
(a)
Interpretation:
Condensed structural formula has to be drawn for the given
Concept Introduction:
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- Expanded structural formula
- Condensed structural formula
- Skeletal structural formula
- Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.
(a)
Answer to Problem 16.29EP
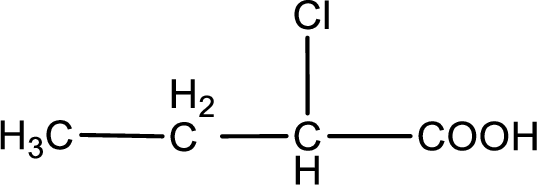
The condensed structural formula is,
Explanation of Solution
Given description about the carboxylic acid is
In the problem statement it is given how the carboxyl group has to be denoted. From the common name it is understood that the carboxylic acid is a four carbon monocarboxylic acid. The chlorine atom is substituted in the alpha carbon atom. Alpha carbon atom in carboxylic acid is the one that is attached to the carboxyl group. Therefore, the structure can be drawn as shown below,
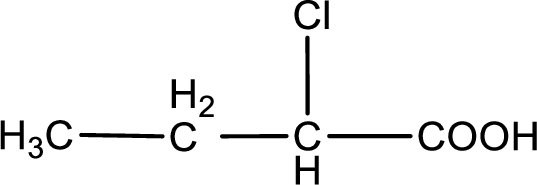
The condensed structural formula for the given carboxylic acid is drawn.
(b)
Interpretation:
Condensed structural formula has to be drawn for the given carboxylic acid.
Concept Introduction:
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- Expanded structural formula
- Condensed structural formula
- Skeletal structural formula
- Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.
(b)
Answer to Problem 16.29EP
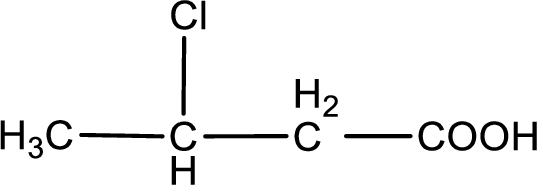
The condensed structural formula is,
Explanation of Solution
Given description about the carboxylic acid is
In the problem statement it is given how the carboxyl group has to be denoted. From the common name it is understood that the carboxylic acid is a four carbon monocarboxylic acid. The chlorine atom is substituted in the beta carbon atom. Beta carbon atom in carboxylic acid is the one that is the second carbon atom from the carboxyl group. Therefore, the structure can be drawn as shown below,
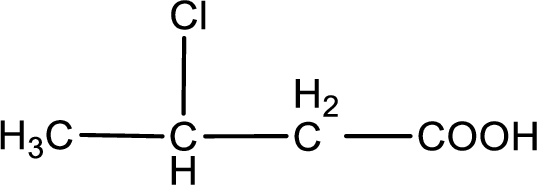
The condensed structural formula for the given carboxylic acid is drawn.
(c)
Interpretation:
Condensed structural formula has to be drawn for the given carboxylic acid.
Concept Introduction:
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- Expanded structural formula
- Condensed structural formula
- Skeletal structural formula
- Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.
(c)
Answer to Problem 16.29EP
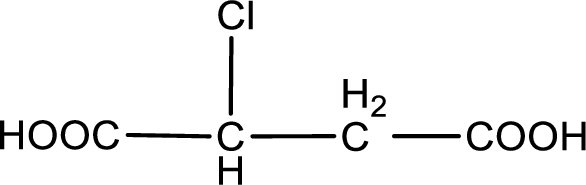
The condensed structural formula is,
Explanation of Solution
Given description about the carboxylic acid is chlorosuccinic acid.
In the problem statement it is given how the carboxyl group has to be denoted. From the common name it is understood that the carboxylic acid is a four carbon dicarboxylic acid. The chlorine atom is substituted in the either of the two carbon atoms as both the carbon atoms present between the two carboxyl groups are identical. Therefore, the structure can be drawn as shown below,
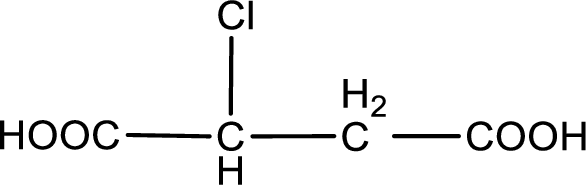
The condensed structural formula for the given carboxylic acid is drawn.
(d)
Interpretation:
Condensed structural formula has to be drawn for the given carboxylic acid.
Concept Introduction:
The structural representation of organic compound can be done in 2D and 3D. In two-dimensional representation, there are four types of representation in which an organic compound can be drawn. They are,
- Expanded structural formula
- Condensed structural formula
- Skeletal structural formula
- Line-angle structural formula
Structural formula which shows all the atoms in a molecule along with all the bonds that is connecting the atoms present in the molecule is known as Expanded structural formula.
Structural formula in which grouping of atoms are done and in which the central atoms along with the other atoms are connected to them are treated as group is known as Condensed structural formula.
Structural formula that shows the bonding between carbon atoms alone in the molecule ignoring the hydrogen atoms being shown explicitly is known as Skeletal structural formula.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula.
(d)
Answer to Problem 16.29EP
The condensed structural formula is,
Explanation of Solution
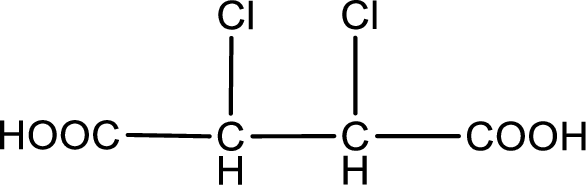
Given description about the carboxylic acid is
In the problem statement it is given how the carboxyl group has to be denoted. From the common name it is understood that the carboxylic acid is a four carbon dicarboxylic acid. The chlorine atom is substituted in the alpha carbon atom and beta carbon atom. Alpha carbon atom in carboxylic acid is the one that is attached to the carboxyl group and the next carbon attached to the alpha carbon atom is the beta carbon atom. Therefore, the structure can be drawn as shown below,
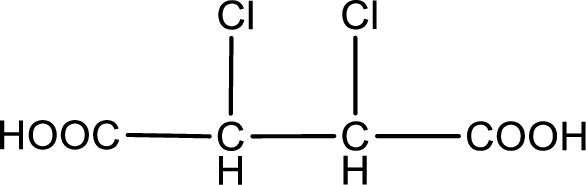
The condensed structural formula for the given carboxylic acid is drawn.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
- please draw in the answeres, thank youarrow_forwardA) What is being shown here?B) What is indicated by the RED arrow?C) What is indicated by the BLUE arrow?arrow_forwardPlease identify the curve shown below. What does this curve represent? Please identify A, B, C, D, and E (the orange oval). What is occurring in these regions?arrow_forward
- Please identify the test shown here. 1) What is the test? 2) What does the test indicate? How is it performed? What is CX? 3) Why might the test be performed in a clinical setting? GEN CZ CX CPZ PTZ CACarrow_forwardDetermine how much ATP would a cell produce when using fermentation of a 50 mM glucose solution?arrow_forwardDetermine how much ATP would a cell produce when using aerobic respiration of a 7 mM glucose solution?arrow_forward
- Determine how much ATP would a cell produce when using aerobic respiration to degrade one small protein molecule into 12 molecules of malic acid, how many ATP would that cell make? Malic acid is an intermediate in the Krebs cycle. Assume there is no other carbon source and no acetyl-CoA.arrow_forwardIdentify each of the major endocrine glandsarrow_forwardCome up with a few questions and answers for umbrella species, keystone species, redunant species, and aquatic keystone speciesarrow_forward
- 19. On the diagram below a. Label the three pictures as: DNA; polypeptide; or RNA. b. Label the arrows as: translation or transcription/RNA processing. c. Add the following details to the diagram. Promoter region TATA box Transcription start site Transcription terminator Intron (A,B,C,D) Exons (1,2,3,4,5) Splice sites 5' cap 5' UTR (untranslated region) 3' poly A tail 3' UTR (untranslated region) Translational start (AUG) Translational stop (UGA, UAG, or UAA) N and C ends of polypeptide 0000arrow_forwardMatch the letter labels in the figure below to the terms. Some letter labels are not used. MNNNNNNIN M C B A M D F E H K G 8arrow_forwardThe diagram below illustrates a quorum sensing pathway from Staphylococcus aureus. Please answer the following questions. 1. Autoinduction is part of the quorum sensing system. Which promoter (P2 or P3) is critical for autoinduction? 2)This staphylococcus aureus grows on human wounds, causing severe infections. You would like to start a clinical trial to treat these wound infections. Please describe: a) What molecule do you recommend for the trial. Why? b) Your trial requires that Staphylococcus aureus be isolated from the wound and submitted to genome sequencing before admittance. Why? What are you testing for? 3) If a mutation arises where the Promoter P3 is constitutively active, how would that influence sensitivity to AIP? Please explain your rationale. 4) This pathway is sensitive to bacterial cell density. Describe two separate mutation that would render the pathway active independent of cell density. Briefly explain your rationale. Mutation 1 Mutation 2arrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage LearningEssentials of Pharmacology for Health ProfessionsNursingISBN:9781305441620Author:WOODROWPublisher:Cengage
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage LearningEssentials of Pharmacology for Health ProfessionsNursingISBN:9781305441620Author:WOODROWPublisher:Cengage





