
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780618974122
Author: Andrei Straumanis
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 8, Problem 21CTQ
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation: Mechanism that accounts for product formation of below reaction with all resonance structures of carbocation 2 should be explained.
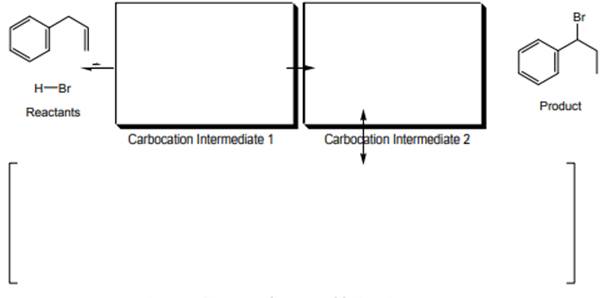
Concept introduction: The carbon-carbon double bond in
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Q6: Provide the reagents and conditions for the following reactions to make the product with a
good yield.
Br
Br
CI
она
CI
Q2: We would not expect the following primary alkyl halide to go through an SN1 reaction.
However, it can go through an SN1 mechanism. Explain why. Hint: Think about what happens
when the leaving group leaves.
CI
NaO
EtOH
H
བྱིས་
H
I performed this experiment, but I'm so confused. How do I find the first two blank columns using the data provided. What is the [I^-] mol/L and [S2O8^-2] mol/L. How do I find this? Please help!
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Ch. 8 - Prob. 1CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 2CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 3CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 4CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 5CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 6CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 7CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 8CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 9CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 10CTQ
Ch. 8 - Draw the products that result from the electron...Ch. 8 - Prob. 12CTQCh. 8 - Draw the products that would result if the arrow...Ch. 8 - Prob. 14CTQCh. 8 - What information (if any) from the following...Ch. 8 - Prob. 16CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 17CTQCh. 8 - The reactants, intermediates, final products, and...Ch. 8 - Prob. 19CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 20CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 21CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 22CTQCh. 8 - Explain how you can tell from the energy diagram...Ch. 8 - Explain why the following mechanism for hydration...Ch. 8 - Prob. 25CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 26CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 27CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 28CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 29CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 30CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 31CTQCh. 8 - The hydration above is one of a family of...Ch. 8 - Prob. 33CTQCh. 8 - Which statement is false? a. A mechanistic step...Ch. 8 - Prob. 35CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 36CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 37CTQCh. 8 - Draw the complete mechanism including the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 2ECh. 8 - Explain why ethene does not react with HX ( X=Cl ,...Ch. 8 - Draw the complete mechanism of each pair of...Ch. 8 - Prob. 5ECh. 8 - Prob. 6ECh. 8 - Prob. 7ECh. 8 - Prob. 8ECh. 8 - Prob. 9ECh. 8 - Prob. 10ECh. 8 - Prob. 11ECh. 8 - Prob. 12ECh. 8 - Prob. 15ECh. 8 - A student proposes the following reaction...Ch. 8 - Prob. 17ECh. 8 - Prob. 18ECh. 8 - Prob. 19E
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Example 3 A molecule is achiral if it has a plane of symmetry in any conformation. The given conformation of 2,3-dibromobutane below does not have a plane of symmetry. Will rotation around the C2-C3 bond form a conformation with a plane of symmetry? Draw the conformation to find out. DIY: Do the same for: H3C Brill rotate H CH3 OH HO Brarrow_forward120 100 20 20 bound drug/free drug (%) 60 40 60 80 80 0 0 Scatchard Plot of Drug Binding 20 20 40 60 80 100 120 bound drug (nM)arrow_forwardUsing diethylmalonate and benzyl bromide as your only as your only source of carbon, propose a synthesis for the following compound.arrow_forward
- please helparrow_forwardWhat is the difference between (+)-(S)-methamphetamine and (-)-(R)-methamphetamine versus levo-methamphetamine and dextro-methamphetamine, D-methamphetamine, and L-methamphetamine, and N-methamphetamine? Please use scholarly sources and in-text citations.arrow_forwardanswer all the questions with explanationarrow_forward
- Please draw a mechanism don't write sentarrow_forwardFrom this COZY spectrum, how do you know which protons are next to each other?arrow_forward5. A buffer consists of 0.45 M NH, and 0.25 M NH-CI (PK of NH 474) Calculate the pH of the butter. Ans: 9.52 BAS PH-9.26 +10g (10.95)) 14-4.59 PH=4.52 6. To 500 ml of the buffer on #5 a 0.20 g of sample of NaOH was added a Write the net ionic equation for the reaction which occurs b. Should the pH of the solution increase or decrease sightly? Calculate the pH of the buffer after the addition Ans: 9.54arrow_forward
- Explain the inductive effect (+I and -I) in benzene derivatives.arrow_forwardThe inductive effect (+I and -I) in benzene derivatives, does it guide ortho, meta or para?arrow_forward19.57 Using one of the reactions in this chapter, give the correct starting material (A-L) needed to produce each structure (a-f). Name the type of reaction used. (b) ہ مرد (d) HO (c) དང་ ་་ཡིན་ད་དང་ (f) HO Br B D of oli H J Br K C 人 ↑arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY