
Concept explainers
In Problems 57-64, use a graphing utility to graph each function over the indicated interval and approximate any
64.
To find: The following values using the given graph,
a. Draw the graph using graphing utility and determine the local maximum and minimum values.
Answer to Problem 60AYU
a. Local maximum point are and and local minimum is .
Explanation of Solution
Given:
It is asked to draw the graph using graphing utility and determine the local maximum and minimum values and also the increasing and decreasing intervals of the given function.
Calculation:
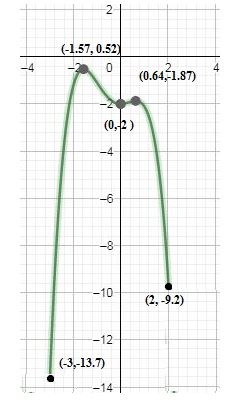
a. By the definition of local maximum, “Let be a function defined on some interval . A function has a local maximum at if there is an open interval containing so that, for all in this open interval, we have . We call a local maximum value of ”, It can be directly concluded from the graph and the definition that the curve has local maximum point at and .
The value of the local maximum at is and is .
Therefore, the local maximum points are and .
By the definition of local minimum, “Let be a function defined on some interval . A function has a local minimum at if there is an open interval containing so that, for all in this open interval, we have . We call a local minimum value of ”, It can be directly concluded from the graph and the definition that the curve has local minimum point at .
The value of the local minimum point at is .
Therefore, the local minimum point is .
To find: The following values using the given graph,
b. Increasing and decreasing intervals of the function .
Answer to Problem 60AYU
b. The function is increasing in the interval and , the function is decreasing in the intervals and . There is no constant interval in the given graph.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
It is asked to draw the graph using graphing utility and determine the local maximum and minimum values and also the increasing and decreasing intervals of the given function.
Calculation:

b. Increasing intervals, decreasing intervals and constant interval if any.
It can be directly concluded from the graph that the curve is increasing from to , then decreasing from to 0, then increasing from 0 to and at last decreasing from to 2.
Therefore, the function is increasing in the interval and , the function is decreasing in the intervals and . There is no constant interval in the given graph.
Chapter 2 Solutions
Precalculus
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Calculus for Business, Economics, Life Sciences, and Social Sciences (14th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
- 5. For the function y-x³-3x²-1, use derivatives to: (a) determine the intervals of increase and decrease. (b) determine the local (relative) maxima and minima. (e) determine the intervals of concavity. (d) determine the points of inflection. (e) sketch the graph with the above information indicated on the graph.arrow_forwardCan you solve this 2 question numerical methodarrow_forward1. Estimate the area under the graph of f(x)-25-x from x=0 to x=5 using 5 approximating rectangles Using: (A) right endpoints. (B) left endpoints.arrow_forward
- 9. Use fundamental theorem of calculus to find the derivative d a) *dt sin(x) b)(x)√1-2 dtarrow_forward3. Evaluate the definite integral: a) √66x²+8dx b) x dx c) f*(2e* - 2)dx d) √√9-x² e) (2-5x)dx f) cos(x)dx 8)²₁₂√4-x2 h) f7dx i) f² 6xdx j) ²₂(4x+3)dxarrow_forward2. Consider the integral √(2x+1)dx (a) Find the Riemann sum for this integral using right endpoints and n-4. (b) Find the Riemann sum for this same integral, using left endpoints and n=4arrow_forward
- Problem 11 (a) A tank is discharging water through an orifice at a depth of T meter below the surface of the water whose area is A m². The following are the values of a for the corresponding values of A: A 1.257 1.390 x 1.50 1.65 1.520 1.650 1.809 1.962 2.123 2.295 2.462|2.650 1.80 1.95 2.10 2.25 2.40 2.55 2.70 2.85 Using the formula -3.0 (0.018)T = dx. calculate T, the time in seconds for the level of the water to drop from 3.0 m to 1.5 m above the orifice. (b) The velocity of a train which starts from rest is given by the fol- lowing table, the time being reckoned in minutes from the start and the speed in km/hour: | † (minutes) |2|4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 v (km/hr) 16 28.8 40 46.4 51.2 32.0 17.6 8 3.2 0 Estimate approximately the total distance ran in 20 minutes.arrow_forwardX Solve numerically: = 0,95 In xarrow_forwardX Solve numerically: = 0,95 In xarrow_forward
- Please as many detarrow_forward8–23. Sketching vector fields Sketch the following vector fieldsarrow_forward25-30. Normal and tangential components For the vector field F and curve C, complete the following: a. Determine the points (if any) along the curve C at which the vector field F is tangent to C. b. Determine the points (if any) along the curve C at which the vector field F is normal to C. c. Sketch C and a few representative vectors of F on C. 25. F = (2½³, 0); c = {(x, y); y − x² = 1} 26. F = x (23 - 212) ; C = {(x, y); y = x² = 1}) , 2 27. F(x, y); C = {(x, y): x² + y² = 4} 28. F = (y, x); C = {(x, y): x² + y² = 1} 29. F = (x, y); C = 30. F = (y, x); C = {(x, y): x = 1} {(x, y): x² + y² = 1}arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





