
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The citric acid cycle diacid intermediate counterpart for lipogenesis C4-ACP monoacid intermediate butyrate has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Lipogenesis is the process employed for the synthesis of fatty acid. The starting precursor for the synthesis is acetyl CoA. The enzyme employed for the process is fatty acid synthase. It is a multienzyme complex that ties the reaction responsible for the synthesis of fatty acid. This process is the reverse of the degradation of fatty acid.
The Citric acid cycle is a series of biochemical reactions that use acetyl CoA (produced by oxidation of pyruvate) to produce carbon dioxide, NADH and FADH2 in a series of
(a)
Answer to Problem 14.105EP
The citric acid cycle diacid intermediate counterpart for lipogenesis C4-ACP monoacid butyrate intermediate is succinate.
Explanation of Solution
Intermediates involved in the lipogenesis are derivative of C4 molecule butyric acid. Butyric acid is a monocarboxylic acid and has 4 carbon atoms. Thus, each intermediate of the lipogenesis is a C4 derivative of monocarboxylic acid. The structure of butyric acid is,
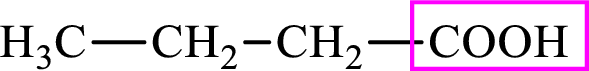
Succinic acid is a dicarboxylic acid and has 4 carbon atoms. Thus, each intermediate of the citric acid cycle is a
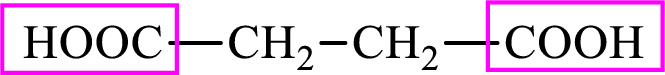
The structure of butyrate is,
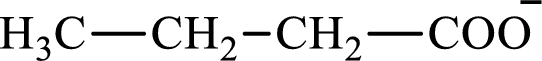
The structure of succinate is,
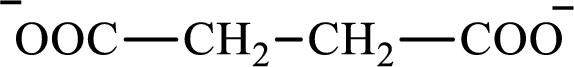
Butyrate and succinate are saturated acids with four carbon atoms in each molecule. Butyrate is a monoacid that is formed as an intermediate in lipogenesis while succinate is a diacid that is formed as an intermediate in the citric acid cycle. Therefore, the citric acid cycle diacid intermediate counterpart for lipogenesis C4-ACP monoacid butyrate intermediate is succinate.
(b)
Interpretation:
The citric acid cycle diacid intermediate counterpart for lipogenesis C4-ACP monoacid intermediate acetoacetate has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Lipogenesis is the process employed for the synthesis of fatty acid. The starting precursor for the synthesis is acetyl CoA. The enzyme employed for the process is fatty acid synthase. It is a multienzyme complex that ties the reaction responsible for the synthesis of fatty acid. This process is the reverse of the degradation of fatty acid.
The Citric acid cycle is a series of biochemical reactions that use acetyl CoA (produced by oxidation of pyruvate) to produce carbon dioxide, NADH and FADH2 in a series of redox reactions.
Intermediates involved in the lipogenesis are derivatives of C4 molecule butyric acid. Butyric acid is a monocarboxylic acid and has 4 carbon atoms. Thus, each intermediate of the lipogenesis is a C4 derivative of monocarboxylic acid. The structure of butyric acid is,
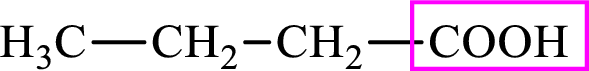
Succinic acid is a dicarboxylic acid and has 4 carbon atoms. Thus, each intermediate of the citric acid cycle is a C4 derivative of dicarboxylic acid. The structure of succinic acid is,
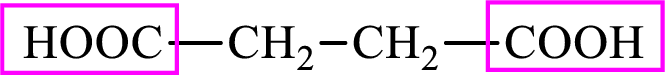
(b)
Answer to Problem 14.105EP
The citric acid cycle diacid intermediate counterpart for lipogenesis C4-ACP monoacid acetoacetate intermediate is oxaloacetate.
Explanation of Solution
Acetoacetate is the intermediate in the lipogenesis. The structure of acetoacetate is,
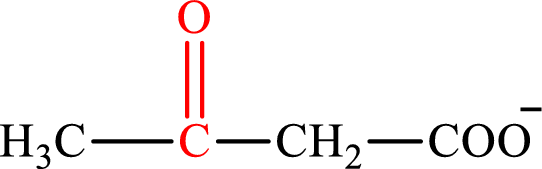
Oxaloacetate is the intermediate in the citric acid cycle. The structure of oxaloacetate is,
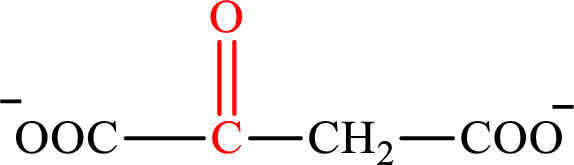
Acetoacetate and oxaloacetate are the keto derivatives of saturated acid with four carbon atoms in each molecule. Acetoacetate is a keto derivative of monocarboxylic acid while oxaloacetate is a keto derivative of dicarboxylic acid. Therefore, the citric acid cycle diacid intermediate counterpart for lipogenesis C4-ACP monoacid acetoacetate intermediate is oxaloacetate.
(c)
Interpretation:
The citric acid cycle diacid intermediate counterpart for lipogenesis C4-ACP monoacid intermediate β-hydroxybutyrate has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Lipogenesis is the process employed for the synthesis of fatty acid. The starting precursor for the synthesis is acetyl CoA. The enzyme employed for the process is fatty acid synthase. It is a multienzyme complex that ties the reaction responsible for the synthesis of fatty acid. This process is the reverse of the degradation of fatty acid.
The Citric acid cycle is a series of biochemical reactions that use acetyl CoA (produced by oxidation of pyruvate) to produce carbon dioxide, NADH and FADH2 in a series of redox reactions.
Intermediates involved in the lipogenesis are derivatives of C4 molecule butyric acid. Butyric acid is a monocarboxylic acid and has 4 carbon atoms. Thus, each intermediate of the lipogenesis is a C4 derivative of monocarboxylic acid. The structure of butyric acid is,
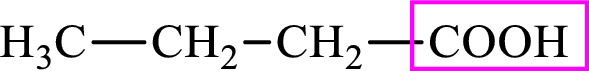
Succinic acid is a dicarboxylic acid and has 4 carbon atoms. Thus, each intermediate of the citric acid cycle is a C4 derivative of dicarboxylic acid. The structure of succinic acid is,
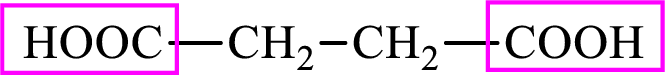
(c)
Answer to Problem 14.105EP
The citric acid cycle diacid intermediate counterpart for lipogenesis C4-ACP monoacid β-hydroxybutyrate intermediate is malate.
Explanation of Solution
β-Hydroxybutyrate is the intermediate in the lipogenesis. The structure of β-hydroxybutyrate is,
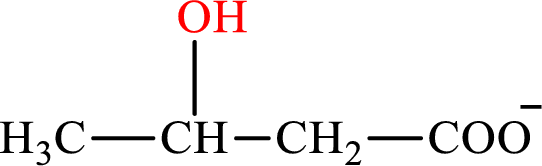
Malate is the intermediate in the citric acid cycle. The structure of Malate is,
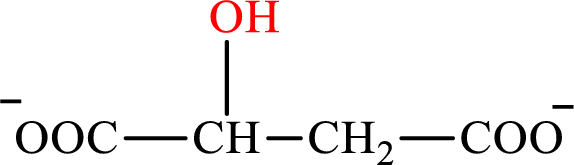
β-Hydroxybutyrate and malate are the hydroxy derivatives of saturated acid with four carbon atoms in each molecule. β-Hydroxybutyrate is a hydroxy derivative of monocarboxylic acid while malate is a hydroxy derivative of dicarboxylic acid. Therefore, the citric acid cycle diacid intermediate counterpart for lipogenesis C4-ACP monoacid β-hydroxybutyrate intermediate is malate.
(d)
Interpretation:
The citric acid cycle diacid intermediate counterpart for lipogenesis C4-ACP monoacid intermediate crotonate has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Lipogenesis is the process employed for the synthesis of fatty acid. The starting precursor for the synthesis is acetyl CoA. The enzyme employed for the process is fatty acid synthase. It is a multienzyme complex that ties the reaction responsible for the synthesis of fatty acid. This process is the reverse of the degradation of fatty acid.
The Citric acid cycle is a series of biochemical reactions that use acetyl CoA (produced by oxidation of pyruvate) to produce carbon dioxide, NADH and FADH2 in a series of redox reactions.
Intermediates involved in the lipogenesis are derivatives of C4 molecule butyric acid. Butyric acid is a monocarboxylic acid and has 4 carbon atoms. Thus, each intermediate of the lipogenesis is a C4 derivative of monocarboxylic acid. The structure of butyric acid is,
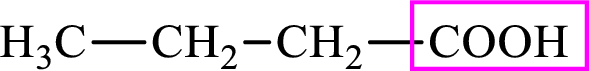
Succinic acid is a dicarboxylic acid and has 4 carbon atoms. Thus, each intermediate of the citric acid cycle is a C4 derivative of dicarboxylic acid. The structure of succinic acid is,
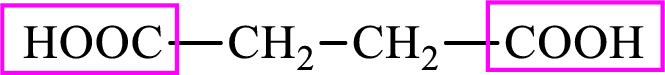
(d)
Answer to Problem 14.105EP
The citric acid cycle diacid intermediate counterpart for lipogenesis C4-ACP monoacid crotonate intermediate is fumarate.
Explanation of Solution
Crotonate is the intermediate in the lipogenesis. The structure of crotonate is,
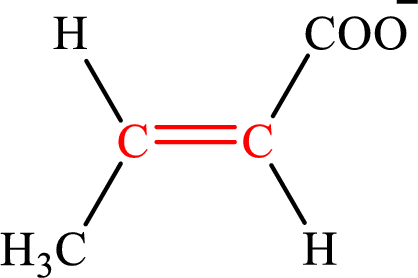
Fumarate is the intermediate in the citric acid cycle. The structure of fumarate is,
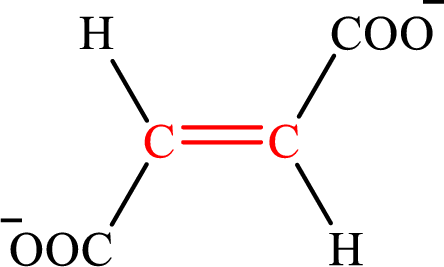
Crotonate and fumarate are the unsaturated derivatives of a
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- What is the final product when hexanedioic acid reacts with 1º PCl5 and 2º NH3.arrow_forwardWhat is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forward
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning




