
(a)
Interpretation: The number of orbitals in the 3p sublevel needs to be determined.
Concept introduction: An atomic orbital explains the position of an electron in an atom. An atomic orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons with opposite spins. The four basic atomic orbitals are s, p, d, and f . The number of electrons in each orbital can be explained with the help of quantum numbers. There are four quantum numbers; principal quantum number ( n ), azimuthal quantum number ( l ), magnetic quantum number (
(a)
Explanation of Solution
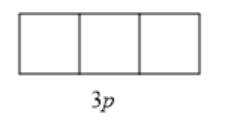
The given sublevel is 3p . Here, the principal quantum number (n) is 3. For p orbital, the value of azimuthal quantum number (l) is 1. Since possible orbitals
will be from -l to +l that is -1, 0, +1 thus, the number of orbitals will be 3. They are represented as follows:
(b)
Interpretation: The number of orbitals in the 2s sublevel needs to be determined.
Concept introduction: An atomic orbital explains the position of an electron in an atom. An atomic orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons with opposite spins. The four basic atomic orbitals are s, p, d, and f . The number of electrons in each orbital can be explained with the help of quantum numbers. There are four quantum numbers; principal quantum number ( n ), azimuthal quantum number ( l ), magnetic quantum number (
(b)
Explanation of Solution
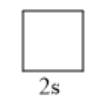
The given sublevel is 2s. Here, the principal quantum number (n) is 2. For s orbital, the value of azimuthal quantum number (l) is 0. Since possible orbitals
will be from -l to +l which is only 0, thus, the number of orbitals will be 1. They are represented as follows:
(c)
Interpretation: The number of orbitals in the 4p sublevel needs to be determined.
Concept introduction: An atomic orbital explains the position of an electron in an atom. An atomic orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons with opposite spins. The four basic atomic orbitals are s, p, d, and f . The number of electrons in each orbital can be explained with the help of quantum numbers. There are four quantum numbers; principal quantum number ( n ), azimuthal quantum number ( l ), magnetic quantum number (
(c)
Explanation of Solution
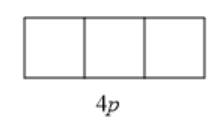
The given sublevel is 4p . Here, the principal quantum number (n) is 4. For p orbital, the value of azimuthal quantum number (l) is 1. Since possible orbitals
will be from -l to +l that is -1, 0, +1, thus, the number of orbitals will be 3. They are represented as follows:
(d)
Interpretation: The number of orbitals in the 3d sublevel needs to be determined.
Concept introduction: An atomic orbital explains the position of an electron in an atom. An atomic orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons with opposite spins. The four basic atomic orbitals are s, p, d, and f . The number of electrons in each orbital can be explained with the help of quantum numbers. There are four quantum numbers; principal quantum number ( n ), azimuthal quantum number ( l ), magnetic quantum number (
(d)
Explanation of Solution
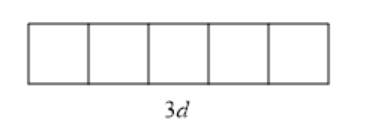
The given sublevel is 3d . Here, the principal quantum number (n) is 3. For d orbital, the value of azimuthal quantum number (l) is 2. Since possible orbitals
(e)
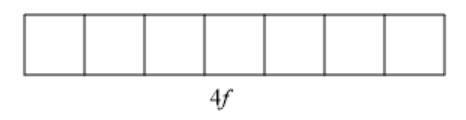
Interpretation: The number of orbitals in the 4f sublevel needs to be determined.
Concept introduction: An atomic orbital explains the position of an electron in an atom. An atomic orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons with opposite spins. The four basic atomic orbitals are s, p, d, and f . The number of electrons in each orbital can be explained with the help of quantum numbers. There are four quantum numbers; principal quantum number ( n ), azimuthal quantum number ( l ), magnetic quantum number (
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The given sublevel is 4f . Here, the principal quantum number (n) is 4. For f orbital, the value of azimuthal quantum number (l) is 3. Since possible orbitals
Chapter 5 Solutions
Chemistry 2012 Student Edition (hard Cover) Grade 11
- Could you crystallize one enantiomer of mandelic acid from a racemic mixture (using the typical achiral solvents found in our lab) without preparing a diastereomeric salt? Why or why not? No, because both enantiomers have the same solubility in achiral solvents. than the other. ооо Yes, because one enantiomer has a higher melting point No, because both enantiomers are liquids. Yes, because one enantiomer is more crystalline than the other.arrow_forwardIf the literature value of specific rotation for a chiral compound is -53.6°, what is the enantiomeric excess of a compound with a measured specific rotation of -40.5°?arrow_forwardThe process to determine the configuration, starts by placing the lowest priority substituent toward the back. If the substituents pointing forward decrease in priority in a clockwise order, the configuration is S. If the substituents decrease in priority in a counterclockwise order, the configuration is R. True Falsearrow_forward
- In the drawing area below, create a hemiacetal with 1 hydroxyl group, 1 methoxy group, and a total of 3 carbon atoms. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Explanation Check Х PO 18 Ar B © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forwardPredict the product of the reaction below (3 pts). hydrazine Ph H₂NNH2 KOH Write the mechanism for the above reaction using curved arrows to show electron movements. show all intermediates in the process (7 pts).arrow_forward↓ Feedback (8/10) Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Incorrect, 2 attempts remaining N H3O+ 0 × Select to Draw + V Retryarrow_forward
- 2. Calculate the branching ratio of the reaction of the methyl peroxy radical with either HO, NO 298K) (note: rate constant can be found in the tropospheric chemistry ppt CH,O,+NO-HCHO+HO, + NO, CH₂O+HO, CH₂00H +0₂ when the concentration of hydroperoxyl radical is DH01-1.5 x 10 molecules and the nitrogen oxide maxing ratio of 10 ppb when the concentration of hydroperoxyl radicalis [H0] +1.5x10 molecules cm" and the nitrogen oxide mixing ratio of 30 p Under which condition do you expect more formaldehyde to be produced and whyarrow_forwardIndicate the product of the reaction of benzene with 1-chloro-2,2-dimethylpropane in the presence of AlCl3.arrow_forwardIn what position will N-(4-methylphenyl)acetamide be nitrated and what will the compound be called.arrow_forward
- DATA: Standard Concentration (caffeine) mg/L Absorbance Reading 10 0.322 20 0.697 40 1.535 60 2.520 80 3.100arrow_forwardIn what position will p-Toluidine be nitrated and what will the compound be called.arrow_forwardIn what position will 4-methylbenzonitrile be nitrated and what will the compound be called.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





