
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether hydration of propene will give one or two products has to be identified based on Markovnikov’s rule.
Concept Introduction:
In this reaction no atoms or group of atoms are removed. Instead the unsaturated bond is reduced to saturated bond. A general scheme for addition reaction of
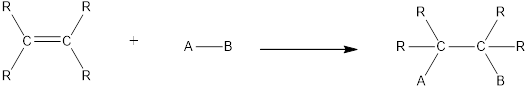
Addition reactions can be classified broadly into two types. They are asymmetrical addition reaction and symmetrical addition reaction.
Symmetrical addition reactions is the one in which the same atom or same group of atoms are added across the carbon‑carbon multiple bonds.
Unsymmetrical addition reactions is the one in which the different atom or different group of atoms are added across the carbon‑carbon multiple bonds.
Markovnikov’s rule:
When an unsymmetrical molecule of formula HQ to an unsymmeterical alkene, the hydrogen atom from HQ gets attached to the unsaturated carbon atom which has the most hydrogen atoms. In other words, it can be said that the hydrogen atom gets attached to the unsaturated carbon atom that is least substituted.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether hydration of 3-hexene will give one or two products has to be identified based on Markovnikov’s rule.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction in which an atom or a group of atoms are added to each carbon atom of a carbon‑carbon multiple bond in a hydrocarbon or hydrocarbon derivative is known as addition reaction.
In this reaction no atoms or group of atoms are removed. Instead the unsaturated bond is reduced to saturated bond. A general scheme for addition reaction of alkene can be given as shown below,

Addition reactions can be classified broadly into two types. They are asymmetrical addition reaction and symmetrical addition reaction.
Symmetrical addition reactions is the one in which the same atom or same group of atoms are added across the carbon‑carbon multiple bonds.
Unsymmetrical addition reactions is the one in which the different atom or different group of atoms are added across the carbon‑carbon multiple bonds.
Markovnikov’s rule:
When an unsymmetrical molecule of formula HQ to an unsymmeterical alkene, the hydrogen atom from HQ gets attached to the unsaturated carbon atom which has the most hydrogen atoms. In other words, it can be said that the hydrogen atom gets attached to the unsaturated carbon atom that is least substituted.
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether hydration of cyclopropene will give one or two products has to be identified based on Markovnikov’s rule.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction in which an atom or a group of atoms are added to each carbon atom of a carbon‑carbon multiple bond in a hydrocarbon or hydrocarbon derivative is known as addition reaction.
In this reaction no atoms or group of atoms are removed. Instead the unsaturated bond is reduced to saturated bond. A general scheme for addition reaction of alkene can be given as shown below,

Addition reactions can be classified broadly into two types. They are asymmetrical addition reaction and symmetrical addition reaction.
Symmetrical addition reactions is the one in which the same atom or same group of atoms are added across the carbon‑carbon multiple bonds.
Unsymmetrical addition reactions is the one in which the different atom or different group of atoms are added across the carbon‑carbon multiple bonds.
Markovnikov’s rule:
When an unsymmetrical molecule of formula HQ to an unsymmeterical alkene, the hydrogen atom from HQ gets attached to the unsaturated carbon atom which has the most hydrogen atoms. In other words, it can be said that the hydrogen atom gets attached to the unsaturated carbon atom that is least substituted.
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether hydration of cyclopentene will give one or two products has to be identified based on Markovnikov’s rule.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction in which an atom or a group of atoms are added to each carbon atom of a carbon‑carbon multiple bond in a hydrocarbon or hydrocarbon derivative is known as addition reaction.
In this reaction no atoms or group of atoms are removed. Instead the unsaturated bond is reduced to saturated bond. A general scheme for addition reaction of alkene can be given as shown below,

Addition reactions can be classified broadly into two types. They are asymmetrical addition reaction and symmetrical addition reaction.
Symmetrical addition reactions is the one in which the same atom or same group of atoms are added across the carbon‑carbon multiple bonds.
Unsymmetrical addition reactions is the one in which the different atom or different group of atoms are added across the carbon‑carbon multiple bonds.
Markovnikov’s rule:
When an unsymmetrical molecule of formula HQ to an unsymmeterical alkene, the hydrogen atom from HQ gets attached to the unsaturated carbon atom which has the most hydrogen atoms. In other words, it can be said that the hydrogen atom gets attached to the unsaturated carbon atom that is least substituted.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
- er your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward5.arrow_forward6.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,





