
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Heating curve of water must be drawn to show the different stages when water is heated from 10°C to 120°C.
Concept Introduction:
Heating curve is the graphical representation of phase change when a substance is heated.
Freezing point and boiling point of water is 0°C and 100°C respectively.
(a)
Answer to Problem SI8RE
Heating curve is shown below.
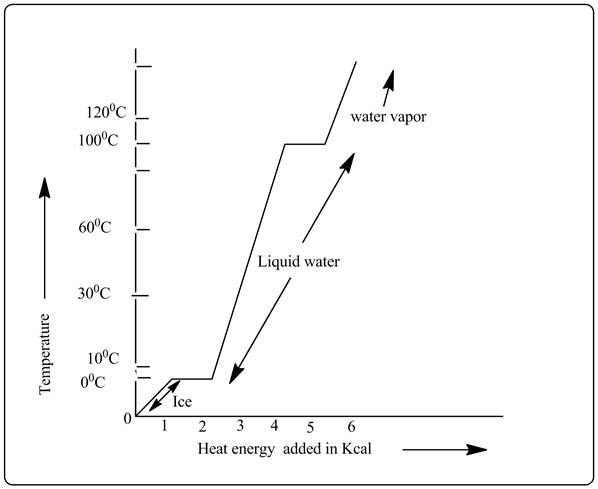
Explanation of Solution
In the heating curve it is shown that when water is heated from 10°C then at 100°C the phase changes from liquid water to water vapor and this is the boiling point. Then temperature is again increasing from 100°C to 120°C when further heat is given.
b)
Interpretation:
Amount of heat energy must be calculated which is transferred to water when the temperature is increased from 10°C to 120°C.
Concept Introduction:
Heat energy can be determined as follows:
Here m, s and t are mass, specific heat and temperature change respectively.
b)
Answer to Problem SI8RE
Heat energy is 5500 cal.
Explanation of Solution
Initial temperature of water is 10°C and final temperature is 120°C. So temperature increase t=110°C. Specific heat(s) of water is 1cal/g.
Mass of the given water is 50 g.
Thus heat required to increase the temperature from 10°C to 120°C can be calculated as follows:
c)
Interpretation:
Which part of the heating process involves most heat transfer must be found from the calculation and heating curve.
Concept Introduction:
Heat energy required for the increase of temperature (t) of mass in grams of any substance with specific heat s can be written as follow:
c)
Answer to Problem SI8RE
Heating of water from 10°C to 100°C involves most heat transfer.
Explanation of Solution
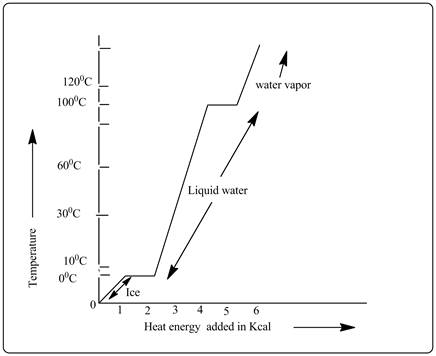
From the heating curve, it is clear that liquid water portion needs more heat as the graph is steeply rising.
The heat energy required for the increase of temperature of 50 g water from 10°C to 100°C
The heat energy required for the increase of temperature of 50 g water vapor from 100°C to 120°C
Chapter U5 Solutions
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
- Using Benzene as starting materid show how each of the Following molecules Contel Ve syntheswed CHI 9. b -50311 с CHY 503H Ночто d. อ •NOV e 11-0-650 NO2arrow_forwardThe molecule PYRIDINE, 6th electrons and is therefore aromatre and is Assigned the Following structure contering Since aromatk moleculoy undergo electrophilic anomatic substitution, Pyridine shodd undergo The Following reaction + HNO3 12504 a. write all of the possible Mononitration Products that could Result From this reaction 18. Bared upon the reaction mechanison determime which of these producty would be the major Product of the hegetionarrow_forwarda. Explain Why electron withdrawing groups tend to be meta-Directors. Your answer Should lyclude all apropriate. Resonance contributing Structures fo. Explain why -ll is an outho -tura drccton even though chlorine has a very High Electronegativityarrow_forward
- 9. Write Me product as well as the reaction Mechanism For each of the Following Vanctions +H₂504 4.50+ T C. +212 Fellz 237 b. Praw the potential energy Diagrams For each OF Mese Rauctions and account For any differences that appear in the two potential Puergy Diagrams which of here two reactions 19 Found to be Reversable, Rationalice your answer based upon the venation mechanisms and the potential energy diagrams.arrow_forward9. Write Me product as well as the reaction Mechanism For each of the Following Veritious +H2504 4.50+ + 1/₂ Felly ◎+ 7 b. Praw he potential energy Diagrams For each OF Mese Ronctions and account for any differences that appeak in the two potential Puergy Diagramsarrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Incorrect, 3 attempts remaining 1. excess Br2, NaOH 2. neutralizing workup Qarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





