting point). From this temperature, the iron will becooled in a water reservoir at temperature T∞ = 300 K. After 20 minutesthe temperature has dropped to 1050 K. Find(a) the cooling rate h and(b) the explicit solution T(t) of the IVP (1)arrow_forwardOnly answer if you are 100% sure otherwise i will downvote... An ASTM B75 copper tube sheathes a heating element that is used to boil water at 1254 kPa. The copper tube is immersed horizontally in the water, and its surface is polished. The tube diameter and length are 5 mm and 9.5 cm, respectively. The maximum use temperature for ASTM B75 copper tube is 204°C. Determine the highest evaporation rate of water that can be achieved by the heater without heating the tube surface above the maximum use temperature. Use the property tables to calculate the properties of water at saturation temperature. The surface tension 0 at 190°C is 0.03995 N/m. Also, Csf 0.0130 and 10 for the boiling water on a polished copper surface. The highest evaporation rate of water is g/s?arrow_forward
- In regions far from the entrance, fluid flow through a circular pipe is one dimensional, and the velocity profile for laminar flow is given as u(r) = umax(1 - r2/R2), where R is the radius of the pipe, r is the radical distance from the center of the pipe, and umax is the maximum flow velocity, which occurs at the center. Obtain the following: A relation for the drag force applied by the fluid on a section of the pipe at length L The value of the drag force for water flow at 20°C with R = 0.07 m, L = 35 m, umax = 4 m/s, and μ = 0.0010 kg/m·sarrow_forwardI need answer within 20 minutes please please with my best wishesarrow_forwardWhat is true optionarrow_forward
 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
