
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The possible resonance structures for the following skeleton structure have to be determined. Also, the most important resonance structure has to be identified.
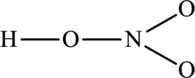
Concept Introduction:
The steps to draw the Lewis structure of the molecule are as follows:
Step 1: Find the central atom and place the other atoms around it. The atom in a compound that has the lowest group number or lowest electronegativity considered as the central atom.
Step 2: Estimate the total number of valence electrons.
Step 3: Connect the other atoms around the central atoms to the central atom with a single bond and lower the value of valence electrons by 2 of every single bond.
Step 4: Allocate the remaining electrons in pairs so that each atom can get 8 electrons.
The formula to calculate formal charge of the atom is as follows:
Some molecules and ions do not have one unique Lewis structure. The Lewis structures that differ only in the placement of multiple bonds are called resonance structures.
Resonance structures are defined as a set of two or more Lewis structures that collectively describe the electronic bonding. The actual bonding is an average of the bonding in the resonance structures. Also, not all resonance structures contribute equally in every case. Resonance structures that have high formal charges or that place charges of the same sign on adjacent atoms do not contribute to the bonding.
(a)
Answer to Problem 9.74QE
The possible resonance structures are as follows:
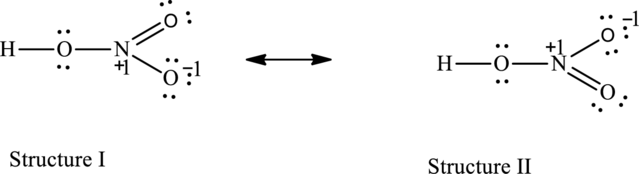
All resonance structures are equally important.
Explanation of Solution
The skeleton structure is as follows:
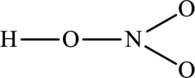
The resonance structures are as follows:
For structure I:
Substitute 5 for valence electrons, 0 for the number of lone pair of electrons and 8 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on nitrogen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for the number of lone pair of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on first oxygen atom connected to nitrogen
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for the number of lone pair of electrons and 2for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on second oxygen atom connected to nitrogen
For structure II:
Substitute 5 for valence electrons, 0 for the number of lone pair of electrons and 8 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on nitrogen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pair of electrons and 2for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on first oxygen atom connected to nitrogen
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pair of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on second oxygen atom connected to nitrogen
Possible resonance structures are as follows:
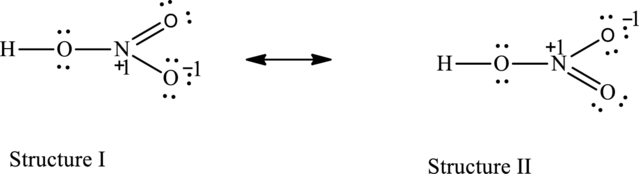
All the structures have same formal charge. Also, the atoms that have charge are same in each structure. Therefore, all structures are equally important.
(b)
Interpretation:
The possible resonance structures for the following skeleton structure have to be determined. Also, the most important resonance structure has to be identified.
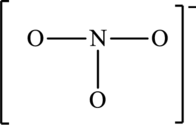
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(b)
Answer to Problem 9.74QE
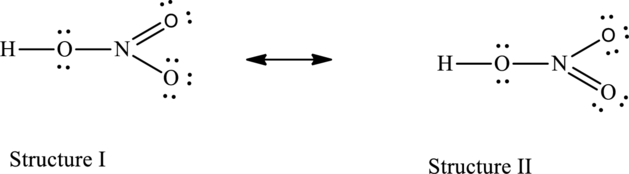
The possible resonance structures are as follows:
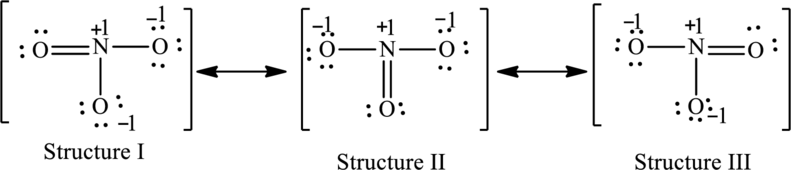
All the structures are equally important.
Explanation of Solution
The skeleton structure is,
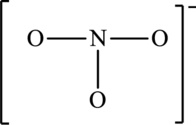
The resonance structures are as follows:
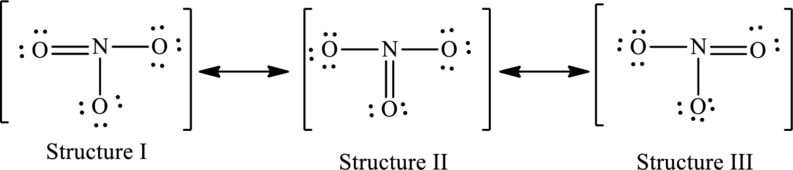
For structure I:
Substitute 5 for valence electrons, 0 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 8 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on nitrogen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on first oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on second oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on third oxygen atom.
For structure II:
Substitute 5 for valence electrons, 0 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 8 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on nitrogen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on first oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on second oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on third oxygen atom.
For structure III:
Substitute 5 for valence electrons, 0 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 8 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on nitrogen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on first oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on second oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on third oxygen atom.
The possible resonance structures are as follows:
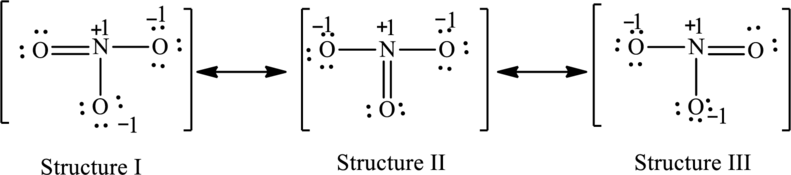
All the structures have the same formal charge. Also, the atoms that have charge are same in each structure. Therefore, all structures are equally important.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Chemistry: Principles and Practice
- Formulate the products obtained by reacting p-toluidine with a sulfonate mixture. Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardConsider this organic reaction: OH Draw the major products of the reaction in the drawing area below. If there won't be any major products, because this reaction won't happen at a significant rate, check the box under the drawing area instead. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. x 0: の Carrow_forwardExplain the reasons for a compound's greater or lesser reactivity toward electrophilic aromatic substitution. Give reasons.arrow_forward
- Draw the products of a reaction of the following alkyle chloride, shown below in the 3D ball and stick model with NaSCH3. Ignore inorganic byproducts. In the figure, a gray ball indicates a carbon atom a white ball indicates a hydrogen atom anda agreen ball indicated a chlorine atomarrow_forwardDraw the most stable cations formed in the mass spectrometer by a deavage of the following compound Draw the most stable cations formed in the mass spectrometer by a cleavage of the following compound онarrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting anand product sytucutrs, draw the curved electron-pusing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic steps. Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bind-making stepsarrow_forward
- Draw the major elimination and substitution products formed in this reavtion. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicatr the stereochemistry of substituents on assymetric centers, wheere applicable. Ignore any inorganic byproducts.arrow_forwardDraw the two possible products produced in this E2 elimination. Ignore any inorganic byproductsarrow_forwardDraw the major products of this SN1 reaction. Ignore any inorganic byproducts.arrow_forward
- Draw the major elimination and substitution products formed in this reaction. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate the stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, wehre applicable. Ignore and inorganic byproducts.arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. Drawing Arrows THE Problem 33 of 35 N. C:0 Na + Submit Drag To Pan +arrow_forwardDraw the product of the E2 reaction shown below. Include the correct stereochemistry. Ignore and inorganic byproducts.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax





