
(a)
To find: the domain of the given function.
(a)
Answer to Problem 39AYU
The domain of the given function is the set of all the real numbers.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Given function
Calculation:
The domain of the function
The value of the function
So, the domain of
Therefore, the domain of the given function is the set of all the real numbers.
(b)
To locate: any intercepts of the given function.
(b)
Answer to Problem 39AYU
The
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Given function
Calculation:
The
The value of the function
Therefore, the
(c)
To sketch: the graph of the given function.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Given function
Calculation:
Graph the greatest integer function,
| 1 2
|
Plot the points and draw the lines to get the graph of the function.
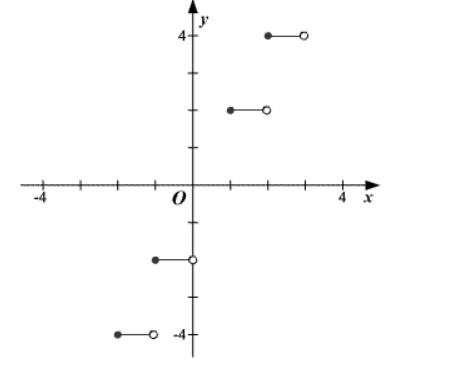
(d)
To find: the range based on the graph.
(d)
Answer to Problem 39AYU
The range of
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Given function
Calculation:
The points on the graph of
So, the range of
(e)
To find: whether
(e)
Answer to Problem 39AYU
The function
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Given function
Calculation:
From the graph, it can be observed that there is a discontinuity at
Chapter 2 Solutions
Precalculus
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Intro Stats, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
- water at a rate of 2 m³/min. of the water height in this tank? 16) A box with a square base and an open top must have a volume of 256 cubic inches. Find the dimensions of the box that will minimize the amount of material used (the surface area). 17) A farmer wishes toarrow_forward#14 Sand pours from a chute and forms a conical pile whose height is always equal to its base diameter. The height o the pile increases at a rate of 5 feet/hour. Find the rate of change of the volume of the sand in the conical pile when the height of the pile is 4 feet.arrow_forward(d)(65in(x)-5 cos(x) dx mins by 5x-2x² 3x+1 dx -dx 20 Evaluate each the following indefinite integralsarrow_forward
- 19 Evaluate each the following definite integrals: a) લ b) (+3) 6) (2-2)(+33) dxarrow_forward#11 If a snowball melts so its surface area decreases at a rate of 1cm²/min, find the rate at which the diameter decreases when the diameter is 6 cm.arrow_forwardUse Deritivitve of the inverse to solve thisarrow_forward
- Evaluate the following Limits: e6x-1 Lim +0Sin3x 7x-5x2 2x-1+ Cos 4x +6 c) Lim b) Lim + x³-x2 X-0 1-e' 4x d) Lim 6x²-3 X+0 6x+2x² Find the derivatives of the following functions using the Limit definition of derivativearrow_forward15A cylindrical tank with radius 8 m is being filled with water at a rate of 2 m³/min. What is the rate of change of the water height in this tank? 6)A box with a square base and an open top must box that will minimiarrow_forward#12 The radius of a sphere increases at a rate of 3 in/sec. How fast is the volume increasing when the diameter is 24arrow_forward
- 84 256 cubic inches. Find the dimensions of the of material used (the surface area). A farmer wishes to enclose a rectangular plot using 200 m of fencing material. One side of the land borders a river and does not need fencing. What is the largest area that can be enclosed? For the function y=x³-3x²-1, use derivatives to: 3 b) 2x - 6x2 (a) determine the intarrow_forwardCan you solve this 6 questions numerical method and teach me how to solve it and what we use.arrow_forward9Wire of length 20m is divided into two pieces and the pieces are bent into a square and a circle. How should this be done in order to minimize the sum of their areas? Round your answer to the nearest hundredth.arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





