
Concept explainers
(E) What does the number (+Z) at the center of each atom in Figure 1.1 represent, and whatnumber would you expect at the center of a representation of a bromine atom (Br)?
Interpretation:
The purpose of the representation of number (+Z) at the centre of each atom in given figure 1.1 should be determined along with the number which is present at the centre of a representation of bromine atom.
Concept Introduction:
In a planetary model of an atom, negative charged electrons are arranged around the positive charged electron in a series of shells which is like orbits.
The electrons present in the outermost energy level or shell is known as valence electrons. These electrons are available for bonding and outermost shell is known as valence shell.
Answer to Problem 1CTQ
+Z represents the nuclear charge of an atom which is equal to the number of protons or atomic number.
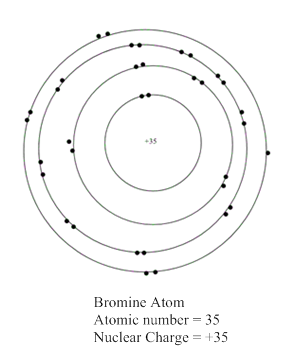
The representation of bromine atom:
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
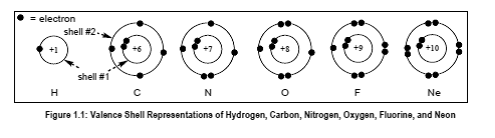
In the given figure, the number Z represents the atomic number of an atom such as atomic number of carbon is 6. +Z represents the nuclear charge which is nothing but atomic number.
The total charge present on all the protons in the nucleus is known as nuclear charge. The value of nuclear charge is equal to atomic number.
The number of protons present in nucleus of an atom is known as atomic number.
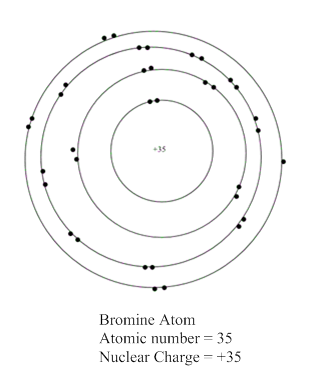
Now, atomic number of bromine atom is equal to 35 which is equal to the number of protons present in bromine atom. In the valence shell representation, +35 is present at the centre of a representation of bromine atom.
Hence, the representation of bromine atom is shown as:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
- (f) SO: Best Lewis Structure 3 e group geometry:_ shape/molecular geometry:, (g) CF2CF2 Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: (h) (NH4)2SO4 Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forward1. Problem Set 3b Chem 141 For each of the following compounds draw the BEST Lewis Structure then sketch the molecule (showing bond angles). Identify (i) electron group geometry (ii) shape around EACH central atom (iii) whether the molecule is polar or non-polar (iv) (a) SeF4 Best Lewis Structure e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: polarity: (b) AsOBr3 Best Lewis Structure e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forward(c) SOCI Best Lewis Structure 2 e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry:_ (d) PCls Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group geometry:_ shape/molecular geometry:_ (e) Ba(BrO2): Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
