
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The resonance structures with an octet about the central atom and a resonance structure that has minimum formal charges for the following structure has to be determined.
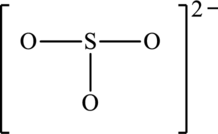
Concept Introduction:
A covalent bond is a bond that is formed from the mutual sharing of electrons between atoms. Lewis structures are representations of the covalent bond. In this, Lewis symbols show how the valence electrons are present in the molecule.
Steps to write Lewis structures are as follows:
1. The skeleton structure with single bonds between all bonded atoms has to be written
2. Sum the valence electrons of the atoms in the molecule.
(a) For cations, one electron is subtracted for each positive charge.
(b) For anions, one electron is added for each negative charge.
3. Subtract two electrons from total number of valence electrons for each bond in the skeleton structure.
4. Count the number of electrons required to satisfy the octet rule for each atom in the structure. If the number of electrons needed is less than the number remaining, add one bond for every two electrons needed between atoms to attain an octet.
5. The remaining electrons are placed as lone pairs on atoms that need them to satisfy the octet rule.
The formula to calculate formal charge of atom is,
Some molecules do not have only one Lewis structure. The Lewis structures that differ only in the arrangement of multiple bonds are called resonance structures.
Resonance structure comprises of two or more Lewis Structures that describes the arrangement of bond of a single species and include fractional bonds and fractional charges.
(a)
Answer to Problem 9.82QE
The resonance structure that has an octet around central atom is as follows:
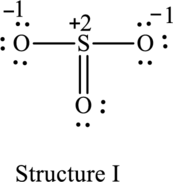
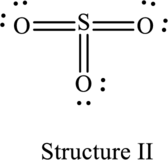
The resonance structure that minimizes formal charge is as follows:
Explanation of Solution
The skeleton structure is as follows:
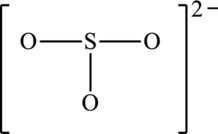
The resonance structures are as follows:
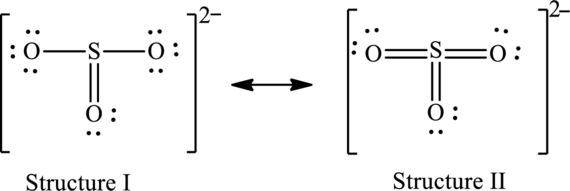
For structure I:
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 0 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 8 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on first oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on second oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on third oxygen atom.
For structure II:
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 0 for the number of lone pairs of electrons and 12 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on first oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on second oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on third oxygen atom.
Possible resonance structures are as follows:
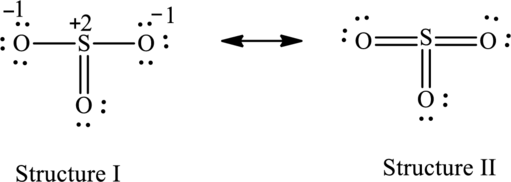
Hence, structure I has an octet around central atom and structure II minimizes the formal charge.
(b)
Interpretation:
The resonance structures with an octet about the central atom and a resonance structure that has minimum formal charges for the following structure has to be determined.
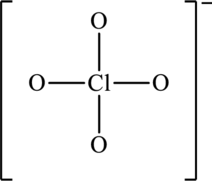
Concept introduction:
Refer to part (a)
(b)
Answer to Problem 9.82QE
The resonance structure that has an octet around central atom is as follows:
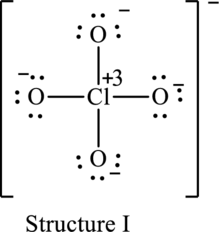
The resonance structure that minimizes formal charge is as follows:
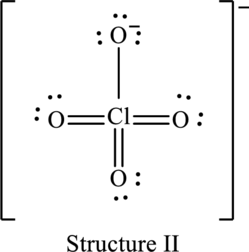
Explanation of Solution
The skeleton structure is as follows:
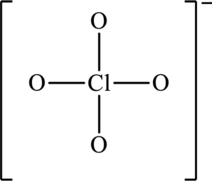
The possible resonance structures are as follows:
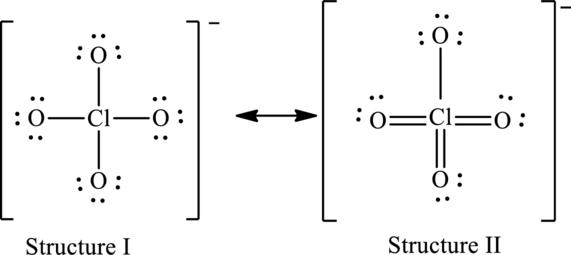
For structure I:
Substitute 7 for valence electrons, 4 for the number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on first oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on second oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on third oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on fourth oxygen atom.
For structure II:
Substitute 7 for valence electrons, 0 for the number of lone pairs of electrons and 8 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on first oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 6 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 2 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on second oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on third oxygen atom.
Substitute 6 for valence electrons, 4 for number of lone pairs of electrons and 4 for the number of shared electrons in equation (1) to calculate the formal charge on fourth oxygen atom.
Possible resonance structures are as follows:
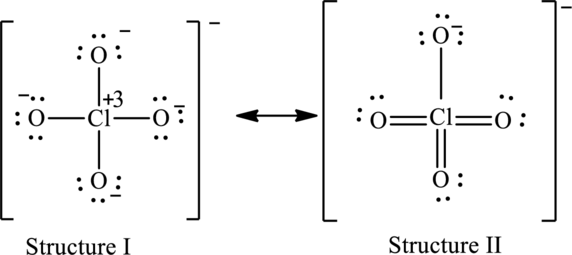
Hence, structure I has an octet around central atom and structure II minimizes the formal charge.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Chemistry: Principles and Practice
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
- er your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward5.arrow_forward6.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





