
Concept explainers
(a)
To find: the initial velocity with which the ball must be shot in order for the ball to go through the hoop.
(a)
Answer to Problem 30AYU
The initial velocity is 30 feet per second.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
A player shoots an underhand foul shot, releasing the ball at a 70 degree angle from a position 3.5 feet above the floor, then the ball can be modeled by the function
Calculation:
Substitute 10 for
Simplify.
Isolate
Multiply
Take the positive square root on both the sides.
The initial velocity is 30 feet per second.
(b)
To write: the function for the path of the ball using the velocity found in part (a).
(b)
Answer to Problem 30AYU
The function is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
A player shoots an underhand foul shot, releasing the ball at a 70 degree angle from a position 3.5 feet above the floor, then the ball can be modeled by the function
Calculation:
We know that the initial velocity is 30 per second. Substitute 30 for
(c)
To find: the height of the ball after it has traveled 9 feet in front of the foul line.
(c)
Answer to Problem 30AYU
The height of the ball after it has traveled 9 feet in front of the foul line is 15.56 feet.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
A player shoots an underhand foul shot, releasing the ball at a 70 degree angle from a position 3.5 feet above the floor, then the ball can be modeled by the function
Calculation:
We know that the function obtained is
Therefore, the height of the ball after it has traveled 9 feet in front of the foul line is 15.56 feet.
(d)
To find: the height of the ball after it has traveled 9 feet in front of the foul line.
(d)
Answer to Problem 30AYU
The height of the ball will be 9.7feet in negative direction.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
A player shoots an underhand foul shot, releasing the ball at a 70 degree angle from a position 3.5 feet above the floor, then the ball can be modeled by the function
Calculation:
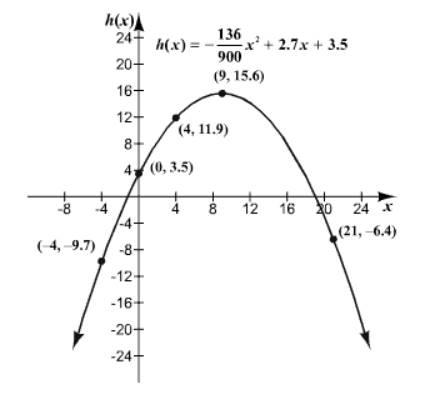
We know that a point on the graph is
Choose some more value for
| 0 | 3.5 |
| 4 | 11.9 |
| 9 | 15.6 |
| 21 |
Plot the points from the table on a coordinate plane and connect them.
Chapter 2 Solutions
Precalculus
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
- Pls help ASAParrow_forward9. a) Determie values of a and b so that the function is continuous. ax - 2b f(x) 2 x≤-2 -2x+a, x ≥2 \-ax² - bx + 1, −2 < x < 2) 9b) Consider f(x): = 2x²+x-3 x-b and determine all the values of b such that f(x) does not have a vertical asymptote. Show work.arrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forward
- 3. True False. If false create functions that prove it is false. Note: f(x) = g(x). a) If_lim ƒ(x) = ∞ and_lim g(x) = ∞,then_lim [ƒ(x) − g(x)] = 0 x→ 0+ x→0+ x→0+ b) If h(x) and g(x) are continuous at x = c, and if h(c) > 0 and g(c) = 0, then h(x) lim. will = x→c g(x) c) If lim f(x) = 0 and lim g(x) = 0 then lim f(x) does not exist. x-a x-a x→a g(x)arrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forward15. a) Consider f(x) = x-1 3x+2 and use the difference quotient to determine the simplified expression in terms of x, for the slope of any tangent to y = f(x). Also, determine the slope at x = 2. 15 b) Determine the equation of the tangent to f(x) at x = 2. Final answer in Standard Form Ax + By + C = 0, A ≥ 0, with no fractions or decimals.arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





