
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The resonance structures with an octet about the central atom and a resonance structure that has minimum formal charges for the following structure has to be determined.
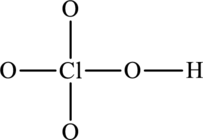
Concept Introduction:
A covalent bond is a bond that is formed from the mutual sharing of electrons between atoms. Lewis structures are representations of the covalent bond. In this, Lewis symbols show how the valence electrons are present in the molecule.
Steps to write Lewis structures are as follows:
1. The skeleton structure with single bonds between all bonded atoms has to be written
2. Sum the valence electrons of the atoms in the molecule.
(a) For cations, one electron is subtracted for each positive charge.
(b) For anions, one electron is added for each negative charge.
3. Subtract two electrons from total number of valence electrons for each bond in the skeleton structure.
4. Count the number of electrons required to satisfy the octet rule for each atom in the structure. If the number of electrons needed is less than the number remaining, add one bond for every two electrons needed between atoms to attain an octet.
5. The remaining electrons are placed as lone pairs on atoms that need them to satisfy the octet rule.
The formula to calculate formal charge of atom is,
Some molecules do not have only one Lewis structure. The Lewis structures that differ only in the arrangement of multiple bonds are called resonance structures.
Resonance structure comprises of two or more Lewis Structures that describes the arrangement of bond of a single species and include fractional bonds and fractional charges.
(a)
Answer to Problem 9.80QE
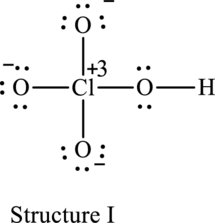
The resonance structure that has an octet around central atom is as follows:
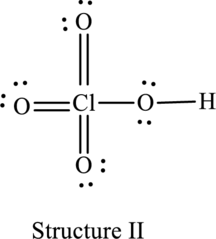
The resonance structure that minimizes formal charge is as follows:
Explanation of Solution
The skeleton structure is as follows:
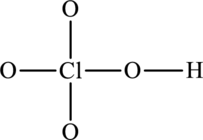
The resonance structures are as follows:
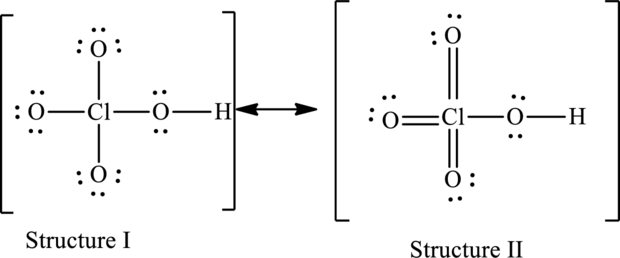
For structure I:
Substitute 7 for valence electrons, 4 for the number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on first oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on second oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on third oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on fourth oxygen atom.
For structure II:
Substitute 7 for valence electrons, 0 for the number of lone pairs of electrons and 8 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on first oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on second oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on third oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on fourth oxygen atom.
Possible resonance structures are as follows:
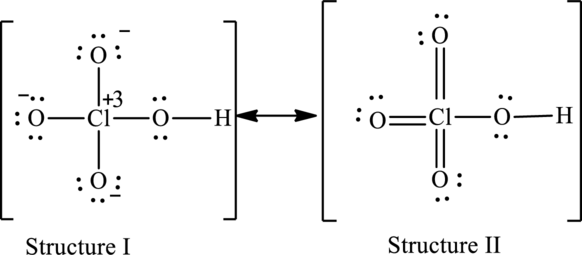
Hence, structure I has an octet around central atom and structure II minimizes the formal charge.
(b)
Interpretation:
The resonance structures with an octet about the central atom and a resonance structure that has minimum formal charges for the following structure has to be determined.
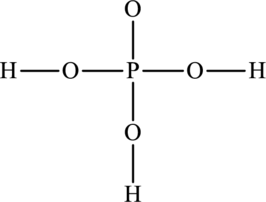
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part(a).
(b)
Answer to Problem 9.80QE
The resonance structure that has an octet around central atom is as follows:
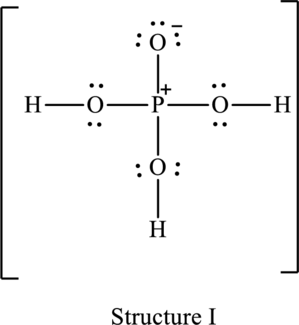
The resonance structure that minimizes formal charge is as follows:
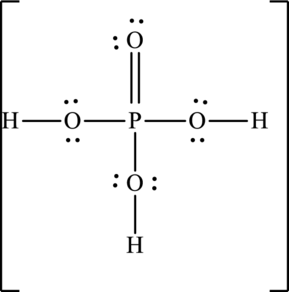
Explanation of Solution
The skeleton structure is as follows:
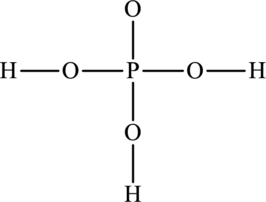
The resonance structures are as follows:
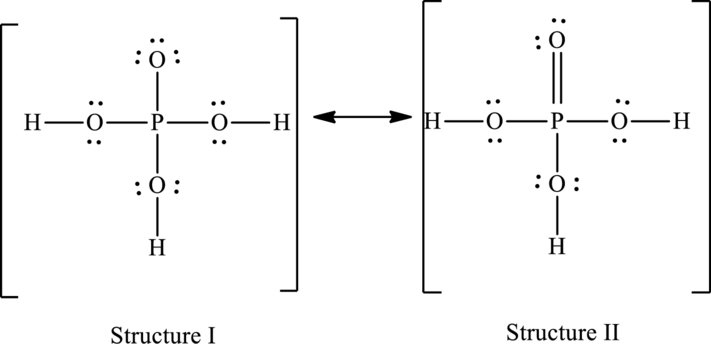
For structure I:
Substitute 5 for valence electrons, 0 for the number of lone pairs of electrons and 8 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on first oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on second oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on third oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on fourth oxygen atom.
For structure II:
Substitute 5 for valence electrons, 0 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 10 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on first oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on second oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on third oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on fourth oxygen atom.
Possible resonance structures are as follows:
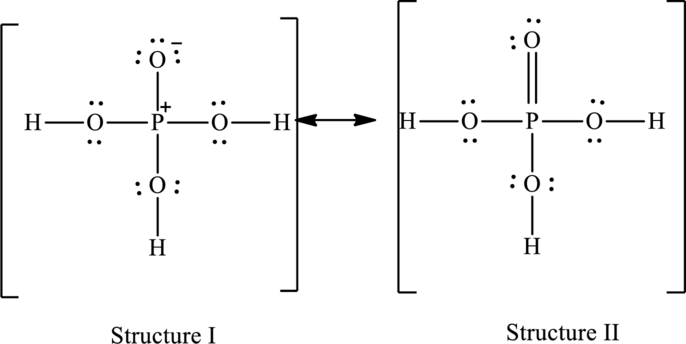
Hence, structure I has an octet around central atom and structure II minimizes the formal charge.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Chemistry: Principles and Practice
- Relative Abundance 20- Problems 501 (b) The infrared spectrum has a medium-intensity peak at about 1650 cm. There is also a C-H out-of-plane bending peak near 880 cm. 100- 80- 56 41 69 M(84) LL 15 20 25 30 35 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 m/zarrow_forwardPolyethylene furanoate is a polymer made from plant-based sources; it is used for packaging. Identify the monomer(s) used in the production of this polymer using a condensation process.arrow_forwardPhenol is the starting material for the synthesis of 2,3,4,5,6-pentachlorophenol, known al-ternatively as pentachlorophenol, or more simply as penta. At one time, penta was widely used as a wood preservative for decks, siding, and outdoor wood furniture. Draw the structural formula for pentachlorophenol and describe its synthesis from phenol.arrow_forward
- 12 Mass Spectrometry (d) This unknown contains oxygen, but it does not show any significant infrared absorption peaks above 3000 cm . 59 100- BO 40 Relative Abundance M(102) - 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 5 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105 mizarrow_forwardDraw a Haworth projection of a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: H HO H HO H HO H H -OH CH2OH Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х : Darrow_forward: Draw the structure of valylasparagine, a dipeptide made from valine and asparagine, as it would appear at physiological pH. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. P Darrow_forward
- Draw the Haworth projection of α-L-mannose. You will find helpful information in the ALEKS Data resource. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : ཊི Х Darrow_forwardDraw the structure of serine at pH 6.8. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : d كarrow_forwardTake a look at this molecule, and then answer the questions in the table below it. CH2OH H H H OH OH OH CH2OH H H H H OH H H OH H OH Is this a reducing sugar? yes α β ロ→ロ no ☑ yes Does this molecule contain a glycosidic bond? If you said this molecule does contain a glycosidic bond, write the symbol describing it. O no 0+0 If you said this molecule does contain a glycosidic bond, write the common names (including anomer and enantiomer labels) of the molecules that would be released if that bond were hydrolyzed. If there's more than one molecule, separate each name with a comma. ☐arrow_forward
- Answer the questions in the table below about this molecule: H₂N-CH₂ -C—NH–CH–C—NH–CH—COO- CH3 CH CH3 What kind of molecule is this? 0= CH2 C If you said the molecule is a peptide, write a description of it using 3-letter codes separated ☐ by dashes. polysaccharide peptide amino acid phospolipid none of the above Хarrow_forwardDraw a Haworth projection of a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: CH₂OH C=O HO H H -OH H OH CH₂OH Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : ☐ Х S '☐arrow_forwardNucleophilic Aromatic Substitution 22.30 Predict all possible products formed from the following nucleophilic substitution reactions. (a) (b) 9 1. NaOH 2. HCI, H₂O CI NH₁(!) +NaNH, -33°C 1. NaOH 2. HCl, H₂Oarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





