
Concept explainers
(a)
To express: the area A of the printed part of the page as a function of the width x of the border.
(a)
Answer to Problem 73RE
The function is A=4x2−39x+93.5 which represent the model of equation of area A of printed part of the page as a width x of the border of the page.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
A page with dimensions of 812 inches by 11 inches has a border of uniform width x surrounding the printed matter of the page, as shown in the figure.
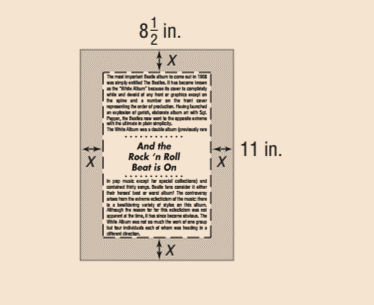
Calculation:
As by given figure, it’s obvious that the width of the inside printed rectangular portion can be obtained by subtraction twice from the original width of whole page as x units margin is there in both left and right side of the printed area.
So the width of the printed area = 8.5−2x inches.
Similarly the length of the printed area = 11−2x inches
Now as,
Are of printed rectangular = length x width
(8.5−2x)×(11−2x)
Now, on using FOIL rule,
(8.5−2x)×(11−2x)=8.5×11−8.5×2x−2x×11−2x×(−2x)=93.5−22x−17x+4x2=4x2−39x+93.5
So, the function is A=4x2−39x+93.5 which represent the model of equation of area A of printed part of the page as a width x of the border of the page.
(b)
To find: the domain and the range of A .
(b)
Answer to Problem 73RE
The Domain of the given function = [0,4.25)
The range of printed page = 0<A<93.5
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
A page with dimensions of 812 inches by 11 inches has a border of uniform width x surrounding the printed matter of the page, as shown in the figure.
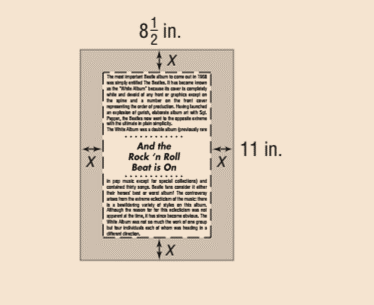
Calculation:
As area is always positive so A>0 , or
4x2−39x+9.5>0
Now on using
a=4,b=−39 and c=+93.5
x=−b±√b2−4ac2a=(−39)±√(−39)2−4(4)(+93.5)2(4)=39±√1521−14968=+39±√258=39±58
Now on taking + sign,
x=39+58=448=5.5
Now on taking (-) sign,
x=39−58=348=4.25
So, the Domain of the given function = [0,4.25)
It’s clear that the minimum area of printed page would be zero and maximum area would be equal to the dimension of its full length and width that is,
8.5×11=93.5
So, the range of printed page = 0<A<93.5
(c)
To find: the area of the printed page for borders of widths 1 inch, 1.2 inches, and 1.5 inches.
(c)
Answer to Problem 73RE
A=58.5 square inches, 52.46 square inches, 44 square inches.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
A page with dimensions of 812 inches by 11 inches has a border of uniform width x surrounding the printed matter of the page, as shown in the figure.
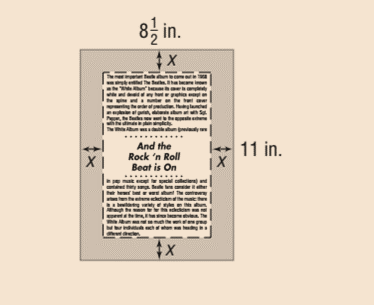
Calculation:
Now at width x=1
A=4(1)2−39×1+93.5=97.5−39=58.5 square inches
So, A=58.5 square inches .
When width x=1.2 inches
A=4(1.2)2−39×1.2+93.5=5.75+46.7=52.46 square inches
So, A=52.46 square inches
When width x=1.5 inches
A=4(1.5)2−39×1.5+93.5=9+35=44 square inches
So, A=44 sqaure inches
(d)
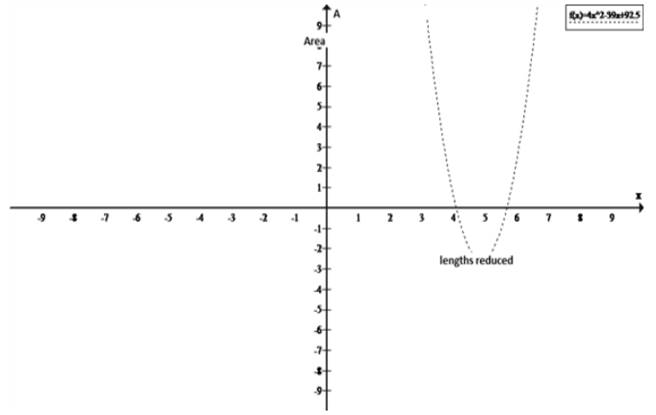
To sketch: the graph of the function A=A(x) .
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
A page with dimensions of 812 inches by 11 inches has a border of uniform width x surrounding the printed matter of the page, as shown in the figure.
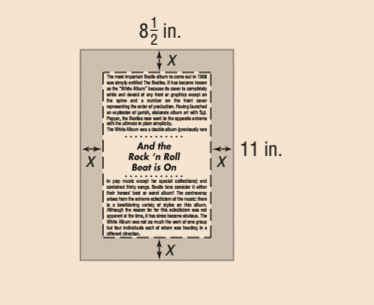
Calculation:
The graph of the quadratic equation, which is a parabola, showing area i.e
A=4x2−39x+93.5 is shown as under when sketched using a graphics utility program:
Chapter 2 Solutions
Precalculus
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Elementary Statistics
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
- Use Laplace transform to solve the initial value problem y' + y = tsin(t), y(0) = 0arrow_forwardThe function g is defined by g(x) = sec² x + tan x. What are all solutions to g(x) = 1 on the interval 0 ≤ x ≤ 2π ? A x = = 0, x == = 3, x = π, x = 7 4 , 4 and x 2π only = B x = 4' 1, x = 1, x = 57 and x = 3 only C x = πk and x = - +πk D , where is any integer П x = +πk and П x = +πk, where k is any integerarrow_forwardVector v = PQ has initial point P (2, 14) and terminal point Q (7, 3). Vector v = RS has initial point R (29, 8) and terminal point S (12, 17). Part A: Write u and v in linear form. Show all necessary work. Part B: Write u and v in trigonometric form. Show all necessary work. Part C: Find 7u − 4v. Show all necessary calculations.arrow_forward
- An object is suspended by two cables attached at a single point. The force applied on one cable has a magnitude of 125 pounds and acts at an angle of 37°. The force on the other cable is 75 pounds at an angle of 150°.Part A: Write each vector in component form. Show all necessary work.Part B: Find the dot product of the vectors. Show all necessary calculations Part C: Use the dot product to find the angle between the cables. Round the answer to the nearest degree. Show all necessary calculations.arrow_forwardAn airplane flies at 500 mph with a direction of 135° relative to the air. The plane experiences a wind that blows 60 mph with a direction of 60°.Part A: Write each of the vectors in linear form. Show all necessary calculations.Part B: Find the sum of the vectors. Show all necessary calculations. Part C: Find the true speed and direction of the airplane. Round the speed to the thousandths place and the direction to the nearest degree. Show all necessary calculations.arrow_forwardUse sigma notation to write the sum. Σ EM i=1 - n 2 4n + n narrow_forward
- Vectors t = 3i + 7j, u = 2i − 5j, and v = −21i + 9j are given.Part A: Find the angle between vectors t and u. Show all necessary calculations. Part B: Choose a value for c, such that c > 1. Find w = cv. Show all necessary work.Part C: Use the dot product to determine if t and w are parallel, orthogonal, or neither. Justify your answer.arrow_forwardA small company of science writers found that its rate of profit (in thousands of dollars) after t years of operation is given by P'(t) = (5t + 15) (t² + 6t+9) ³. (a) Find the total profit in the first three years. (b) Find the profit in the sixth year of operation. (c) What is happening to the annual profit over the long run? (a) The total profit in the first three years is $ (Round to the nearest dollar as needed.)arrow_forwardFind the area between the curves. x= -2, x = 7, y=2x² +3, y=0 Set up the integral (or integrals) needed to compute this area. Use the smallest possible number of integrals. Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer boxes to complete your choice. A. 7 [[2x² +3] dx -2 B. [[ ] dx+ -2 7 S [ ] dx The area between the curves is (Simplify your answer.)arrow_forward
- The rate at which a substance grows is given by R'(x) = 105e0.3x, where x is the time (in days). What is the total accumulated growth during the first 2.5 days? Set up the definite integral that determines the accumulated growth during the first 2.5 days. 2.5 Growth = (105e0.3x) dx 0 (Type exact answers in terms of e.) Evaluate the definite integral. Growth= (Do not round until the final answer. Then round to one decimal place as needed.)arrow_forwardFind the total area of the shaded regions. y 18- 16- 14- 12- 10- 8- 6- y=ex+1-e 4- 2- 0- 2 3 4 5 -2 -4- X ☑ The total area of the shaded regions is (Type an integer or decimal rounded to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardThe graph of f(x), shown here, consists of two straight line segments and two quarter circles. Find the 19 value of f(x)dx. 小 Srxdx. 19 f(x)dx y 7 -7 2 12 19 X ☑arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





