
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether crotonate, a C4 species is a (1) hydroxy acid, (2) keto acid, (3) saturated acid, or (4) unsaturated acid has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
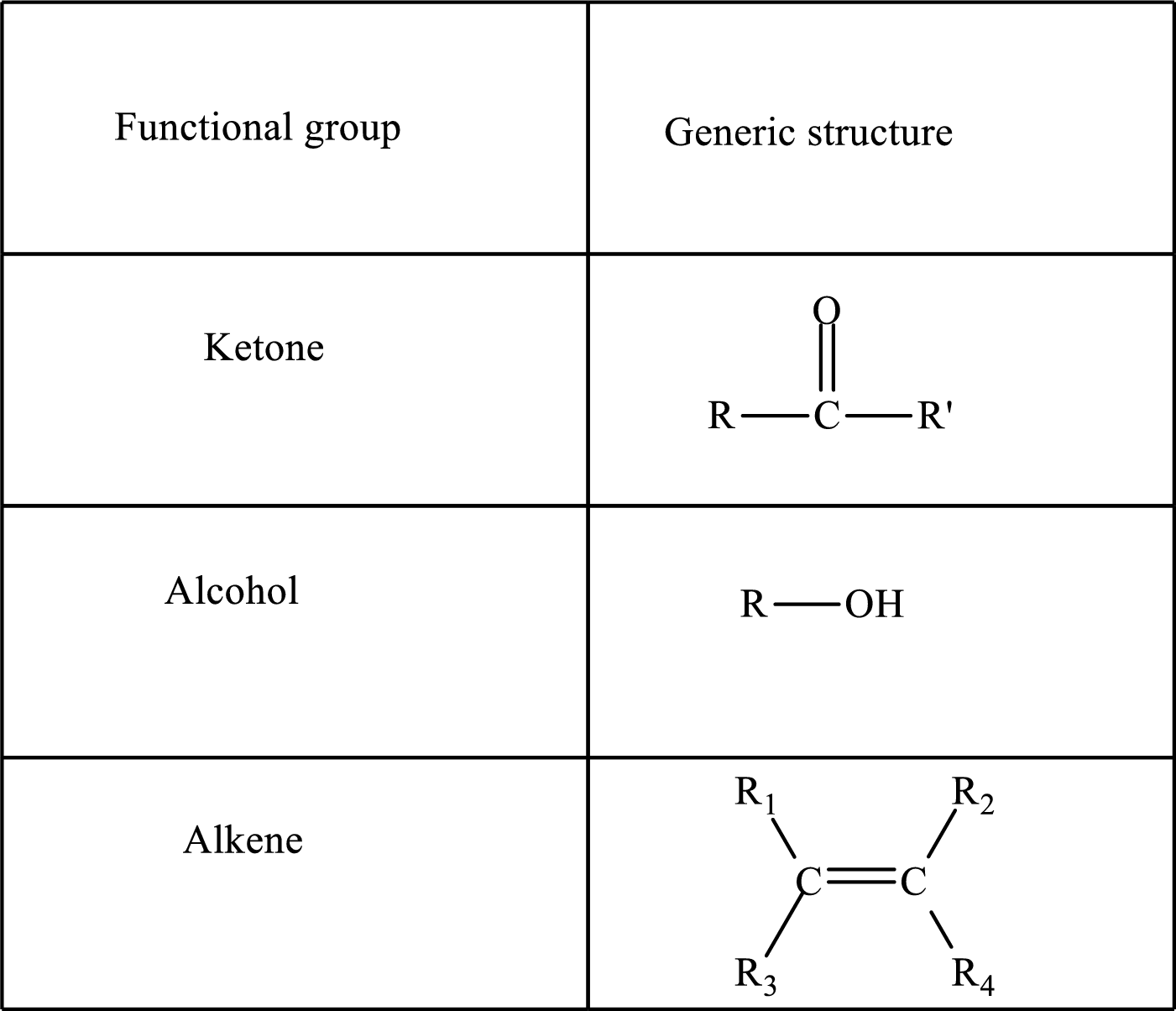
Here, R and R’ represent an alkyl group. In alkene, R1, R2, R3, and R4 can be the same or different or can be hydrogen.
Keto acid has a
A carboxylate group is formed by the removal of the acidic hydrogen from the carboxylic group. The conjugate base is formed by the removal of acidic hydrogen from the corresponding acid.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether oxaloacetate, a C4 species is a (1) hydroxy acid, (2) keto acid, (3) saturated acid, or (4) unsaturated acid has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Functional groups are defined as the group of atoms which are attached to the carbon backbone of organic compounds. These are generally heteroatoms which are attached to the parent hydrocarbon chain. Some examples of functional groups are as follows:
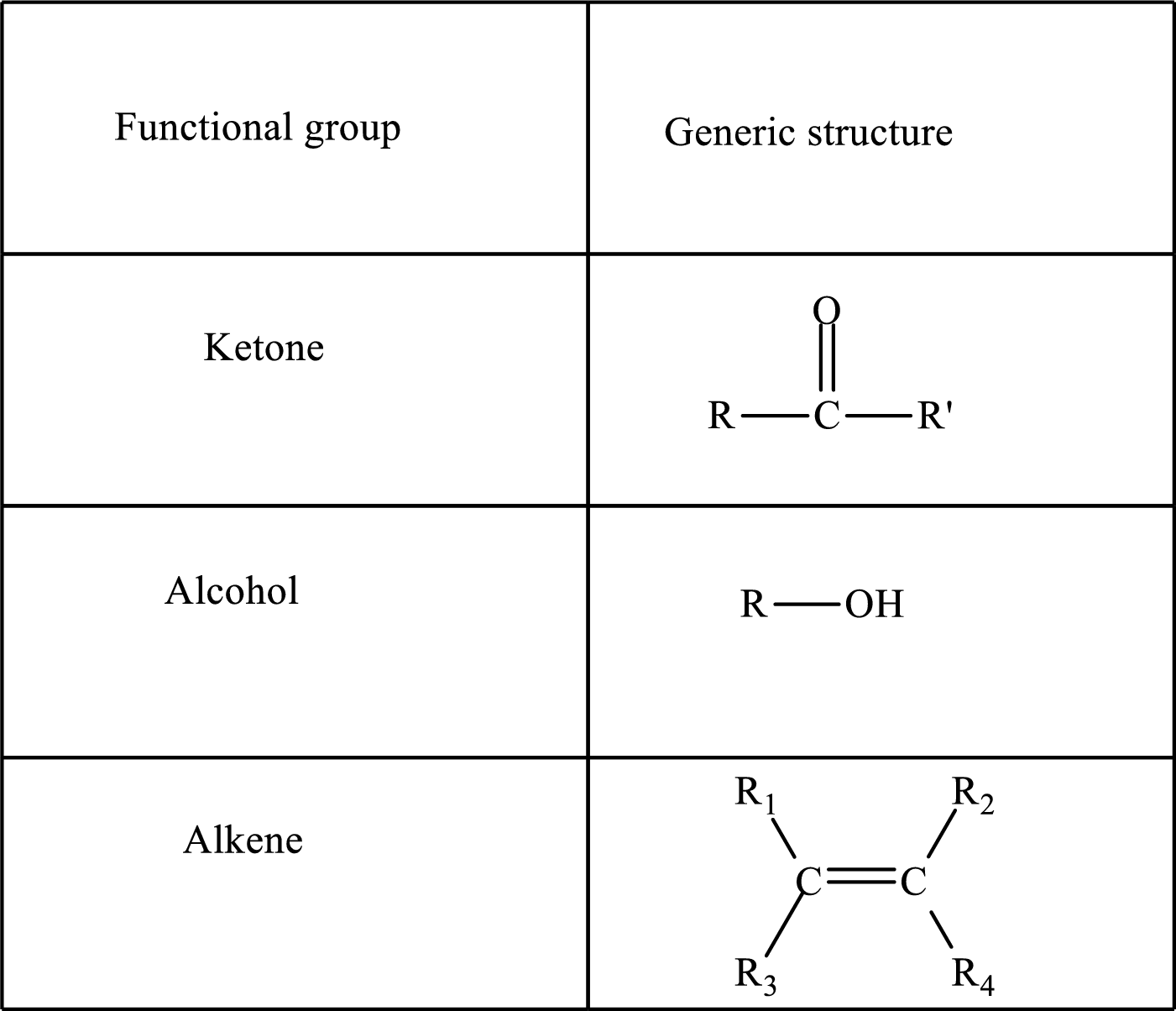
Here, R and R’ represent an alkyl group. In alkene, R1, R2, R3, and R4 can be the same or different or can be hydrogen. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that contain covalently bonded hydrogen and carbon atoms. Alkenes have a double bond, hence; they are unsaturated compounds.
Keto acid has a ketone and a carboxylic acid (-COOH) group. Hydroxy acid has a hydroxy (-OH) group and a carboxylic acid (-COOH) group. Saturated acids contain single bonds between carbon atoms and a carboxylic group. Unsaturated acid contains a double or triple bond between carbon atoms and a carboxylic group.
A carboxylate group is formed by the removal of the acidic hydrogen from the carboxylic group. The conjugate base is formed by the removal of acidic hydrogen from the corresponding acid.
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether acetoacetate, a C4 species is a (1) hydroxy acid, (2) keto acid, (3) saturated acid, or (4) unsaturated acid has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Functional groups are defined as the group of atoms which are attached to the carbon backbone of organic compounds. These are generally heteroatoms which are attached to the parent hydrocarbon chain. Some examples of functional groups are as follows:
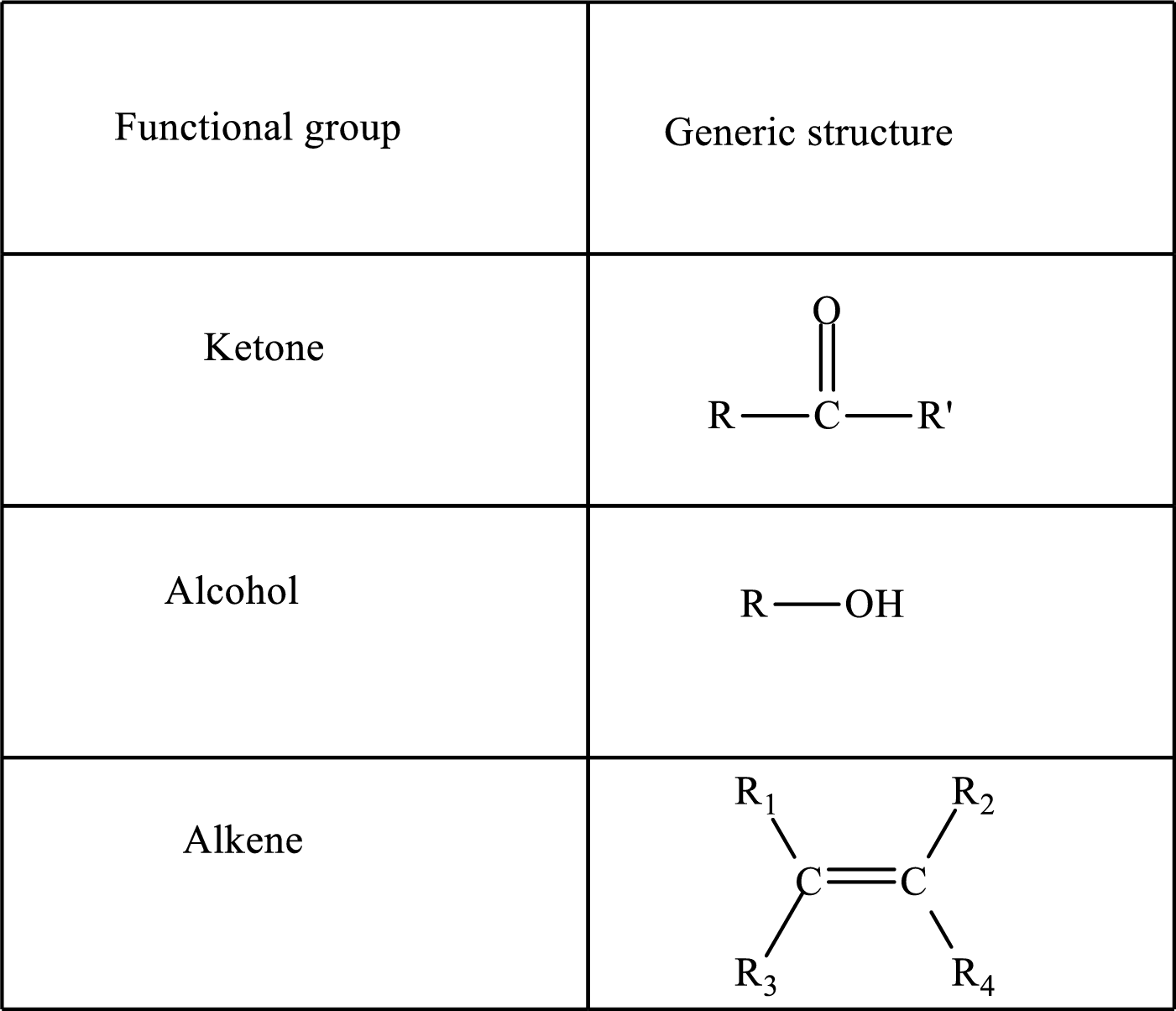
Here, R and R’ represent an alkyl group. In alkene, R1, R2, R3, and R4 can be the same or different or can be hydrogen. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that contain covalently bonded hydrogen and carbon atoms. Alkenes have a double bond, hence; they are unsaturated compounds.
Keto acid has a ketone and a carboxylic acid (-COOH) group. Hydroxy acid has a hydroxy (-OH) group and a carboxylic acid (-COOH) group. Saturated acids contain single bonds between carbon atoms and a carboxylic group. Unsaturated acid contains a double or triple bond between carbon atoms and a carboxylic group.
A carboxylate group is formed by the removal of the acidic hydrogen from the carboxylic group. The conjugate base is formed by the removal of acidic hydrogen from the corresponding acid.
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether malate, a C4 species is a (1) hydroxy acid, (2) keto acid, (3) saturated acid, or (4) unsaturated acid has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Functional groups are defined as the group of atoms which are attached to the carbon backbone of organic compounds. These are generally heteroatoms which are attached to the parent hydrocarbon chain. Some examples of functional groups are as follows:
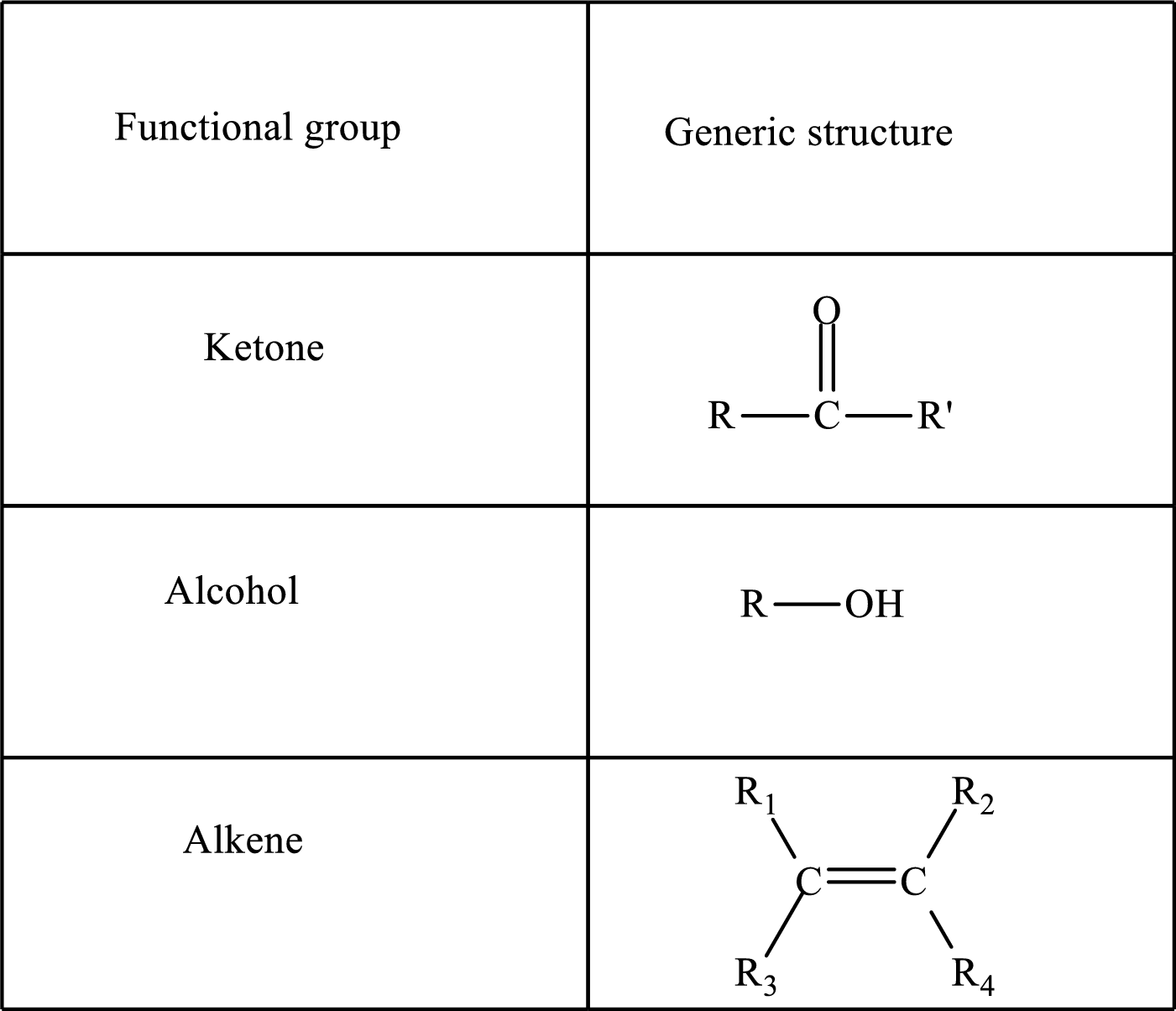
Here, R and R’ represent an alkyl group. In alkene, R1, R2, R3, and R4 can be the same or different or can be hydrogen. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that contain covalently bonded hydrogen and carbon atoms. Alkenes have a double bond, hence; they are unsaturated compounds.
Keto acid has a ketone and a carboxylic acid (-COOH) group. Hydroxy acid has a hydroxy (-OH) group and a carboxylic acid (-COOH) group. Saturated acids contain single bonds between carbon atoms and a carboxylic group. Unsaturated acid contains a double or triple bond between carbon atoms and a carboxylic group.
A carboxylate group is formed by the removal of the acidic hydrogen from the carboxylic group. The conjugate base is formed by the removal of acidic hydrogen from the corresponding acid.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 25 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
- Every chemist knows to ‘add acid to water with constant stirring’ when diluting a concentrated acid in order to keep the solution from spewing boiling acid all over the place. Explain how this one fact is enough to prove that strong acids and water do not form ideal solutions.arrow_forwardThe predominant components of our atmosphere are N₂, O₂, and Ar in the following mole fractions: χN2 = 0.780, χO2 = 0.21, χAr = 0.01. Assuming that these molecules act as ideal gases, calculate ΔGmix, ΔSmix, and ΔHmix when the total pressure is 1 bar and the temperature is 300 K.arrow_forwarddG = Vdp - SdT + μA dnA + μB dnB + ... so that under constant pressure and temperature conditions, the chemical potential of a component is the rate of change of the Gibbs energy of the system with respect to changing composition, μJ = (∂G / ∂nJ)p,T,n' Using first principles prove that under conditions of constant volume and temperature, the chemical potential is a measure of the partial molar Helmholtz energy (μJ = (∂A / ∂nJ)V,T,n')arrow_forward
- The vapor pressure of dichloromethane at 20.0 °C is 58.0 kPa and its enthalpy of vaporization is 32.7 kJ/mol. Estimate the temperature at which its vapor pressure is 66.0 kPa.arrow_forwardDraw the structure of A, the minor E1 product of the reaction. Cl Skip Part Check F1 esc CH_CH OH, D 3 2 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 80 R3 F4 F2 F3 @ 2 # $ 4 3 Q W 95 % KO 5 F6 A F7 × G ☐ Save For Later Sub 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy C ►II A A F8 F9 F10 FL 6 7 88 & * 8 9 LLI E R T Y U A S D lock LL F G H 0 P J K L Z X C V B N M 9 Harrow_forwardFrom the choices given, which two substances have the same crystal structure? (Select both) Group of answer choices ZnS (zincblende) Diamond TiO2 (rutile) ZnS (wurtzite)arrow_forward
- Potassium (K) blends with germanium (Ge) to form a Zintl phase with a chemical formula of K4Ge4. Which of the following elements would you expect potassium to blend with to form an alloy? Electronegativities: As (2.0), Cl (3.0), Ge (1.8), K (0.8), S (2.5), Ti (1.5) Group of answer choices Arsenic (As) Sulfur (S) Chlorine (Cl) Titanium (Ti)arrow_forwardConsider two elements, X and Z. Both have cubic-based unit cells with the same edge lengths. X has a bcc unit cell while Z has a fcc unit cell. Which of the following statements is TRUE? Group of answer choices Z has a larger density than X X has more particles in its unit cell than Z does X has a larger density than Z Z has a larger unit cell volume than Xarrow_forwardHow many particles does a face-centered cubic (fcc) unit cell contain? Group of answer choices 2 14 8 4arrow_forward
- V Highlight all of the carbon atoms that have at least one beta (B) hydrogen, using red for one ẞ hydrogen, blue for two ẞ hydrogens, and green for three ẞ hydrogens. If none of the carbon atoms have ẞ hydrogens, check the box underneath the molecule. ED X None of the carbon atoms have ẞ hydrogens. Explanation esc 2 Check * F1 F2 1 2 80 # 3 Q W tab A caps lock shift fn control F3 N S option O 694 $ F4 F5 F6 005 % E R D F LL 6 olo 18 Ar B © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility A DII F7 F8 87 & * 8 T Y U G H 4 F9 F10 ( 9 0 E F11 F12 உ J K L + || X C V B N M H H command option commandarrow_forwardConsider the reaction below and answer the following questions. Part 1 of 4 Br NaOCH2CH3 Identify the mechanisms involved. Check all that apply. SN 1 SN 2 E1 E2 None of the above Part 2 of 4 Skip Part Check esc F1 F2 lock 1 2 Q W A S #3 80 F3 F4 F5 F6 Save For © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms ˇˇ % & 4 5 6 89 7 IK A 分 བ F7 F8 F9 F * E R T Y U 8 9 D F G H K V B N M 0 Oarrow_forwardWhat kind of holes are not generated when solid-state particles adopt a close packing pattern? Group of answer choices tetrahedral cubic octahedral None of the other choices are correctarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





