
(a)
Interpretation: The mechanism for formation of the alcohol product should be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The product formed is governed by Markovnikov’s Rule. Rule suggests that negative part of halo acid HX must go to the carbon that has more alkyl substituents or less
The order of relative stability of various possible carbocation species is as follows:
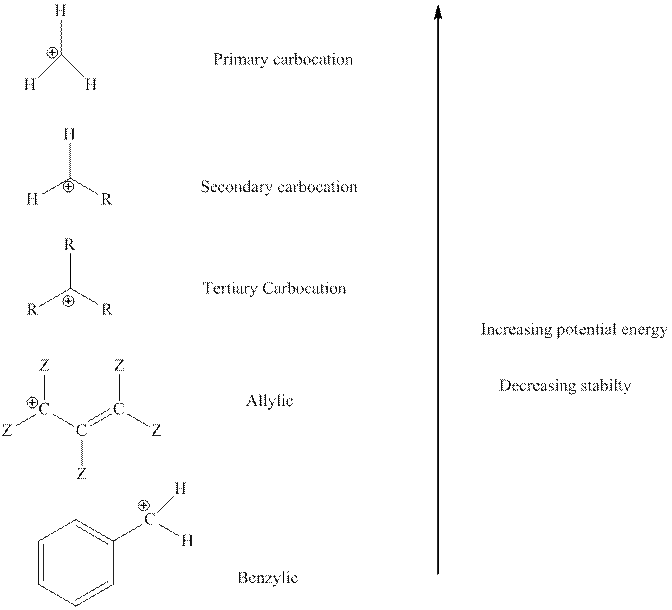
(b)
Interpretation: The expected product of reaction was carried out in methanol instead of water should be drawn.
Concept introduction: Alkenes are regarded electron-rich and often undergo addition reaction in presence of electrophilic halo acids or nucleophilic sodium cyanide. The intermediate formed in former is tertiary carbocation and finally nucleophilic part of halo acid attacks in a rapid step to give addition product.
The product formed is governed by Markovnikov’s Rule. Rule suggests that negative part of halo acid HX must go to the carbon that has more alkyl substituents or less
The order of relative stability of various possible carbocation species is as follows:
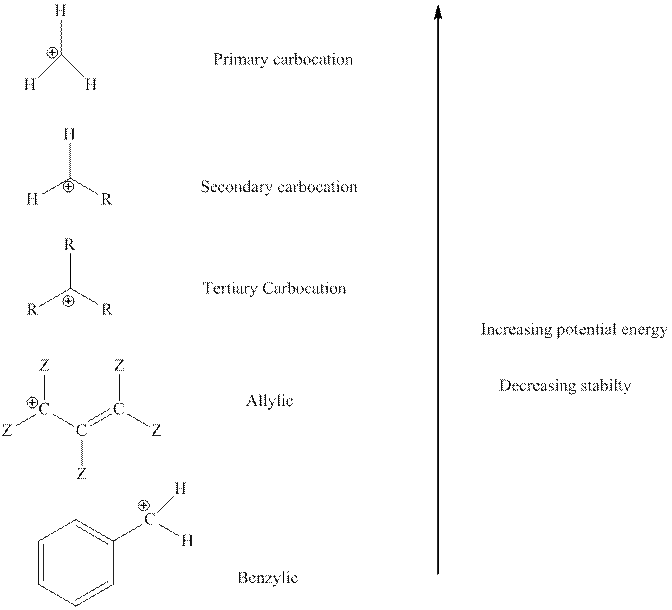
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
- Provide the drawing of the unknown structure that corresponds with this data.arrow_forward20.44 The Diels-Alder reaction is not limited to making six-membered rings with only car- bon atoms. Predict the products of the following reactions that produce rings with atoms other than carbon in them. OCCH OCCH H (b) CH C(CH₂)s COOCH མ་ནས་བ (c) N=C H -0.X- (e) H C=N COOCHS + CH2=CHCH₂ →→arrow_forwardGiven the attached data, provide the drawing for the corresponding structure.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
