
Concept explainers
Interpretation: Each carbocation in below figure should be labelled as
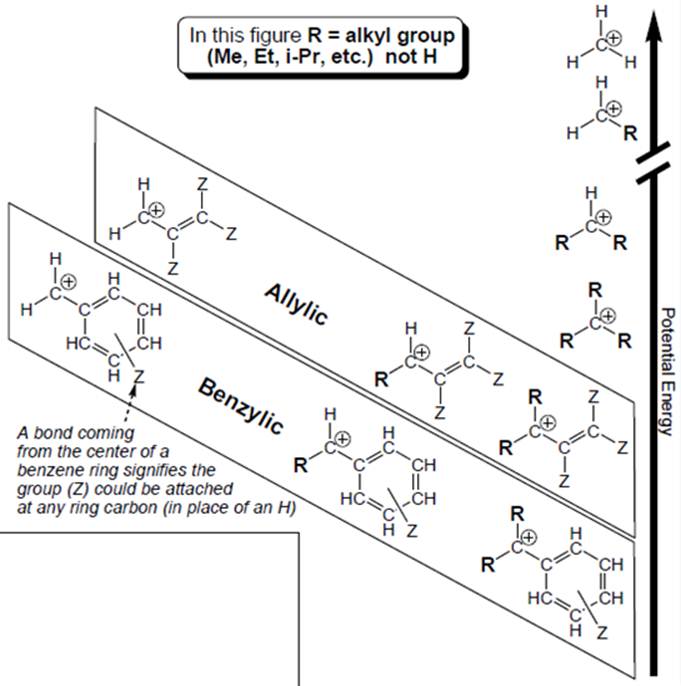
Concept introduction: Organic compounds are covalent in nature that undergoes a reaction by heterolytic cleavage or homolytic cleavage.
In heterolytic cleavage, shared pair of electrons is taken away by one of the atoms which result in charged species. In homolytic cleavage, shared pair of electrons are equally distributed between two atom that results in free radicals.
Carbocation is a general term employed for a postively charged carbon irrespective of valency of carbon. In carbocation, carbon is bonded to 3 atoms or groups and has only sextet of electrons so it behaves as an electron-deficient species. It is
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
- To convert cyclopentane-CH2-CHO to cyclopentane-CH2-CH3, compound A is added, followed by (CH3)3CO-K+, DMS at 100oC. Indicate which compound A is.arrow_forwardIndicate how to obtain the compound 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol.arrow_forwardIndicate the reagent needed to go from cyclopentane-CH2-CHO to cyclopentane-CH2-CH=CH-C6H5.arrow_forward
- esc Write the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure CH3 CH3-C=CH2 CH3-CH2-C-CH2-CH3 CH-CH3 CH3 ☐ ☐ ☐ CI-CH-CH=CH2 Explanation Check F1 F2 name 80 F3 F4 F5 F6 A 7 ! 2 # 3 4 % 5 6 & 7 Q W E R Y FT 2025 Mcarrow_forwardTwo reactants X and Z are required to convert the compound CH3-CH2-CH2Br to the compound CH3-CH2-CH=P(C6H5)3. State reactants X and Z.arrow_forward2. Write a reasonable mechanism that converts the reactants into the products. Avoid issues A-U from the previous page. You can use any number of steps (it does not have to be a one-step mechanism). Do not use any other chemicals (solvents, acids, bases, etc.) in your mechanism. 2 2 H ΗΘarrow_forward
- For the following reaction, the partial pressures were determined for the reaction components as shownbelow. Is the reaction at equilibrium? If not, in which direction will it proceed?I2 (g) + Cl2 (g) ⇋ 2 ICl (g) Kp = 81.9 partial pressures: I2 = 0.114 atm; Cl2 = 0.102 atm; ICl = 0.355 atmarrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. H3O+ + Oarrow_forwardWrite the law of mass action for the following quilibrium 2N2O5(g) --> 4 NO2(g) + O2(g).arrow_forward
- State the products (formulas) of the reaction of acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardCh. 4- Precipitation Reactions Worksheet Write balanced, complete ionic, and net ionic equations for the following reactions that mav produce precipitates. Use NR to indicate no reaction Ave 1\ +3 =6 Fe + V-2 Na S04 13. Write the balanced equation for the reaction of iron (III) phosphate with sodium sulfate to make iron (III) sulfate and sodium phosphate. 2FePO4 + M, Soy a) If you perform this reaction with 25 grams of iron (III) phosphate and an excess of sodium sulfate, how many grams of iron (III) sulfate can you make? 21 Fe 2 3x 1 Na 3 25g Fe Ingle 150,829 Indes 2 nol 3 1335 349.89 35.90 Ihol & Sanz Fez Bak heck 3x1 50ab) If 18.5 grams of iron (III) sulfate are actually made when you do this reaction, what is your Poy percent yield? 118.5 259-1-100 51.4% (0.74)x100610 335 If you do this reaction with 15 grams of sodium sulfate and get a 65.0% yield, how many grams of sodium phosphate will you make? 10.59 14. Ammonia is produced from the reaction of nitrogen and hydrogen according…arrow_forward== Functional Groups Identifying and drawing hemiacetals and acetals In the drawing area below, create an acetal with 1 isopropoxy group, 1 hydroxyl group, and a total of 10 carbon atoms. Explanation Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Check G +arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
