
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
From, the given information, aufbau principle, needs to be explained.
Concept introduction:
Aufbau principle: According to Aufbau principle, the electron filling in different orbital takes place from lower to higher energy level. That is electron in lowest energy level fills before the highest energy level.
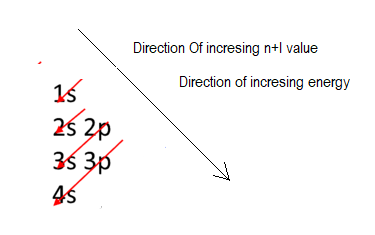
Answer to Problem 14STP
From the given electron configuration for silicon that is 1s2 2s2 2p63s2 3p2, it can be understand that is electron in lowest energy level fills before the highest energy level that is the Aufbau principle, which states that electron filling in different orbital takes place from lower to higher energy level.
Aufbau principle: According to Aufbau principle, the electron filling in different orbital takes place from lower to higher energy level. That is electron in lowest energy level fills before the highest energy level.
From the given electron configuration for silicon that is 1s2 2s2 2p63s2 3p2, it can be understand that is electron in lowest energy level fills before the highest energy level.
Energy of a level can be drived from its n+l value, which is lower for 1+0=1, than 2s which 2+0 and 2p which is 2+1.
That is electron first fill in 1s orbital then is 2s, which is higher in energy than 1s, after that electron fills in 2p which is higher in energy than 2s, then electron fills in 3s, which is higher in energy than 2p, after that electron fills in 3p which is higher in energy than 3s.
Explanation of Solution
Aufbau principle: According to Aufbau principle, the electron filling in different orbital takes place from lower to higher energy level. That is electron in lowest energy level fills before the highest energy level.
From the given electron configuration for silicon that is 1s2 2s2 2p63s2 3p2, it can be understand that is electron in lowest energy level fills before the highest energy level.
Energy of a level can be drived from its n+l value, which is lower for 1+0=1, than 2s which 2+0 and 2p which is 2+1.
That is electron first fill in 1s orbital then is 2s, which is higher in energy than 1s, after that electron fills in 2p which is higher in energy than 2s, then electron fills in 3s, which is higher in energy than 2p, after that electron fills in 3p which is higher in energy than 3s.
Chapter 14 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
- 10:04 AM Tue Mar 25 Sunday 9:30 AM 95% Edit Draw the corresponding structures in each of the boxes below: Ester Name Methyl butyrate (Example) Alcohol Structure H3C-OH Acid Structure Ester Structure Isoamyl acetate Ethyl butyrate Propyl acetate Methyl salicylate Octyl acetate Isobutyl propionate Benzyl butyrate Benzyl acetate Ethyl acetate H₂C OH HCarrow_forward2) For each of the following reactions: (i) (ii) Fill in the missing reactant, reagent, or product (s), indicating stereochemistry where appropriate using dashed and wedged bonds. If the reaction forms a racemic mixture, draw both structures in the box and write the word "racemic". (a) (b) 1) R₂BH 2) H₂O2, NaOH (aq) HBr Br racemic Br + Br Br racemicarrow_forwardFor each of the following reactions: Fill in the missing reactant, reagent, or product (s), indicating stereochemistry where appropriate using dashed and wedged bonds. If the reaction forms a racemic mixture, draw both structures in the box and write the word “racemic”.arrow_forward
- 1) Draw the correct chemical structure (using line-angle drawings / "line structures") from their given IUPAC name: a. hept-3-yne b. 5-bromo-1-fluoro-4-methylpent-2-ynearrow_forward15. How many absorptions are expected in the H-NMR spectra of fee songs? Explain your were a) CH,CH,CCH,CH, O CHUCH CHCHarrow_forwardFirefly luciferin exhibits three rings. Identify which of the rings are aromatic. Identify which lone pairs are involved in establishing aromaticity. The lone pairs are labeled A-D below.arrow_forward
- What is the [OH⁻] of a 1.80 M solution of pyridine (C₅H₅N, Kb = 1.70 × 10⁻⁹)?arrow_forwardWhat is the percent ionization in a 0.260 M solution of formic acid (HCOOH) (Ka = 1.78 × 10⁻⁴)?arrow_forwardDetermine the pH of solution of HC3H5O2 By constructing an ICE table writing the equilibrium constant expression, and using this information to determine the pH. The Ka of HC3H5O2 is 1.3 x 10-5arrow_forward
- Determine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction LiNO3arrow_forwardAn unknown weak acid with a concentration of 0.410 M has a pH of 5.600. What is the Ka of the weak acid?arrow_forward(racemic) 19.84 Using your reaction roadmaps as a guide, show how to convert 2-oxepanone and ethanol into 1-cyclopentenecarbaldehyde. You must use 2-oxepanone as the source of all carbon atoms in the target molecule. Show all reagents and all molecules synthesized along the way. & + EtOH H 2-Oxepanone 1-Cyclopentenecarbaldehydearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





