
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Chemical equation that shows reactants, product and catalyst needed for the reaction of ethene with chlorine has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
In this reaction no atoms or group of atoms are removed. Instead the unsaturated bond is reduced to saturated bond. A general scheme for addition reaction of
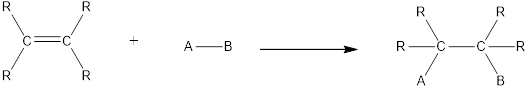
Halogenation reaction is an example of addition reaction. In this reaction, the halogen atoms are added across the double bonds. Chlorination and bromination are the most commonly used halogenation reaction. For halogenation reaction, no catalyst is required.
(b)
Interpretation:
Chemical equation that shows reactants, product and catalyst needed for the reaction of ethene with hydrogen chloride has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction in which an atom or a group of atoms are added to each carbon atom of a carbon‑carbon multiple bond in a hydrocarbon or hydrocarbon derivative is known as addition reaction.
In this reaction no atoms or group of atoms are removed. Instead the unsaturated bond is reduced to saturated bond. A general scheme for addition reaction of alkene can be given as shown below,

Asymmetrical addition reaction is the one in which two different atoms or group of atoms are substituted across the multiple bond resulting in the formation of product. No catalyst is required for this reaction.
(c)
Interpretation:
Chemical equation that shows reactants, product and catalyst needed for the reaction of ethene with hydrogen has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction in which an atom or a group of atoms are added to each carbon atom of a carbon‑carbon multiple bond in a hydrocarbon or hydrocarbon derivative is known as addition reaction.
In this reaction no atoms or group of atoms are removed. Instead the unsaturated bond is reduced to saturated bond. A general scheme for addition reaction of alkene can be given as shown below,

Hydrogenation is a type of addition reaction. In this reaction, hydrogen atoms are added across the multiple bonds present in organic molecule. In case of alkenes to undergo hydrogenation, heating the alkene with presence of catalyst such as nickel or platinum is required.
(d)
Interpretation:
Chemical equation that shows reactants, product and catalyst needed for the reaction of ethene with hydrogen bromide has to be written.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical reaction in which an atom or a group of atoms are added to each carbon atom of a carbon‑carbon multiple bond in a hydrocarbon or hydrocarbon derivative is known as addition reaction.
In this reaction no atoms or group of atoms are removed. Instead the unsaturated bond is reduced to saturated bond. A general scheme for addition reaction of alkene can be given as shown below,

Asymmetrical addition reaction is the one in which two different atoms or group of atoms are substituted across the multiple bond resulting in the formation of product. No catalyst is required for this reaction.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- What is the final product when hexanedioic acid reacts with 1º PCl5 and 2º NH3.arrow_forwardWhat is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forward
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning





