
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: Mechanism for the first synthetic step of oxymercuration-demercuration reaction shown below should be drawn.
Concept introduction:
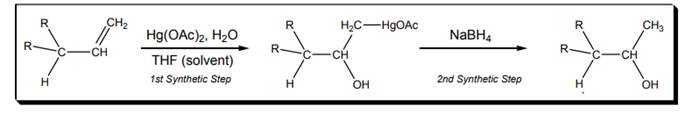
(b)
Interpretation: A Lewis structure of
Concept introduction: Lewis structures depict covalent bonds and describe valence electrons are present in the molecule. The sequence that leads to the Lewis structure of the molecule is as follows:
- Identify the central atom and arrange various other atoms around it. This atom so chosen is the least electronegative one.
- Estimate the total valence electrons.
- First, place a single bond between each pair.
- The remaining electrons can be allocated as lone pairs to satisfy the octet rule for each atom.
(c)
Interpretation: Particular characteristics of oxymercuration reaction shown below should be explained.
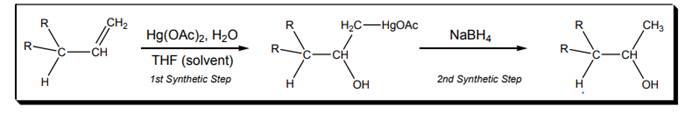
Concept introduction: Oxymercuration takes place in the presence of
(d)
Interpretation: Mechanism for acid-catalyzed hydration of below alkene substrate should be drawn.
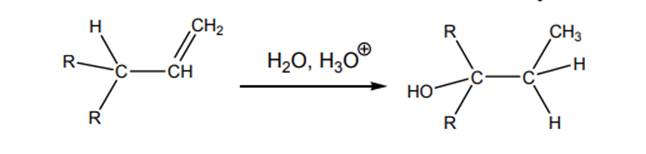
Concept introduction: Acid-catalyzed hydration is the electrophilic addition of water. The reactive species that act as a catalyst are
.In the second stage water, itself acts as a nucleophile and abstracts a proton to hydration product. The carbocation rearrangement can also be found in such reactions.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
- Synthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIf possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forward
- Synthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forwardWe mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward
- Question 3 (4 points), Draw a full arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reaction Please draw all structures clearly. Note that this intramolecular cyclization is analogous to the mechanism for halohydrin formation. COH Br + HBr Brarrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if 2,2-dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if 2,2-dimethylpropanal and acetaldehyde are reacted with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
