
Concept explainers
In Problems 57-64, use a graphing utility to graph each function over the indicated interval and approximate any
57.
To find: The following values using the given graph:
a. Draw the graph using graphing utility and determine the local maximum and minimum values.
b. Increasing and decreasing intervals of the function .
Answer to Problem 53AYU
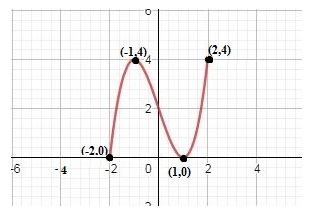
a. Local maximum point is and local minimum is .
b. The function is increasing in the intervals andand the function is decreasing in the interval . There is no constant interval in the given graph.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
It is asked to draw the graph using graphing utility and determine the local maximum and minimum values and also find the increasing and decreasing intervals of the given function.
Graph:
Interpretation:
a. By the definition of local maximum, “Let be a function defined on some interval . A function has a local maximum at if there is an open interval containing so that, for all in this open interval, we have . We call a local maximum value of ”, It can be directly concluded from the graph and the definition that the curve has local maximum point at .
The value of the local maximum at is 4.
Therefore, the local maximum point is .
By the definition of local minimum, “Let be a function defined on some interval . A function has a local minimum at if there is an open interval containing so that, for all in this open interval, we have . We call a local minimum value of ”, It can be directly concluded from the graph and the definition that the curve has local minimum point at .
The value of the local minimum point at is 0.
Therefore, the local minimum point is .
b. Increasing intervals, decreasing intervals and constant interval if any.
It can be directly concluded from the graph that the curve is increasing from to , then decreasing from to 1 and at last increasing from 1 to 2.
Therefore, the function is increasing in the intervals and and the function is decreasing in the interval . There is no constant interval in the given graph.
Chapter 2 Solutions
Precalculus
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Introductory Statistics
Elementary Statistics
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
- For the curve defined by r(t) = (e** cos(t), et sin(t)) find the unit tangent vector, unit normal vector, normal acceleration, and tangential acceleration at t = πT 3 T (1) N Ň (1) 133 | aN = 53 ar = = =arrow_forwardFind the tangential and normal components of the acceleration vector for the curve - F(t) = (2t, −3t³, −3+¹) at the point t = 1 - ā(1) = T + Ñ Give your answers to two decimal placesarrow_forwardFind the unit tangent vector to the curve defined by (t)=(-2t,-4t, √√49 - t²) at t = −6. T(−6) =arrow_forward
- An airplane flies due west at an airspeed of 428 mph. The wind blows in the direction of 41° south of west at 50 mph. What is the ground speed of the airplane? What is the bearing of the airplane? 428 mph 41° 50 mph a. The ground speed of the airplane is b. The bearing of the airplane is mph. south of west.arrow_forwardRylee's car is stuck in the mud. Roman and Shanice come along in a truck to help pull her out. They attach one end of a tow strap to the front of the car and the other end to the truck's trailer hitch, and the truck starts to pull. Meanwhile, Roman and Shanice get behind the car and push. The truck generates a horizontal force of 377 lb on the car. Roman and Shanice are pushing at a slight upward angle and generate a force of 119 lb on the car. These forces can be represented by vectors, as shown in the figure below. The angle between these vectors is 20.2°. Find the resultant force (the vector sum), then give its magnitude and its direction angle from the positive x-axis. 119 lb 20.2° 377 lb a. The resultant force is (Tip: omit degree notations from your answers; e.g. enter cos(45) instead of cos(45°)) b. It's magnitude is lb. c. It's angle from the positive x-axis isarrow_forwardFind a plane containing the point (3, -3, 1) and the line of intersection of the planes 2x + 3y - 3z = 14 and -3x - y + z = −21. The equation of the plane is:arrow_forward
- Determine whether the lines L₁ : F(t) = (−2, 3, −1)t + (0,2,-3) and L2 : ƒ(s) = (2, −3, 1)s + (−10, 17, -8) intersect. If they do, find the point of intersection. ● They intersect at the point They are skew lines They are parallel or equalarrow_forwardAnswer questions 2arrow_forwardHow does a fourier transform works?arrow_forward
- Determine the radius of convergence of a power series:12.6.5, 12.6.6, 12.6.7, 12.6.8Hint: Use Theorem12.5.1 and root test, ratio test, integral testarrow_forwardCan you answer this question and give step by step and why and how to get it. Can you write it (numerical method)arrow_forwardCan you answer this question and give step by step and why and how to get it. Can you write it (numerical method)arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





