
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:The molecular view diagram of resulting mixture is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:The resulting solution formed by the mixing of two components having different chemical composition is known as mixture.The molecules are not uniformly distributed in water when slightly soluble compound is added to it.
(a)
Answer to Problem SV3RE
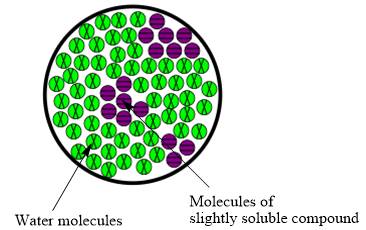
The molecular view diagram of resulting mixture is
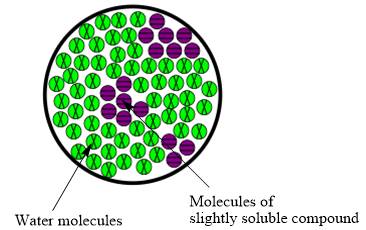
Explanation of Solution
When a slightly soluble compound is added to water only few molecules of slightly soluble compound comes in contact with water molecules. The bond between molecules of slightly soluble compound is not completely broken. The molecules form small patches in water.
(b)
Interpretation: The resulting mixture is homogeneous or heterogeneous is to be stated.
Concept introduction:The resulting solution formed by the mixing of two components having different chemical composition is known as mixture. The molecules are not uniformly distributed in water when slightly soluble compound is added to it.
(b)
Answer to Problem SV3RE
The resulting mixture of slightly soluble compound with water is heterogeneous mixture.
Explanation of Solution
The resulting solution formed by the mixing of two components having different chemical composition is known as mixture. When the molecules of solute are completely distributed in solvent then the mixture is classified as homogeneous mixture. However, when molecules are not uniformly distributed in solvent it is known as heterogeneous mixture. Therefore, the resulting mixture of slightly soluble compound with water is heterogeneous mixture.
Chapter U4 Solutions
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
- An einstein is the amount of energy needed to dissociate 1 mole of a substance. If we have 0.58 moles, do we need 0.58 einsteins to dissociate that substance?arrow_forwardIf the energy absorbed per mole of gas is 480 kJ mol-1, indicate the number of Einsteins per mole.Data: Energy of each photon: 0.7835x10-18 J.arrow_forwardIf the energy absorbed per mole of gas is 480 kJ mol-1, indicate the number of Einsteins per mole.arrow_forward
- The quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. Calculating the moles of HI per kJ of radiant energy can be decayed knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.arrow_forwardThe quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. Calculate the number of Einsteins absorbed per mole knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.arrow_forwardThe quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. How many moles of HI per kJ of radiant energy can be decayed knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.arrow_forward
- If the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 450 kJ, the number of Einsteins absorbed per 1 mole.arrow_forwardWhen propionic aldehyde in vapor form at 200 mmHg and 30°C is irradiated with radiation of wavelength 302 nm, the quantum yield with respect to the formation of CO is 0.54. If the intensity of the incident radiation is 1.5x10-3 W, find the rate of formation of CO.arrow_forwardDraw mechanismarrow_forward
- Does Avogadro's number have units?arrow_forwardExplain why the total E in an Einstein depends on the frequency or wavelength of the light.arrow_forwardIf the dissociation energy of one mole of O2 is 5.17 eV, determine the wavelength that must be used to dissociate it with electromagnetic radiation. Indicate how many Einstein's of this radiation are needed to dissociate 1 liter of O2 at 25°C and 1 atm of pressure.Data: 1 eV = 96485 kJ mol-1; R = 0.082 atm L K-1; c = 2.998x108 m s-1; h = 6.626x10-34 J s; NA = 6.022x 1023 mol-1arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





