
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
IUPAC name for the given compound has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
For naming an acid anhydride, it can be structurally viewed in a way that contains two carbonyl groups that is joined by a single oxygen atom. This can also be said as two acyl group joined by a single oxygen atom.
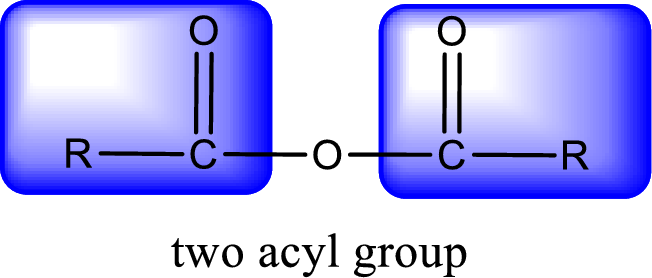
Rules to obtain IUPAC name and common name for an acid anhydride:
- IUPAC name and common name for Symmetric anhydride is obtained by replacing the acid present in the name of parent
carboxylic acid with the word anhydride. - IUPAC name and common name for mixed anhydride is obtained by using the names of the parent carboxylic acids arranged in alphabetical order that is followed by the word anhydride.
(b)
Interpretation:
IUPAC name for the given compound has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
For naming an acid chloride, it can be structurally viewed in a way that contains one acyl group with a chlorine atom bonded to the carbonyl group
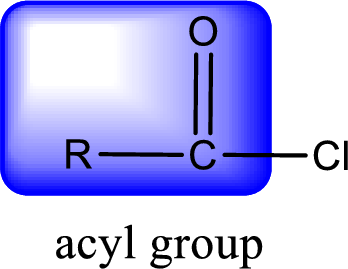
Rules to obtain IUPAC name and common name for an acid chloride:
- IUPAC name for acid chloride can be obtained from the parent carboxylic acid name. In the parent carboxylic acid name, the ending “-oic acid” is replaced by “-oyl chloride”.
- Common name for acid chloride can be obtained from the parent carboxylic acid name. In the parent carboxylic acid name, the ending “-ic acid” is replaced by “-yl chloride”.
(c)
Interpretation:
IUPAC name for the given compound has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
For naming an acid chloride, it can be structurally viewed in a way that contains one acyl group with a chlorine atom bonded to the carbonyl group
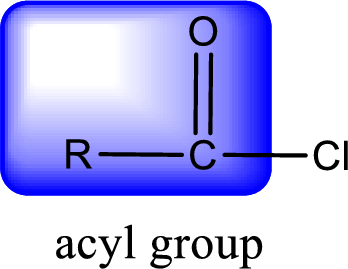
Rules to obtain IUPAC name and common name for an acid chloride:
- IUPAC name for acid chloride can be obtained from the parent carboxylic acid name. In the parent carboxylic acid name, the ending “-oic acid” is replaced by “-oyl chloride”.
- Common name for acid chloride can be obtained from the parent carboxylic acid name. In the parent carboxylic acid name, the ending “-ic acid” is replaced by “-yl chloride”.
(d)
Interpretation:
IUPAC name for the given compound has to be assigned.
Concept Introduction:
For naming an acid anhydride, it can be structurally viewed in a way that contains two carbonyl groups that is joined by a single oxygen atom. This can also be said as two acyl group joined by a single oxygen atom.
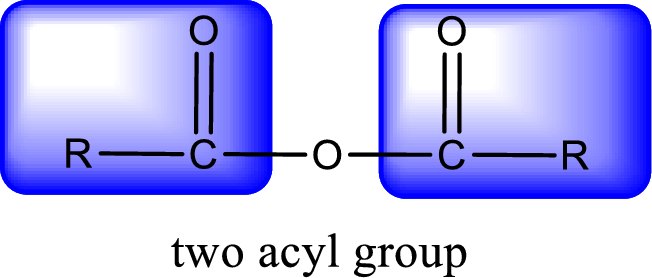
Rules to obtain IUPAC name and common name for an acid anhydride:
- IUPAC name and common name for Symmetric anhydride is obtained by replacing the acid present in the name of parent carboxylic acid with the word anhydride.
- IUPAC name and common name for mixed anhydride is obtained by using the names of the parent carboxylic acids arranged in alphabetical order that is followed by the word anhydride.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 16 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
- A. Draw the structure of each of the following alcohols. Then draw and name the product you would expect to produce by the oxidation of each. a. 4-Methyl-2-heptanol b. 3,4-Dimethyl-1-pentanol c. 4-Ethyl-2-heptanol d. 5,7-Dichloro-3-heptanolarrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this.arrow_forward
- Determine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this?arrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning


