
Concept explainers
Apply your knowledge of polarity and solubility topredict whether solvation is possible in each situationshown in Table 14.9. Explain your answers.
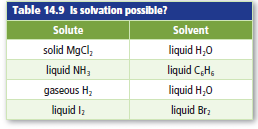
Interpretation:
Using knowledge of polarity and solubility the solvation of a solute in a particular solvent have to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Solvation is the process where the solute particles are surrounded by the solvent molecules to form a solution. “Like dissolves like” rule is applied to determine whether solvation will occur in a specific solvent.
Answer to Problem 104A
- MgCl2(s) is dissolved in H2O(l)
- NH3(l) is not dissolved in C6H6(l)
- H2(g) is not dissolved in H2O(l)
- I2(l) is dissolved in Br2(l).
Explanation of Solution
“Like dissolves like” rule is applied to determine whether solvation will occur in a specific solvent. The polar molecules like to dissolve in polar solvent and the nonpolar molecules like to dissolve in nonpolar solvent.
- Both MgCl2 and H2O are polar molecule. So, MgCl2(s) likes todissolve in H2O(l).
- NH3is a polar molecule while C6H6 is a nonpolar solvent. So, NH3(l) is not dissolved in C6H6(l)
- H2 is a nonpolar molecule while H2O is a polar solvent. So, H2(g) is not dissolved in H2O(l)
- Both I2and Br2 are nonpolar liquid. So, I2(l) is dissolved in Br2(l).
Chapter 14 Solutions
Chemistry: Matter and Change
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
- What is the final product when hexanedioic acid reacts with 1º PCl5 and 2º NH3.arrow_forwardWhat is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forward
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





