
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for ethyl butyrate has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
General structure of ester can be represented as shown below,
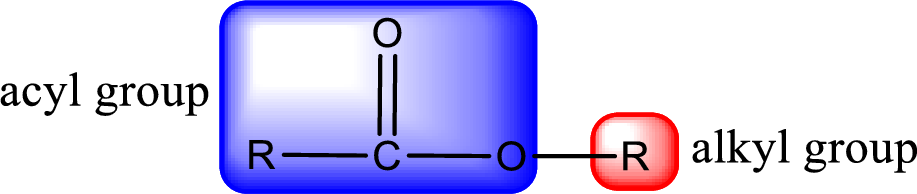
From an IUPAC name, the structure of the ester can be derived. IUPAC name of ester consists of two parts. In an IUPAC name of ester, the first part of the name is the alkyl part and the second part is the acyl part. Alkyl group have come from the alcohol and acyl part from
The same rule applies for deriving a structure from common name. The only difference is the acyl part name. The acyl part is named using the common name of carboxylic acid.
(b)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for butyl ethanoate has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
General structure of ester can be represented as shown below,
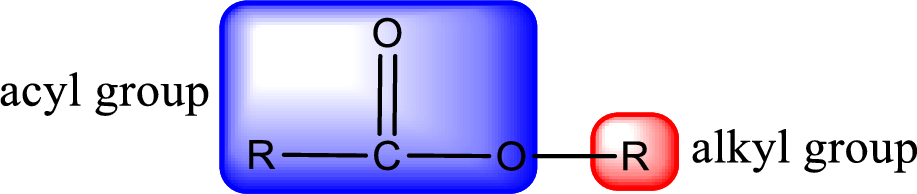
From an IUPAC name, the structure of the ester can be derived. IUPAC name of ester consists of two parts. In an IUPAC name of ester, the first part of the name is the alkyl part and the second part is the acyl part. Alkyl group have come from the alcohol and acyl part from carboxylic acid.
The same rule applies for deriving a structure from common name. The only difference is the acyl part name. The acyl part is named using the common name of carboxylic acid.
(c)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for 2-methylpropyl formate has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
General structure of ester can be represented as shown below,
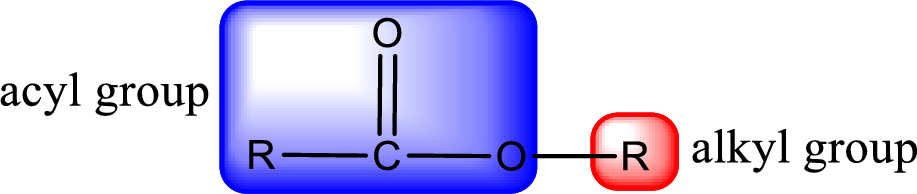
From an IUPAC name, the structure of the ester can be derived. IUPAC name of ester consists of two parts. In an IUPAC name of ester, the first part of the name is the alkyl part and the second part is the acyl part. Alkyl group have come from the alcohol and acyl part from carboxylic acid.
The same rule applies for deriving a structure from common name. The only difference is the acyl part name. The acyl part is named using the common name of carboxylic acid.
(d)
Interpretation:
Structural formula for ethyl
Concept Introduction:
General structure of ester can be represented as shown below,
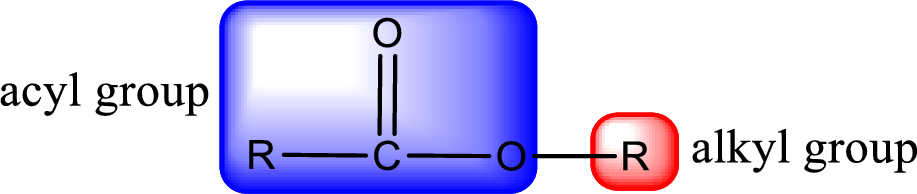
From an IUPAC name, the structure of the ester can be derived. IUPAC name of ester consists of two parts. In an IUPAC name of ester, the first part of the name is the alkyl part and the second part is the acyl part. Alkyl group have come from the alcohol and acyl part from carboxylic acid.
The same rule applies for deriving a structure from common name. The only difference is the acyl part name. The acyl part is named using the common name of carboxylic acid.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 5 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward
- 5.arrow_forward6.arrow_forward0/5 alekscgi/x/sl.exe/1o_u-IgNglkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBaHhvlTCeeBZbufuBYTi0Hz7m7D3ZcSLEFovsXaorzoFtUs | AbtAURtkqzol 1HRAS286, O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 3 pressure (atm) + 0- 0 5+ 200 temperature (K) 400 Explanation Check X 0+ F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Accessibility Q Search LUCR + F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 * % & ( 5 6 7 8 9 Y'S Dele Insert PrtSc + Backsarrow_forward
- 5.arrow_forward9arrow_forwardalekscgi/x/lsl.exe/1o_u-IgNslkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBanHhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTI0Hz7m7D3ZS18w-nDB10538ZsAtmorZoFusYj2Xu9b78gZo- O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 3- 200 temperature (K) Explanation Chick Q Sowncharrow_forward
- 0+ aleksog/x/lsl.exe/1ou-lgNgkr7j8P3H-IQs pBaHhviTCeeBZbufuBYTOHz7m7D3ZStEPTBSB3u9bsp3Da pl19qomOXLhvWbH9wmXW5zm O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 Gab The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 0.75 atm and -229. °C is increased until the sample sublimes. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.50 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. F3 pressure (atm) 0- 0 200 Explanation temperature (K) Check F4 F5 ☀+ Q Search Chill Will an 9 ENG F6 F7 F8 F9 8 Delete F10 F11 F12 Insert PrtSc 114 d Ararrow_forwardx + LEKS: Using a phase diagram a X n/alekscgi/x/lsl.exe/10_u-IgNsikr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBan HhvlTCeeBZbufu BYTI0Hz7m7D3ZcHYUt80XL-5alyVpw ○ States of Matter Using a phase diagram to find a phase transition temperature or pressure Use the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the melting point of X when the pressure above the solid is 1.1 atm. pressure (atm) 16 08- solid liquid- 0 200 400 gas 600 temperature (K) Note: your answer must be within 25 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct. × 5arrow_forwardS: Using a phase diagram leksogi/x/sl.exe/1ou-IgNs kr 7j8P3jH-IQs_pBan HhvTCeeBZbufuBYTI0Hz7m7D3ZdHYU+80XL-5alyVp O States of Matter Using a phase diagram to find a phase transition temperature or pressure se the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the boiling point of X when the pressure on the liquid is 1.6 atm. pressure (atm) 32- 16- solid liquid 0. gas 100 200 temperature (K) 300 Note: your answer must be within 12.5 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct. 10 Explanation Check § Q Search J 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Researrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





