
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the given molecule has to be assigned including the prefix cis- or trans-.
Concept Introduction:
- The suffix –ane has to be replaced with the suffix –ene. This is used to indicate the presence of double bond.
- The longest continuous chain of carbon atoms has to be chosen that contains both carbon atoms of the double bond.
- The parent carbon chain has to be numbered in a way so that the numbering begins at the end near to the double bond. In case if the double bond is equidistant from both ends, then numbering has to be done from the end that is closer to substituents.
- The position of the double bond has to be given a single number which is lower‑numbered carbon atom that is present in the double bond.
- Suffixes like –diene, -triene, -tetrene, and so on are used when the compound contains more than one double bond.
- In case of cycloalkenes which do not have any substitution, the numbering is not needed to locate the double bond because the bond is assumed to be between the carbons 1 and 2.
- In case if substituents are present in cycloalkene, then the double‑bonded carbon
atoms are numbered 1 and 2 in a direction where the substituent gets the lower number. - If the cycloalkenes contain more than one double bond, then one double bond is assigned the numbers 1 and 2 followed by the other double bond so that the lowest number possible is given.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula. To indicate a double bond between carbon atom, double line is used.
If stereoisomers are possible for the alkene, the stereoinformation is shown in the IUPAC name by adding prefix cis- or trans- with respect to the groups present on the same side of double bond or opposite side of double bond.
(a)
Answer to Problem 2.50EP
The IUPAC name for the given compound is chloroethene.
Explanation of Solution
Given compound is,
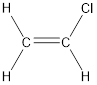
The longest continuous carbon chain present in the given compound is two carbon atoms. Hence, the parent
As the given compound contains a double bond, the suffix –ane is replaced by –ene. Therefore, the name obtained is ethene.
Numbering has to be given in a way that the carbon atoms present in the double bond gets the least numbering followed by least numbering to the substituents. Therefore, the name of the given compound is chloroethene. This is because both carbon atoms are identical.
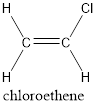
In order to include the stereo information, the groups attached to the double‑bonded carbon atoms are looked into.
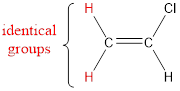
The carbon atom bears identical groups that are attached to the double bond. Therefore, stereoisomerism is not possible. Hence, the IUPAC name can be given as chloroethene.
IUPAC name for the given molecule is assigned.
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the given molecule has to be assigned including the prefix cis- or trans-.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC nomenclature for alkene: There are about eight rules to be followed in giving IUPAC name for alkene.
- The suffix –ane has to be replaced with the suffix –ene. This is used to indicate the presence of double bond.
- The longest continuous chain of carbon atoms has to be chosen that contains both carbon atoms of the double bond.
- The parent carbon chain has to be numbered in a way so that the numbering begins at the end near to the double bond. In case if the double bond is equidistant from both ends, then numbering has to be done from the end that is closer to substituents.
- The position of the double bond has to be given a single number which is lower‑numbered carbon atom that is present in the double bond.
- Suffixes like –diene, -triene, -tetrene, and so on are used when the compound contains more than one double bond.
- In case of cycloalkenes which do not have any substitution, the numbering is not needed to locate the double bond because the bond is assumed to be between the carbons 1 and 2.
- In case if substituents are present in cycloalkene, then the double‑bonded carbon atoms are numbered 1 and 2 in a direction where the substituent gets the lower number.
- If the cycloalkenes contain more than one double bond, then one double bond is assigned the numbers 1 and 2 followed by the other double bond so that the lowest number possible is given.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula. To indicate a double bond between carbon atom, double line is used.
If stereoisomers are possible for the alkene, the stereo information is shown in the IUPAC name by adding prefix cis- or trans- with respect to the groups present on the same side of double bond or opposite side of double bond.
(b)
Answer to Problem 2.50EP
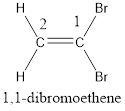
The IUPAC name for the given compound is cis-1,2-dibromoethene.
Explanation of Solution
Given compound is,
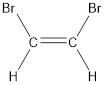
The longest continuous carbon chain present in the given compound is two carbon atoms. Hence, the parent alkane is ethane.
As the given compound contains a double bond, the suffix –ane is replaced by –ene. Therefore, the name obtained is ethene.
Numbering has to be given in a way that the carbon atoms present in the double bond gets the least numbering. This is followed by the substituents present in the given molecule. It is found that an bromine atom is present on the second carbon atom and bromine atom is present on the first carbon atom. As the substituents are same, prefix di- is added. Therefore, the name of the given compound is 1,2-dibromoethene.
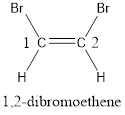
In order to include the stereo information, the groups attached to the double‑bonded carbon atoms are looked into.
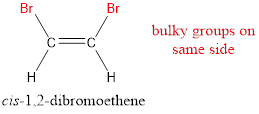
The bulky groups are present on same side of the double bond. Hence, the configuration of the given molecule is cis-. Therefore, the IUPAC name can be given as cis-1,2-dibromoethene.
IUPAC name for the given molecule is assigned.
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the given molecule has to be assigned including the prefix cis- or trans-.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC nomenclature for alkene: There are about eight rules to be followed in giving IUPAC name for alkene.
- The suffix –ane has to be replaced with the suffix –ene. This is used to indicate the presence of double bond.
- The longest continuous chain of carbon atoms has to be chosen that contains both carbon atoms of the double bond.
- The parent carbon chain has to be numbered in a way so that the numbering begins at the end near to the double bond. In case if the double bond is equidistant from both ends, then numbering has to be done from the end that is closer to substituents.
- The position of the double bond has to be given a single number which is lower‑numbered carbon atom that is present in the double bond.
- Suffixes like –diene, -triene, -tetrene, and so on are used when the compound contains more than one double bond.
- In case of cycloalkenes which do not have any substitution, the numbering is not needed to locate the double bond because the bond is assumed to be between the carbons 1 and 2.
- In case if substituents are present in cycloalkene, then the double‑bonded carbon atoms are numbered 1 and 2 in a direction where the substituent gets the lower number.
- If the cycloalkenes contain more than one double bond, then one double bond is assigned the numbers 1 and 2 followed by the other double bond so that the lowest number possible is given.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula. To indicate a double bond between carbon atom, double line is used.
If stereoisomers are possible for the alkene, the stereoinformation is shown in the IUPAC name by adding prefix cis- or trans- with respect to the groups present on the same side of double bond or opposite side of double bond.
(c)
Answer to Problem 2.50EP
The IUPAC name for the given compound is trans-2-butene.
Explanation of Solution
Given compound is,
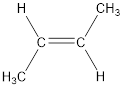
The longest continuous carbon chain present in the given compound is four carbon atoms. Hence, the parent alkane is butane.
As the given compound contains a double bond, the suffix –ane is replaced by –ene. Therefore, the name obtained is butene.
Numbering has to be given so that the double bond gets the least numbering. This gives the name as 2-butene.
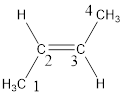
Regarding the stereo informaton, the groups attached to the double‑bonded carbon atom has to be considered.
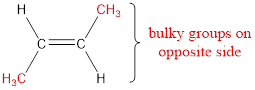
In this case, the methyl groups are present on opposite side of the double bond. Hence, trans- has to be included before the IUPAC name. The IUPAC name can be given as, trans-2-butene.
IUPAC name for the given molecule is assigned.
(d)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the given molecule has to be assigned including the prefix cis- or trans-.
Concept Introduction:
IUPAC nomenclature for alkene: There are about eight rules to be followed in giving IUPAC name for alkene.
- The suffix –ane has to be replaced with the suffix –ene. This is used to indicate the presence of double bond.
- The longest continuous chain of carbon atoms has to be chosen that contains both carbon atoms of the double bond.
- The parent carbon chain has to be numbered in a way so that the numbering begins at the end near to the double bond. In case if the double bond is equidistant from both ends, then numbering has to be done from the end that is closer to substituents.
- The position of the double bond has to be given a single number which is lower‑numbered carbon atom that is present in the double bond.
- Suffixes like –diene, -triene, -tetrene, and so on are used when the compound contains more than one double bond.
- In case of cycloalkenes which do not have any substitution, the numbering is not needed to locate the double bond because the bond is assumed to be between the carbons 1 and 2.
- In case if substituents are present in cycloalkene, then the double‑bonded carbon atoms are numbered 1 and 2 in a direction where the substituent gets the lower number.
- If the cycloalkenes contain more than one double bond, then one double bond is assigned the numbers 1 and 2 followed by the other double bond so that the lowest number possible is given.
Structural formula where a line represent carbon‑carbon bond and the carbon atom is considered to be present in each point and the end of lines is known as Line-angle structural formula. To indicate a double bond between carbon atom, double line is used.
If stereoisomers are possible for the alkene, the stereoinformation is shown in the IUPAC name by adding prefix cis- or trans- with respect to the groups present on the same side of double bond or opposite side of double bond.
(d)
Answer to Problem 2.50EP
The IUPAC name for the given compound is 1,1-dibromoethene.
Explanation of Solution
Given compound is,
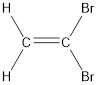
The longest continuous carbon chain present in the given compound is two carbon atoms. Hence, the parent alkane is ethane.
As the given compound contains a double bond, the suffix –ane is replaced by –ene. Therefore, the name obtained is ethene.
Numbering has to be given in a way that the carbon atoms present in the double bond gets the least numbering. Therefore, the name of the given compound is ethene. The substituent present on the longest carbon chain are bromine atoms that is present on the first carbon atom. Therefore, the name of the given molecule can be given as,
In order to include the stereo information, the groups attached to the double‑bonded carbon atoms are looked into.
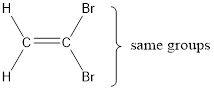
The bulky groups are present on same carbon atom of the double bond. Hence, isomerism is not possible. Therefore, the IUPAC name of the given molecule is 1,1-dibromoethene.
IUPAC name for the given molecule is assigned.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- 4. True or false: This skeletal structure represents a saturated fatty acid. Ini to 0 fale) me OH faistong starrow_forwardBy malonic or acetylacetic synthesis, synthesize 5-Methyl-2-hexanone (with the formulas of the compounds).arrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the first photo attached*arrow_forward
- Draw the formula for 3-chlorobenzoic acetic anhydride.arrow_forwardBy malonic or acetylacetic synthesis, synthesize 2-methylbutanoic acid (indicate the formulas of the compounds).arrow_forwardObtain 2-methylbutanoic acid by malonic or acetylacetic synthesis (indicate the formulas of the compounds involved).arrow_forward
- EFFICIENTS SAMPLE READINGS CONCENTRATIONS Pigiadient) TOMATO SAUCE (REGULAR) TOMATO (REDUCED SALT) TOMATO SAUCE (REGULAR) TOMATO (REDUCED SALT) 58 6.274 3.898 301.7 151.2 14150 5.277 3.865 348.9 254.8 B 5.136 3.639 193.7 85.9 605 4.655 3.041 308.6 199.6 05 5.135 3.664 339.5 241.4 0139 4.676 3.662 160.6 87.6 90148 5.086 3.677 337.7 242.5 0092 6.348 3.775 464.7 186.4 PART3 5.081 3.908 223.5 155.8 5.558 3.861 370.5 257.1 4.922 3.66 326.6 242.9 4.752 3.641 327.5 253.3 50 5.018 3.815 336.1 256.0 84 4.959 3.605 317.9 216.6 38 4.96 3.652 203.8 108.7 $3 5.052 3.664 329.8 239.0 17 5.043 3.767 221.9 149.7 052 5.058 3.614 331.7 236.4 5.051 4.005 211.7 152.1 62 5.047 3.637 309.6 222.7 5.298 3.977 223.4 148.7 5.38 4.24 353.7 278.2 5 5.033 4.044 334.6 268.7 995 4.706 3.621 305.6 234.4 04 4.816 3.728 340.0 262.7 16 4.828 4.496 304.3 283.2 0.011 4.993 3.865 244.7 143.6 AVERAGE STDEV COUNT 95% CI Confidence Interval (mmol/L) [Na+] (mg/100 mL) 95% Na+ Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)arrow_forwardIf we have two compounds: acetone (CH₃COCH₃) and acetic acid (CH₃COOH), applying heat to them produces an aldol condensation of the two compounds. If this is correct, draw the formula for the final product.arrow_forwardIf we have two compounds: acetone (CH3COCH3) and acetic acid (CH3COOH); if we apply heat (A), what product(s) are obtained?arrow_forward
- QUESTION: Fill out the answers to the empty green boxes attached in the image. *Ensure you all incorporate all 27 values (per column)*arrow_forwardYou need to make a buffer by dissolving benzoic acid and sodium benzoate in water. What is the mass of benzoic acid that you would weigh out, in mg, to create 50 mL of a buffer at pH = 4.7 that will change pH no more than 0.10 units with the addition of 0.001 moles of acid or base? Enter just the answer without the units (mg) - just the number will do!arrow_forwardDraw the formula for 3-isopropylcyclopentane-1-carbonyl chloride.arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co


