
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780618974122
Author: Andrei Straumanis
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 8, Problem 33CTQ
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation: Number of synthetic steps below reaction should be stated.
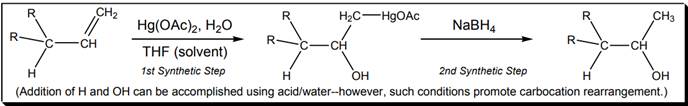
Concept introduction: The carbon-carbon double bond in
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
1. Determine the relationship between the following molecules as identical, diastereomers, or enantiomers (6
points, 2 points each).
OH
OH
OH
A-A
OH
HOT
HO-
ACHN
and
HO-
ACHN
OH
HO
HO
°
OH
and
OH
OH
SH
and
...SH
20,0
Complete the electron pushing mechanism to
y drawing the necomery unicaciones and carved on for
Step 1: Add curved arms for the tint step, traiment with NalilĻ. The Nation
458
Step 2: Added for the second step, inalment with), how the "counterion
bar
Step 3: Daw the products of the last simplom organic and one incoganic spacient, including all nonbonding
please provide the structure for this problem, thank you!
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Ch. 8 - Prob. 1CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 2CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 3CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 4CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 5CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 6CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 7CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 8CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 9CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 10CTQ
Ch. 8 - Draw the products that result from the electron...Ch. 8 - Prob. 12CTQCh. 8 - Draw the products that would result if the arrow...Ch. 8 - Prob. 14CTQCh. 8 - What information (if any) from the following...Ch. 8 - Prob. 16CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 17CTQCh. 8 - The reactants, intermediates, final products, and...Ch. 8 - Prob. 19CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 20CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 21CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 22CTQCh. 8 - Explain how you can tell from the energy diagram...Ch. 8 - Explain why the following mechanism for hydration...Ch. 8 - Prob. 25CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 26CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 27CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 28CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 29CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 30CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 31CTQCh. 8 - The hydration above is one of a family of...Ch. 8 - Prob. 33CTQCh. 8 - Which statement is false? a. A mechanistic step...Ch. 8 - Prob. 35CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 36CTQCh. 8 - Prob. 37CTQCh. 8 - Draw the complete mechanism including the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 2ECh. 8 - Explain why ethene does not react with HX ( X=Cl ,...Ch. 8 - Draw the complete mechanism of each pair of...Ch. 8 - Prob. 5ECh. 8 - Prob. 6ECh. 8 - Prob. 7ECh. 8 - Prob. 8ECh. 8 - Prob. 9ECh. 8 - Prob. 10ECh. 8 - Prob. 11ECh. 8 - Prob. 12ECh. 8 - Prob. 15ECh. 8 - A student proposes the following reaction...Ch. 8 - Prob. 17ECh. 8 - Prob. 18ECh. 8 - Prob. 19E
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Draw the Fischer projection from the skeletal structure shown below. HO OH OH OH OH H Q Drawing Atoms, Bonds and Rings Charges I ☐ T HO H H OH HO I CH2OH H OH Drag H OH -CH2OH CHO -COOH Undo Reset Remove Donearrow_forwardplease provide the structure for this problem, thank youarrow_forwardpresented by Morallen Lig Intermine the hand product for the given mution by adding atoms, bonds, nonhonding diarion panda скуль Step 3: Comp the draw the product Step 2: Agama workup Compithe 429 ملولةarrow_forward
- Reaction A 0,0arrow_forwardpresented by Morillon Leaning Predict the organic product for the min кусур HSC Adithane carved arnown to come than that to the condon slchroruis in acid in in aquishri with ноюarrow_forward6.15PM Sun Mar 30 K Draw the major product of this reaction. Include any relevant stereochemistry. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Problem 1 of O H [PhзPCH2CH3]*C|¯ NaH Drawing > Q Atoms, Bonds and Draw or tap a nearrow_forward
- 8:17 PM Sun Mar 30 Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HSCH2CH2CH2SH, BF3 Probler Drawing Ato Bonds Clarrow_forwardpresented by Mr L How the coprion. (Il Done in no wraction, dew the starting redential) доarrow_forward8:16 PM Sun Mar 30 K Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Proble 1. CH3MgBr 2. H3O+ F Drawingarrow_forward
- о но оarrow_forwardName the major organic product of the following action of 4-chloro-4-methyl-1-pentanol in neutral pollution 10+ Now the product. The product has a molecular formula f b. In a singly hain, the starting, material again converts into a secule with the molecular kormula CIO. but with comply Draw the major organic structure inhalationarrow_forwardMacmillan Learning Alcohols can be oxidized by chromic acid derivatives. One such reagent is pyridinium chlorochromate, (C,H,NH*)(CICTO3), commonly known as PCC. Draw the proposed (neutral) intermediate and the organic product in the oxidation of 1-butanol by PCC when carried out in an anhydrous solvent such as CH₂C₁₂. PCC Intermediate OH CH2Cl2 Draw the intermediate. Select Draw Templates More с H Cr о Product Draw the product. Erase Select Draw Templates More H о Erasearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning