
(a)
Interpretation:
The direction of energy transferred in the process of conversion of water to ice is to be discussed.
Concept introduction:
Whenever the state of a substance changes, a transfer of heat takes place.
Conversion of solid to liquid or liquid to gas requires heat and gas to liquid or liquid to solid releases heat.
(a)
Answer to Problem SI4RE
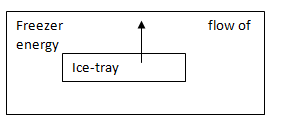
Energy is transferred from water to the freezer.
Explanation of Solution
When the water is in a liquid form in the freezer, it is converted to ice which is a solid form. A fixed amount of energy is released when liquid is converted to solid. So, there is a transfer of energy from water to the freezer.
(b)
Interpretation:
The energy transferred in the process of conversion of water to ice is whether endothermic or exothermic for ice tray is to be discussed.
Concept introduction:
Whenever the state of a substance changes, a transfer of heat takes place.
Conversion of solid to liquid or liquid to gas requires heat and gas to liquid or liquid to solid releases heat.
A process is endothermic when there is an absorption of heat and exothermic when there is a release of heat.
(b)
Answer to Problem SI4RE
The process is exothermic for the ice tray.
Explanation of Solution
When the water is in a liquid form in the freezer, it is converted to ice which is a solid form. A fixed amount of energy is released when liquid is converted to solid. So, there is a transfer of energy from water to the freezer. So, the process is exothermic by virtue of tray.
(c)
Interpretation:
The amount of heat transferred for one ice cube is to be calculated.
Concept introduction:
Whenever the state of a substance changes, a transfer of heat takes place.
Conversion of solid to liquid or liquid to gas requires heat and gas to liquid or liquid to solid releases heat.
A process is endothermic when there is an absorption of heat and exothermic when there is a release of heat.
The amount of heat released when 1 mol of water freezes is called enthalpy of freezing.
(c)
Answer to Problem SI4RE
Amount of heat released
Explanation of Solution
The heat released when 1 mol water freezes
Density of water=
Therefore,
Thus,heat released when
So, heat released when
(d)
Interpretation:
The amount of heat transferred for full ice tray is to be calculated.
Concept introduction:
Whenever the state of a substance changes, a transfer of heat takes place.
Conversion of solid to liquid or liquid to gas requires heat and gas to liquid or liquid to solid releases heat.
A process is endothermic when there is an absorption of heat and exothermic when there is a release of heat.
The amount of heat released when 1 mol of water freezes is called enthalpy of freezing.
(d)
Answer to Problem SI4RE
Amount of heat released
Explanation of Solution
The heat released when 1 mol water freezes
Density of water=
Therefore,
Thus,heat released when
So, heat released when
Number of moulds in ice tray
Therefore,
Heat released when full tray is frozen
Chapter U5 Solutions
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
- b) 8. Indicate whether the following carbocation rearrangements are likely to occur Please explain your rational using 10 words or less not likely to occur • The double bond is still in the Same position + Likely to oc occur WHY? -3 H3C Brave Chair Conformers. Draw the chair conformer of the following substituted cyclohexane. Peform a RING FLIP and indicate the most stable conformation and briefly explain why using 20 words or less. CI 2 -cobs ?? MUST INDICATE H -2 -2 Br EQ Cl OR AT Br H& most stable WHY? - 4arrow_forwardCH 12 Conformational Analysis. Draw all 6 conformers (one above each letter) of the compound below looking down the indicated bond. Write the letter of the conformer with the HIGHEST and LOWEST in energies on the lines provided. NOTE: Conformer A MUST be the specific conformer of the structure as drawn below -4 NOT HOH OH 3 Conformer A: Br OH A Samo Br H 04 Br H H3 CH₂ H anti stagere Br CH clipsed H Brott H IV H MISSING 2 -2 B C D E F X 6 Conformer with HIGHEST ENERGY: 13. (1 structure LOWEST ENERGY: Nomenclature. a) Give the systematic (IUPAC) name structure. b) Draw the corresponding to this name. HINT: Do not forget to indicate stereochemistry when applicable. a) ८८ 2 "Br {t༐B,gt)-bemn€-nehpརི་ཚ༐lnoa Parent name (noname) 4 Bromo Sub = 2-methylethyl-4 Bromo nonane b) (3R,4S)-3-chloro-4-ethyl-2,7-dimethyloctane # -2 -2arrow_forwardin the scope of the SCH4U course! please show all steps as im still learning how to format my answers in the format given, thank you!arrow_forward
- help me solve this HWarrow_forwardMolecules of the form AH2 can exist in two potential geometries: linear or bent. Construct molecular orbital diagrams for linear and bent CH2. Identify the relevant point group, include all of the appropriate symmetry labels and pictures, and fill in the electrons. Which geometry would you predict to be more stable, and why? (Please draw out the diagram and explain)arrow_forwardIndicate the variation in conductivity with concentration in solutions of strong electrolytes and weak electrolytes.arrow_forward
- The molar conductivity of a very dilute solution of NaCl has been determined. If it is diluted to one-fourth of the initial concentration, qualitatively explain how the molar conductivity of the new solution will compare with the first.arrow_forwardWhat does the phrase mean, if instead of 1 Faraday of electricity, Q coulombs (Q/F Faradays) pass through?arrow_forwardWhat characteristics should an interface that forms an electrode have?arrow_forward
- For a weak acid AcH, calculate the dissociated fraction (alpha), if its concentration is 1.540 mol L-1 and the concentration [H+] is 5.01x10-4 mol L-1.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





