
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The diagram which represents endothermic reaction needs to be identified.
Concept Introduction : Endothermic reaction is the reaction in which the energy is consumed by the reaction and exothermic reaction is the reaction in which energy is released by the reaction. For endothermic reaction heat is expressed as positive value and for exothermic reaction heat is expressed as negative value.
(a)
Answer to Problem 4E
The diagram which represents endothermic reaction is,
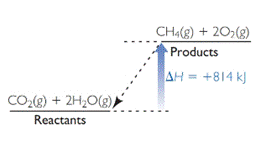
Explanation of Solution
Two diagrams are given. One is for the reaction of methane and oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water and
(b)
Interpretation: The substances having lowest potential energy are to be identified.
Concept Introduction : The energy in a system is a combination of potential and kinetic energy. The energy of motion is the kinetic energy and the stored energy within a physical energy is termed as potential energy.
(b)
Answer to Problem 4E
Explanation of Solution
For an exothermic reaction, potential energy of the system decreases as conversion of reactants to product occurs which results increase of kinetic energy. So for combustion reaction, products, that is,
(c)
Interpretation: What happens to kinetic energy when methane undergoes combustion reaction to form water and carbon dioxide needs to be explained.
Concept Introduction : The energy in a system is a combination of potential and kinetic energy. The energy of motion is the kinetic energy and the stored energy within a physical energy is termed as potential energy.
(c)
Answer to Problem 4E
Kinetic energy increases when methane undergoes combustion reaction to form water and carbon dioxide.
Explanation of Solution
Energy is conserved in every
(d)
Interpretation: The need of constant input of energy in the reverse reaction needs to be explained.
Concept Introduction: In a chemical process, energy is conserved. This means, net exchange of energy in a forward process is equal and opposite to exchange of net energy in the reverse process. If a forward reaction exothermic, the reverse reaction is endothermic.
(d)
Answer to Problem 4E
Reverse reaction is endothermic reaction. So, constant amount of energy must be supplied.
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of methane and oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water is an exothermic reaction. As the energy is conserved, the reverse reaction to form methane and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water is an endothermic reaction. An endothermic reaction always required supply of energy to result the reaction. So, there is need of constant input of energy in the reverse reaction.
(e)
Interpretation: The heat of the reaction needs to be calculated using the bond energies and the calculated value is to be compared with the value given the energy diagram.
Concept Introduction: To estimate the energy of an entire chemical reaction, the reaction is to considered as it takes place in two parts, that is, energy in for bond breaking and energy out for bond making. The energy of bond breaking is positive and bond making is negative.
(e)
Answer to Problem 4E
The calculated value of heat energy for the reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The combustion reaction of methane is,
Here,
Taking values from chapter 104,
In bond making bond energies are taken as negative values as energy added from system to the surroundings.
Net energy is the summation of energy of bond breaking and bond making.
The heat energy for the reaction given in the diagram is
Chapter U5 Solutions
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
- Determine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. NaN₃arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this?arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this?arrow_forward
- Use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to calculate pH of a buffer containing 0.050M benzoic acidand 0.150M sodium benzoate. The Ka of benzoic acid is 6.5 x 10-5arrow_forwardA. Draw the structure of each of the following alcohols. Then draw and name the product you would expect to produce by the oxidation of each. a. 4-Methyl-2-heptanol b. 3,4-Dimethyl-1-pentanol c. 4-Ethyl-2-heptanol d. 5,7-Dichloro-3-heptanolarrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forward
- Can I please get help with this.arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





