
(a)
To find: the domain and the range of
(a)
Answer to Problem 26RE
The domain is
The range is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The graph of the function
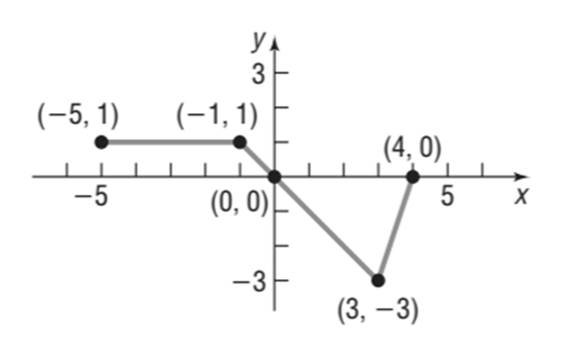
Calculation:
From the graph given in question
(b)
To find: value of
(b)
Answer to Problem 26RE
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The graph of the function
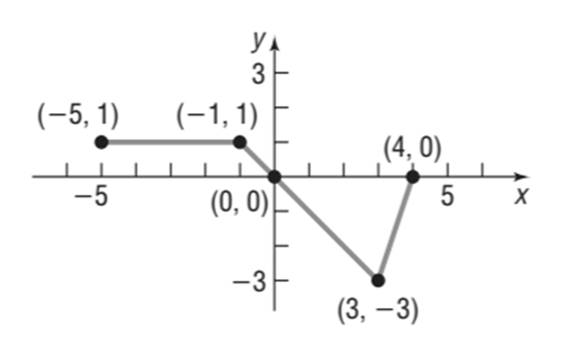
Calculation:
From the given in question
(c)
To list: the intercepts.
(c)
Answer to Problem 26RE
The
The
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The graph of the function
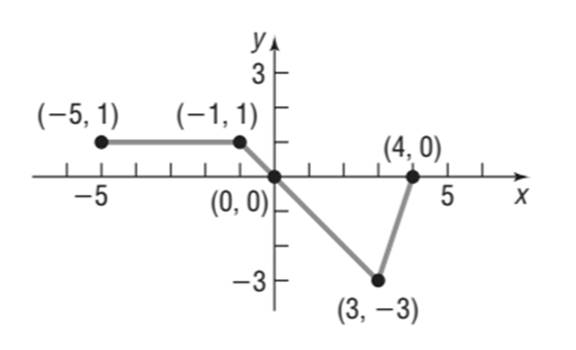
Calculation:
From the graph given in question that
The
The
(d)
To find: the value of
(d)
Answer to Problem 26RE
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The graph of the function
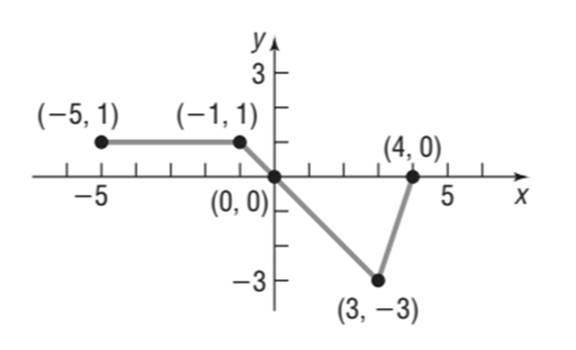
Calculation:
From the graph given in question that
(e)
To solve:
(e)
Answer to Problem 26RE
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The graph of the function
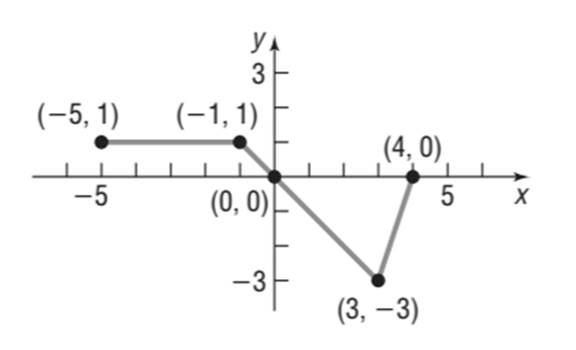
Calculation:
From the graph that
Hence the solution set is
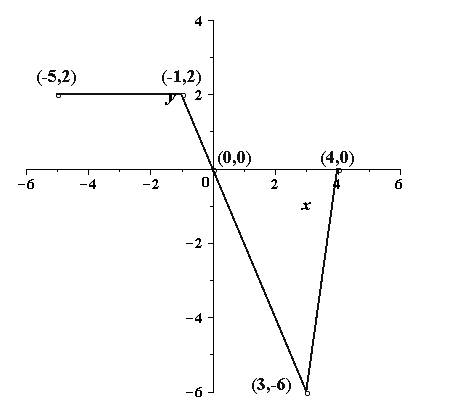
(f)
To sketch: the graph of
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The graph of the function
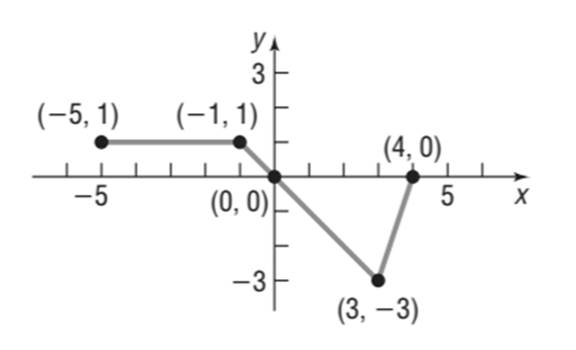
Calculation:
The following points lie on the graph of
The graph is a horizontal shift to right by 2 units of the graph of
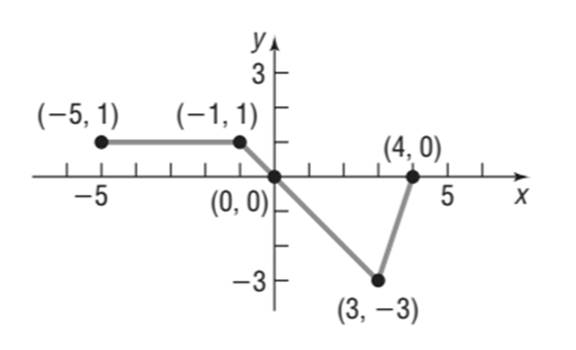
(g)
To sketch: the graph of
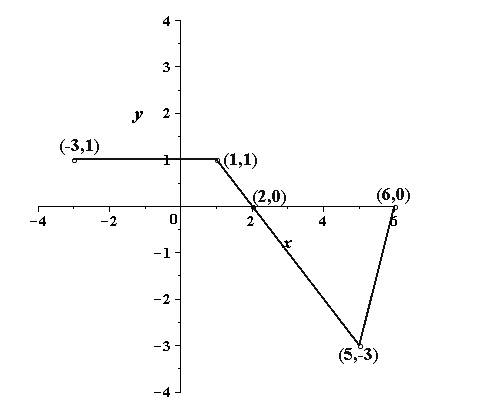
(g)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The graph of the function
Calculation:
The following points lie on the graph of
The graph is a horizontal shift to right by 1 units of the graph of
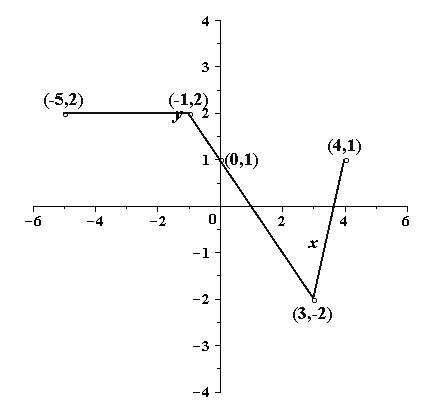
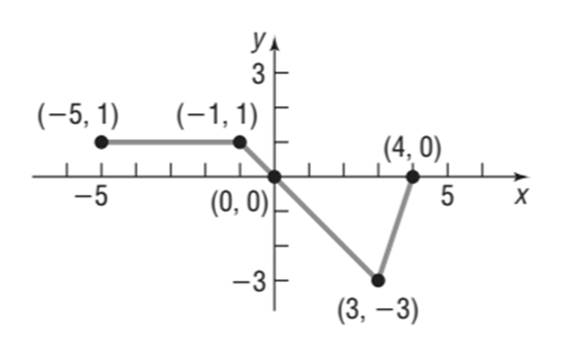
(h)
To sketch: the graph of
(h)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The graph of the function
Calculation:
The following points lie on the graph of
The graph is a horizontal shift to right by 2 units of the graph of
Chapter 2 Solutions
Precalculus
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
College Algebra with Modeling & Visualization (5th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
College Algebra (7th Edition)
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
- Consider the function f(x) = 2x² - 8x + 3 over the interval 0 ≤ x ≤ 9. Complete the following steps to find the global (absolute) extrema on the interval. Answer exactly. Separate multiple answers with a comma. a. Find the derivative of f (x) = 2x² - 8x+3 f'(x) b. Find any critical point(s) c within the intervl 0 < x < 9. (Enter as reduced fraction as needed) c. Evaluate the function at the critical point(s). (Enter as reduced fraction as needed. Enter DNE if none of the critical points are inside the interval) f(c) d. Evaluate the function at the endpoints of the interval 0 ≤ x ≤ 9. f(0) f(9) e. Based on the above results, find the global extrema on the interval and where they occur. The global maximum value is at a The global minimum value is at xarrow_forwardDetermine the values and locations of the global (absolute) and local extrema on the graph given. Assume the domain is a closed interval and the graph represents the entirety of the function. 3 y -6-5-4-3 2 1 -1 -2 -3 Separate multiple answers with a comma. Global maximum: y Global minimum: y Local maxima: y Local minima: y x 6 at a at a at x= at x=arrow_forwardA ball is thrown into the air and its height (in meters) is given by h (t) in seconds. -4.92 + 30t+1, where t is a. After how long does the ball reach its maximum height? Round to 2 decimal places. seconds b. What is the maximum height of the ball? Round to 2 decimal places. metersarrow_forward
- Determine where the absolute and local extrema occur on the graph given. Assume the domain is a closed interval and the graph represents the entirety of the function. 1.5 y 1 0.5 -3 -2 -0.5 -1 -1.5 Separate multiple answers with a comma. Absolute maximum at Absolute minimum at Local maxima at Local minima at a x 2 3 аarrow_forwardA company that produces cell phones has a cost function of C = x² - 1000x + 36100, where C is the cost in dollars and x is the number of cell phones produced (in thousands). How many units of cell phones (in thousands) minimizes this cost function? Round to the nearest whole number, if necessary. thousandarrow_forwardUnder certain conditions, the number of diseased cells N(t) at time t increases at a rate N'(t) = Aekt, where A is the rate of increase at time 0 (in cells per day) and k is a constant. (a) Suppose A = 60, and at 3 days, the cells are growing at a rate of 180 per day. Find a formula for the number of cells after t days, given that 200 cells are present at t = 0. (b) Use your answer from part (a) to find the number of cells present after 8 days. (a) Find a formula for the number of cells, N(t), after t days. N(t) = (Round any numbers in exponents to five decimal places. Round all other numbers to the nearest tenth.)arrow_forward
- The marginal revenue (in thousands of dollars) from the sale of x handheld gaming devices is given by the following function. R'(x) = 4x (x² +26,000) 2 3 (a) Find the total revenue function if the revenue from 125 devices is $17,939. (b) How many devices must be sold for a revenue of at least $50,000? (a) The total revenue function is R(x) = (Round to the nearest integer as needed.) given that the revenue from 125 devices is $17,939.arrow_forwardUse substitution to find the indefinite integral. S 2u √u-4 -du Describe the most appropriate substitution case and the values of u and du. Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer boxes within your choice. A. Substitute u for the quantity in the numerator. Let v = , so that dv = ( ) du. B. Substitute u for the quantity under the root. Let v = u-4, so that dv = (1) du. C. Substitute u for the quantity in the denominator. Let v = Use the substitution to evaluate the integral. so that dv= ' ( du. 2u -du= √√u-4arrow_forwardUse substitution to find the indefinite integral. Зи u-8 du Describe the most appropriate substitution case and the values of u and du. Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer boxes within your choice. A. Substitute u for the quantity in the numerator. Let v = , so that dv = ( ( ) du. B. Substitute u for the quantity under the root. Let v = u-8, so that dv = (1) du. C. Substitute u for the quantity in the denominator. Let v = so that dv= ( ) du. Use the substitution to evaluate the integral. S Зи -du= u-8arrow_forward
- Find the derivative of the function. 5 1 6 p(x) = -24x 5 +15xarrow_forward∞ 2n (4n)! Let R be the radius of convergence of the series -x2n. Then the value of (3" (2n)!)² n=1 sin(2R+4/R) is -0.892 0.075 0.732 -0.812 -0.519 -0.107 -0.564 0.588arrow_forwardFind the cost function if the marginal cost function is given by C'(x) = x C(x) = 2/5 + 5 and 32 units cost $261.arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





