
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The types of carbonyl group in the given molecule should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Carbonyl group:
A carbon atom is double-bonded to an oxygen atom
If the carbonyl carbon is attached with two alkyl or aryl group is called as ketone, if the carbonyl carbon is attached with one hydrogen atom and one alkyl or aryl group is called as aldehyde.
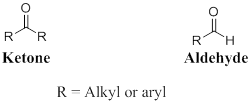
One
Carboxylic acid can be represented as,
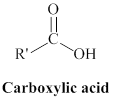
The derivatives of carboxylic acid are ester, amide.
One
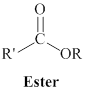
One
Amides can be represented as,
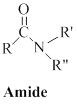
(b)
Interpretation:
The carbonyl group in the given molecule should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Functional group: They are certain substitutes in the organic molecules which are determine the characteristic reactions taking place in it.
Carbonyl group:
A carbon atom is double-bonded to an oxygen atom
If the carbonyl carbon is attached with two alkyl or aryl group is called as ketone, if the carbonyl carbon is attached with one hydrogen atom and one alkyl or aryl group is called as aldehyde.
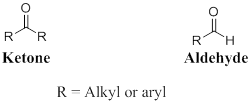
One
Carboxylic acid can be represented as,

The derivatives of carboxylic acid are ester, amide.
One
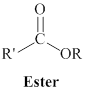
One
Amides can be represented as,

(c)
Interpretation:
The carbonyl group in the given molecule should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Functional group: They are certain substitutes in the organic molecules which are determine the characteristic reactions taking place in it.
Carbonyl group:
A carbon atom is double-bonded to an oxygen atom
If the carbonyl carbon is attached with two alkyl or aryl group is called as ketone, if the carbonyl carbon is attached with one hydrogen atom and one alkyl or aryl group is called as aldehyde.
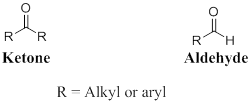
One
Carboxylic acid can be represented as,

The derivatives of carboxylic acid are ester, amide.
One
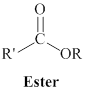
One
Amides can be represented as,

(d)
Interpretation:
The carbonyl group in the given molecule should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Functional group: They are certain substitutes in the organic molecules which are determine the characteristic reactions taking place in it.
Carbonyl group:
A carbon atom is double-bonded to an oxygen atom
If the carbonyl carbon is attached with two alkyl or aryl group is called as ketone, if the carbonyl carbon is attached with one hydrogen atom and one alkyl or aryl group is called as aldehyde.
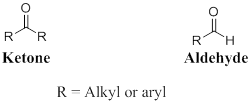
One
Carboxylic acid can be represented as,

The derivatives of carboxylic acid are ester, amide.
One
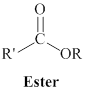
One
Amides can be represented as,

(e)
Interpretation:
The carbonyl group in the given molecule should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Functional group: They are certain substitutes in the organic molecules which are determine the characteristic reactions taking place in it.
Carbonyl group:
A carbon atom is double-bonded to an oxygen atom
If the carbonyl carbon is attached with two alkyl or aryl group is called as ketone, if the carbonyl carbon is attached with one hydrogen atom and one alkyl or aryl group is called as aldehyde.
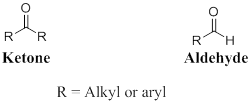
One
Carboxylic acid can be represented as,

The derivatives of carboxylic acid are ester, amide.
One
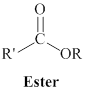
One
Amides can be represented as,

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 23 Solutions
General Chemistry: Atoms First
- If CH3COCH2CH(OCH3)2 (4,4-dimethoxy-2-butanone) and hydrazine react, two isomeric products are formed. State their structure and which will be the majority.arrow_forward+ Reset Provide the correct IUPAC name for the compound shown here. 4-methylhept-2-ene (Z)- (E)- 1-6-5-2-3-4- cyclo iso tert- sec- di tri hept hex oct meth eth pent ane yne ene ylarrow_forward+ Provide the correct IUPAC name for the compound shown here. Reset H3C H H C CH3 CH-CH3 1-3-methylpent ene trans- cis- 5-6-3-1-2-4- tert- tri sec- di cyclo iso but pent hex meth prop eth yl ane ene yne ☑arrow_forward
- drawing, no aiarrow_forwarddrawing, no aiarrow_forwardDraw the major organic product when each of the bellow reagents is added to 3,3-dimethylbutere. ✓ 3rd attempt Part 1 (0.3 point) H.C CH CH + 1. BHG THF 210 NaOH NJ 10000 Part 2 (0.3 point) HC- CH HC 2741 OH a Search 1. He|DA HO 2. NIBH さ 士 Ju See Periodic Table See Hint j = uz C H F F boxarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





