
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Among the given designations, the one or more which may be correct for the given situation has to be chosen.
Concept Introduction:
Carbonyl groups are the one which contain a double bond between carbon and oxygen atom.
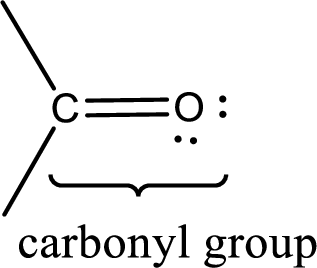
If a hydroxyl group is attached to a carbonyl group means it is known as carboxyl group. This can be represented as shown below,
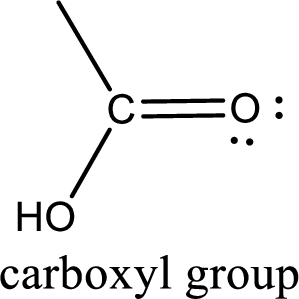
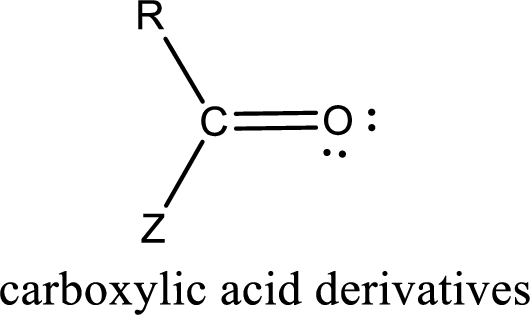
Carbon bonded to an oxygen atom through double bond is known as carbonyl group. The carbonyl group bonded to a R group means it is known as acyl group. If the acyl group is bonded to oxygen, nitrogen or halogen atom then the compound is known as acyl compound. If the acyl group is bonded to a carbon or hydrogen atom, then the compound is known as carbonyl compound. If the carbonyl carbon atom is bonded to a hydroxyl group then it is a carboxylic acid.
(b)
Interpretation:
Among the given designations, the one or more which may be correct for the given situation has to be chosen.
Concept Introduction:
Carbonyl groups are the one which contain a double bond between carbon and oxygen atom. Aldehydes and ketones possess this carbonyl functional group in it. The structural representation of a carbonyl group can be given as shown below,
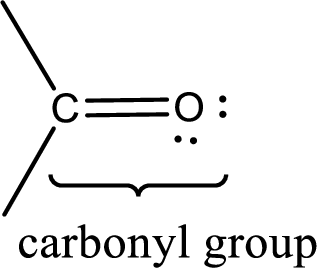
If a hydroxyl group is attached to a carbonyl group means it is known as carboxyl group. This can be represented as shown below,
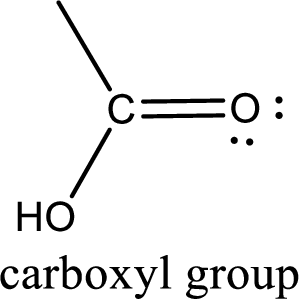
Carboxylic acid derivatives are the ones that are synthesized from or converted to a carboxylic acid. The generalized structural representation of carboxylic acid derivatives is shown below,
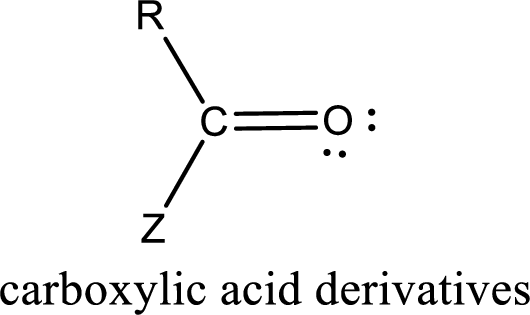
Carbon bonded to an oxygen atom through double bond is known as carbonyl group. The carbonyl group bonded to a R group means it is known as acyl group. If the acyl group is bonded to oxygen, nitrogen or halogen atom then the compound is known as acyl compound. If the acyl group is bonded to a carbon or hydrogen atom, then the compound is known as carbonyl compound. If the carbonyl carbon atom is bonded to a hydroxyl group then it is a carboxylic acid.
(c)
Interpretation:
Among the given designations, the one or more which may be correct for the given situation has to be chosen.
Concept Introduction:
Carbonyl groups are the one which contain a double bond between carbon and oxygen atom. Aldehydes and ketones possess this carbonyl functional group in it. The structural representation of a carbonyl group can be given as shown below,
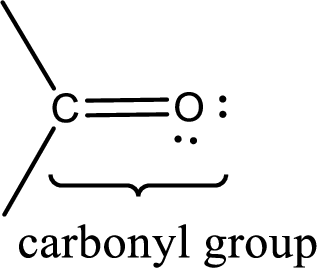
If a hydroxyl group is attached to a carbonyl group means it is known as carboxyl group. This can be represented as shown below,
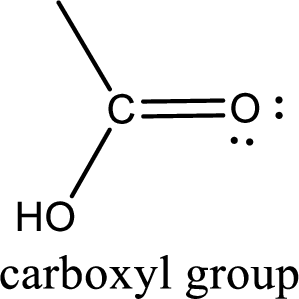
Carboxylic acid derivatives are the ones that are synthesized from or converted to a carboxylic acid. The generalized structural representation of carboxylic acid derivatives is shown below,
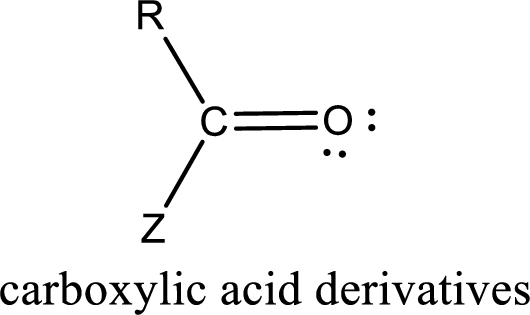
Carbon bonded to an oxygen atom through double bond is known as carbonyl group. The carbonyl group bonded to a R group means it is known as acyl group. If the acyl group is bonded to oxygen, nitrogen or halogen atom then the compound is known as acyl compound. If the acyl group is bonded to a carbon or hydrogen atom, then the compound is known as carbonyl compound. If the carbonyl carbon atom is bonded to a hydroxyl group then it is a carboxylic acid.
(d)
Interpretation:
Among the given designations, the one or more which may be correct for the given situation has to be chosen.
Concept Introduction:
Carbonyl groups are the one which contain a double bond between carbon and oxygen atom. Aldehydes and ketones possess this carbonyl functional group in it. The structural representation of a carbonyl group can be given as shown below,
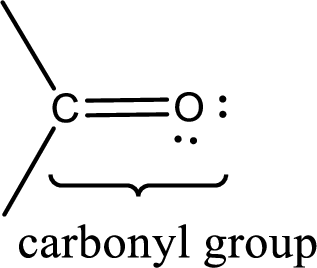
If a hydroxyl group is attached to a carbonyl group means it is known as carboxyl group. This can be represented as shown below,
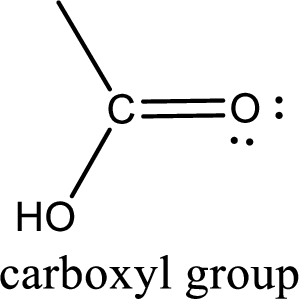
Carboxylic acid derivatives are the ones that are synthesized from or converted to a carboxylic acid. The generalized structural representation of carboxylic acid derivatives is shown below,
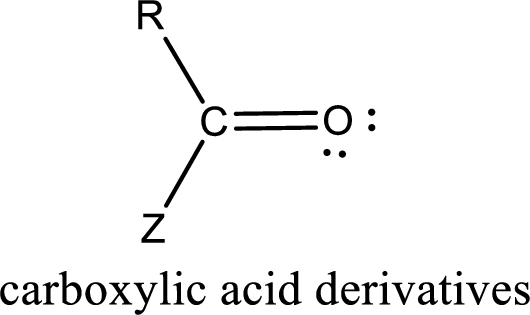
Carbon bonded to an oxygen atom through double bond is known as carbonyl group. The carbonyl group bonded to a R group means it is known as acyl group. If the acyl group is bonded to oxygen, nitrogen or halogen atom then the compound is known as acyl compound. If the acyl group is bonded to a carbon or hydrogen atom, then the compound is known as carbonyl compound. If the carbonyl carbon atom is bonded to a hydroxyl group then it is a carboxylic acid.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 16 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
- The quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. Calculating the moles of HI per kJ of radiant energy can be decayed knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.arrow_forwardThe quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. Calculate the number of Einsteins absorbed per mole knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.arrow_forwardThe quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. How many moles of HI per kJ of radiant energy can be decayed knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.arrow_forward
- If the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 450 kJ, the number of Einsteins absorbed per 1 mole.arrow_forwardWhen propionic aldehyde in vapor form at 200 mmHg and 30°C is irradiated with radiation of wavelength 302 nm, the quantum yield with respect to the formation of CO is 0.54. If the intensity of the incident radiation is 1.5x10-3 W, find the rate of formation of CO.arrow_forwardDraw mechanismarrow_forward
- Does Avogadro's number have units?arrow_forwardExplain why the total E in an Einstein depends on the frequency or wavelength of the light.arrow_forwardIf the dissociation energy of one mole of O2 is 5.17 eV, determine the wavelength that must be used to dissociate it with electromagnetic radiation. Indicate how many Einstein's of this radiation are needed to dissociate 1 liter of O2 at 25°C and 1 atm of pressure.Data: 1 eV = 96485 kJ mol-1; R = 0.082 atm L K-1; c = 2.998x108 m s-1; h = 6.626x10-34 J s; NA = 6.022x 1023 mol-1arrow_forward
- Indicate the number of Einsteins that are equivalent to 550 kJ mol⁻¹ of absorbed energy (wavelength 475 nm).arrow_forwardIndicate the number of einsteins that are equivalent to 550 kJ mol⁻¹ of absorbed energy?arrow_forwardA unit used in photochemistry is the einstein. If 400 kJ mol-1 of energy has been absorbed, how many einsteins is this equivalent to?arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning 
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning





