
Interpretation: Structural features that boxed carbocations have other than unboxed carbocations should be determined.
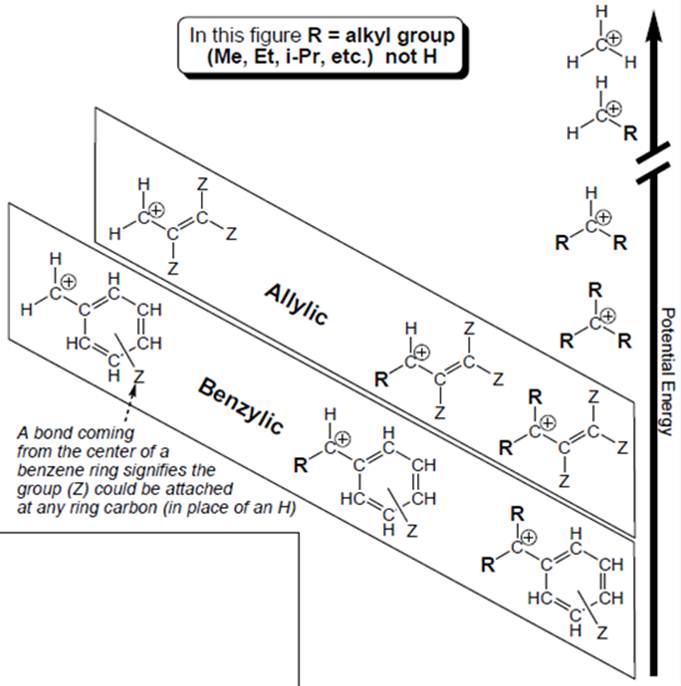
Concept introduction: Organic compounds are covalent in nature which undergo a reaction by heterolytic cleavage or homolytic cleavage.
In heterolytic cleavage, shared pair of electrons is taken away by one of the atoms which result in charged species. In homolytic cleavage, shared pair of electrons are equally distributed between two atom that results in free radicals.
Carbocation is a general term employed for a postively charged carbon irrespective of valency of carbon. In carbocation, carbon is bonded to 3 atoms or groups and has only sextet of electrons so it behaves as an electron-deficient species. It is
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
- What is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. NaN₃arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this?arrow_forward
- Can I please get help with this?arrow_forwardUse the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to calculate pH of a buffer containing 0.050M benzoic acidand 0.150M sodium benzoate. The Ka of benzoic acid is 6.5 x 10-5arrow_forwardA. Draw the structure of each of the following alcohols. Then draw and name the product you would expect to produce by the oxidation of each. a. 4-Methyl-2-heptanol b. 3,4-Dimethyl-1-pentanol c. 4-Ethyl-2-heptanol d. 5,7-Dichloro-3-heptanolarrow_forward
- What is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this.arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,
Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

