
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of nitrogen-containing compound that is obtained when the given amide undergoes basic hydrolysis has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Amides are derivatives of
Acidic hydrolysis of amides gives the product as carboxylic acid and
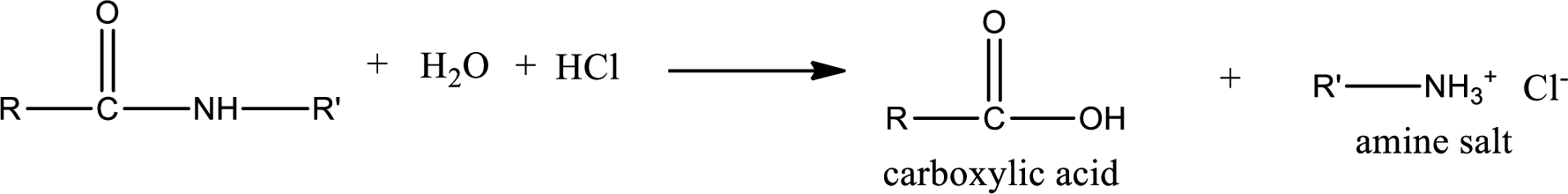
Basic hydrolysis of amides gives the product as carboxylic acid salt and amine. Carboxylic acid salt is obtained because in basic conditions the carboxylic acid is converted into carboxylic acid salt.
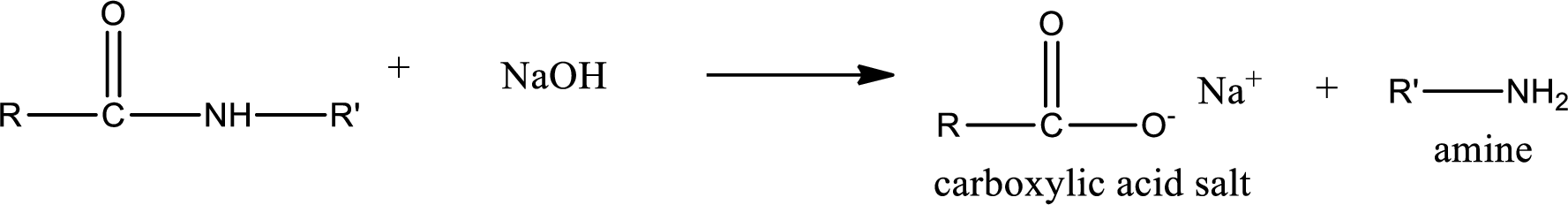
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of nitrogen-containing compound that is obtained when the given amide undergoes basic hydrolysis has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Amides are derivatives of carboxylic acid. Amides are not much reactive as of carboxylic acids. They are also stable relatively in aqueous solution. But under strenuous conditions amides undergo hydrolysis. The conditions are presence of acid, base or enzymes.
Acidic hydrolysis of amides gives the product as carboxylic acid and amine salt. Amine salt is obtained because in acidic conditions the amine is converted into amine salt.
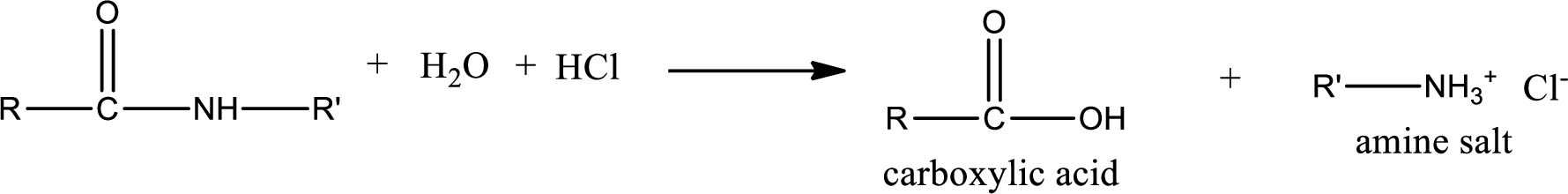
Basic hydrolysis of amides gives the product as carboxylic acid salt and amine. Carboxylic acid salt is obtained because in basic conditions the carboxylic acid is converted into carboxylic acid salt.
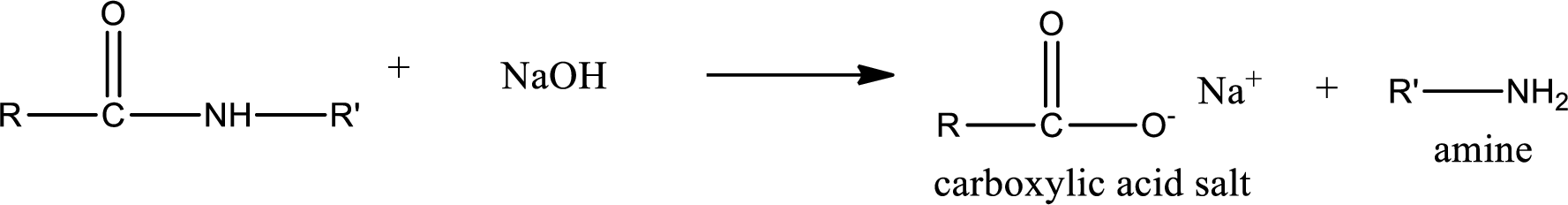
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of nitrogen-containing compound that is obtained when the given amide undergoes basic hydrolysis has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Amides are derivatives of carboxylic acid. Amides are not much reactive as of carboxylic acids. They are also stable relatively in aqueous solution. But under strenuous conditions amides undergo hydrolysis. The conditions are presence of acid, base or enzymes.
Acidic hydrolysis of amides gives the product as carboxylic acid and amine salt. Amine salt is obtained because in acidic conditions the amine is converted into amine salt.
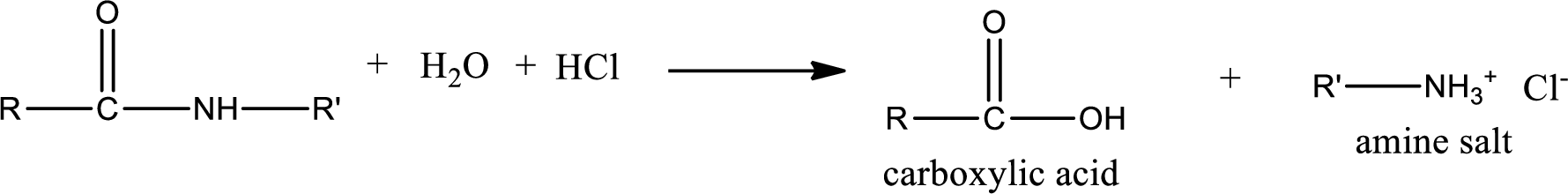
Basic hydrolysis of amides gives the product as carboxylic acid salt and amine. Carboxylic acid salt is obtained because in basic conditions the carboxylic acid is converted into carboxylic acid salt.
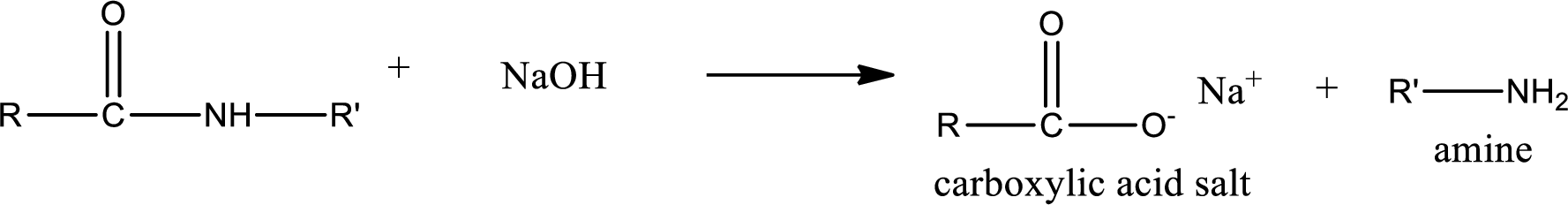
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of nitrogen-containing compound that is obtained when the given amide undergoes basic hydrolysis has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Amides are derivatives of carboxylic acid. Amides are not much reactive as of carboxylic acids. They are also stable relatively in aqueous solution. But under strenuous conditions amides undergo hydrolysis. The conditions are presence of acid, base or enzymes.
Acidic hydrolysis of amides gives the product as carboxylic acid and amine salt. Amine salt is obtained because in acidic conditions the amine is converted into amine salt.
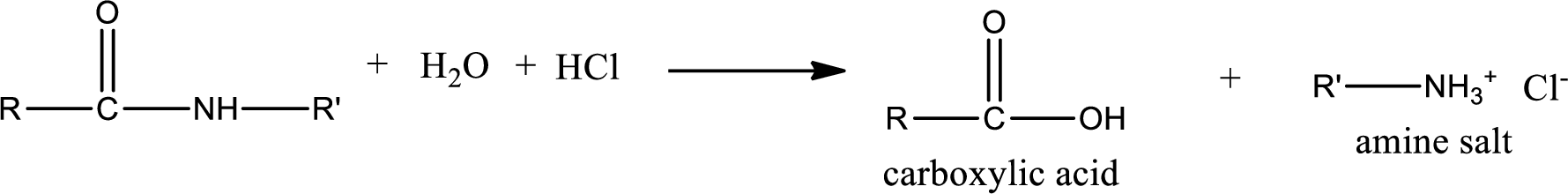
Basic hydrolysis of amides gives the product as carboxylic acid salt and amine. Carboxylic acid salt is obtained because in basic conditions the carboxylic acid is converted into carboxylic acid salt.
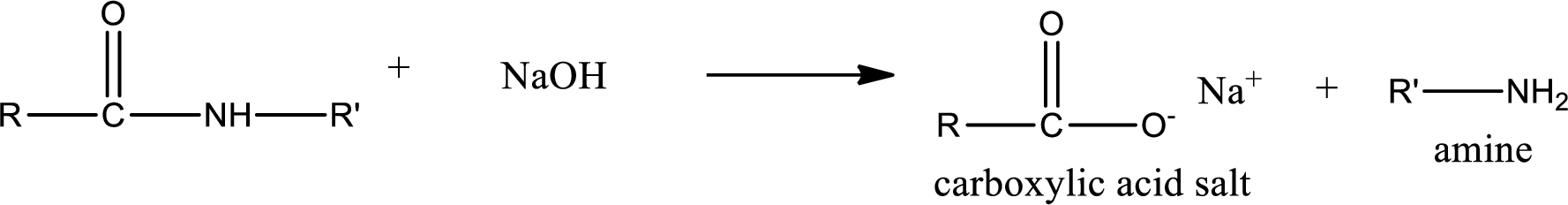
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC AND BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,

