
An aluminum heat sink
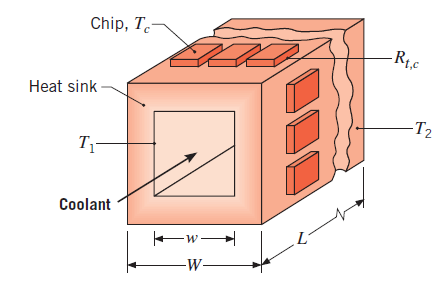
If
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Introduction to Heat Transfer
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
- CORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. I REALLY NEED FBD. The cantilevered spandrel beam shown whose depth tapers from d1 to d2, has a constant width of 120mm. It carries a triangularly distributed end reaction.Given: d1 = 600 mm, d2 = 120 mm, L = 1 m, w = 100 kN/m1. Calculate the maximum flexural stress at the support, in kN-m.2. Determine the distance (m), from the free end, of the section with maximum flexural stress.3. Determine the maximum flexural stress in the beam, in MPa.ANSWERS: (1) 4.630 MPa; (2) 905.8688 m; (3) 4.65 MPaarrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. I REALLY NEED FBD A concrete wall retains water as shown. Assume that the wall is fixed at the base. Given: H = 3 m, t = 0.5m, Concrete unit weight = 23 kN/m3Unit weight of water = 9.81 kN/m3(Hint: The pressure of water is linearly increasing from the surface to the bottom with intensity 9.81d.)1. Find the maximum compressive stress (MPa) at the base of the wall if the water reaches the top.2. If the maximum compressive stress at the base of the wall is not to exceed 0.40 MPa, what is the maximum allowable depth(m) of the water?3. If the tensile stress at the base is zero, what is the maximum allowable depth (m) of the water?ANSWERS: (1) 1.13 MPa, (2) 2.0 m, (3) 1.20 marrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. I NEED FBD A short plate is attached to the center of the shaft as shown. The bottom of the shaft is fixed to the ground.Given: a = 75 mm, h = 125 mm, D = 38 mmP1 = 24 kN, P2 = 28 kN1. Calculate the maximum torsional stress in the shaft, in MPa.2. Calculate the maximum flexural stress in the shaft, in MPa.3. Calculate the maximum horizontal shear stress in the shaft, in MPa.ANSWERS: (1) 167.07 MPa; (2) 679.77 MPa; (3) 28.22 MPaarrow_forward
- CORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. I REALLY NEED FBD. The roof truss shown carries roof loads, where P = 10 kN. The truss is consisting of circular arcs top andbottom chords with radii R + h and R, respectively.Given: h = 1.2 m, R = 10 m, s = 2 m.Allowable member stresses:Tension = 250 MPaCompression = 180 MPa1. If member KL has square section, determine the minimum dimension (mm).2. If member KL has circular section, determine the minimum diameter (mm).3. If member GH has circular section, determine the minimum diameter (mm).ANSWERS: (1) 31.73 mm; (2) 35.81 mm; (3) 18.49 mmarrow_forwardPROBLEM 3.23 3.23 Under normal operating condi- tions a motor exerts a torque of magnitude TF at F. The shafts are made of a steel for which the allowable shearing stress is 82 MPa and have diameters of dCDE=24 mm and dFGH = 20 mm. Knowing that rp = 165 mm and rg114 mm, deter- mine the largest torque TF which may be exerted at F. TF F rG- rp B CH TE Earrow_forward1. (16%) (a) If a ductile material fails under pure torsion, please explain the failure mode and describe the observed plane of failure. (b) Suppose a prismatic beam is subjected to equal and opposite couples as shown in Fig. 1. Please sketch the deformation and the stress distribution of the cross section. M M Fig. 1 (c) Describe the definition of the neutral axis. (d) Describe the definition of the modular ratio.arrow_forward
- using the theorem of three moments, find all the moments, I only need concise calculations with minimal explanations. The correct answers are provided at the bottomarrow_forwardMechanics of materialsarrow_forwardusing the theorem of three moments, find all the moments, I need concise calculations onlyarrow_forward
 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
