
(a)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for
Concept Introduction:
In
In organic chemistry, reduction reaction is referred to the number
Alcohols undergo
Aldehyde undergoes oxidation to give carboxylic acid as the product while ketone does not undergo oxidation reaction.
(a)
Answer to Problem 5.45EP
The structural formula of the expected product is,
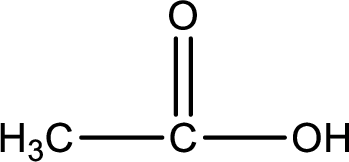
Explanation of Solution
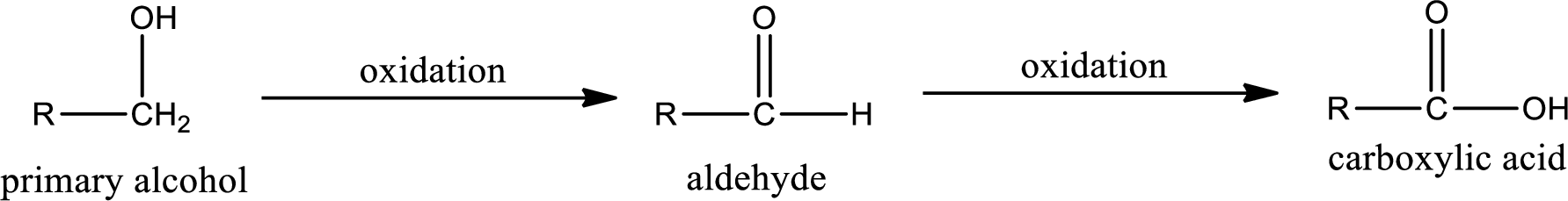
Primary alcohol on oxidation gives aldehyde as intermediate product. This on further oxidation gives carboxylic acid as the product. The general scheme can be represented as shown below,
Given substance is,
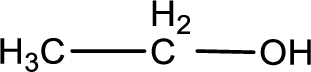
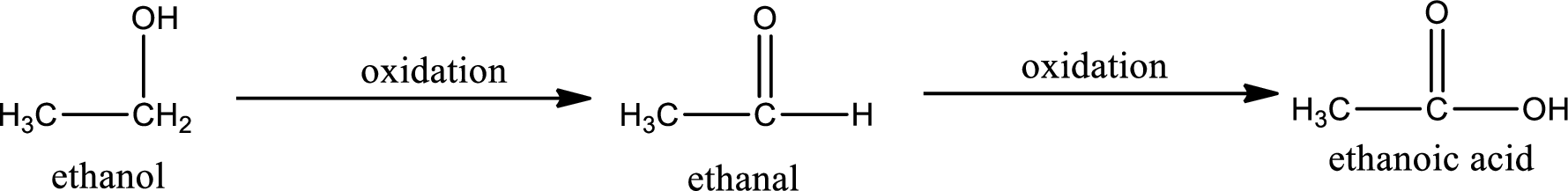
This is a primary alcohol. The given compound is ethanol. Ethanol on oxidation gives ethanal as the intermediate product. The formed ethanal on oxidation gives ethanoic acid as the product. The complete scheme can be represented as shown below,
The carboxylic acid that is formed on oxidation of the given substance is ethanoic acid. The structural formula of ethanoic acid is given below,
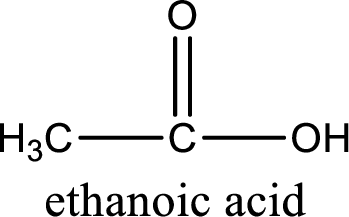
Structural formula of the carboxylic acid formed by the oxidation of given substance is drawn.
(b)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for carboxylic acid that is expected to be formed on oxidation of the given substance has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
In organic chemistry, oxidation reaction is referred to the number
In organic chemistry, reduction reaction is referred to the number
Alcohols undergo oxidation reaction and reduction reaction. This depends upon the number of hydrogen atoms that is bonded to the alpha carbon atom. Primary and secondary alcohol undergoes oxidation reaction while tertiary alcohol does not undergo oxidation reaction. Primary alcohols undergo oxidation to give aldehyde and carboxylic acid as product. Secondary alcohol undergoes oxidation to give ketone as the product.
Aldehyde undergoes oxidation to give carboxylic acid as the product while ketone does not undergo oxidation reaction.
Aromatic carboxylic acids are prepared from alkyl substituted benzenes.
(b)
Answer to Problem 5.45EP
The structural formula of the expected product is,
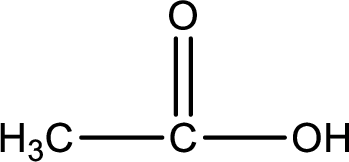
Explanation of Solution
Aldehyde on oxidation gives carboxylic acid as the product. The general scheme can be represented as shown below,

Given substance is,
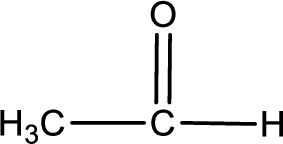
The given compound is ethanal and it is an aldehyde. Ethanal on oxidation gives ethanoic acid as the product. The complete scheme can be represented as shown below,

The carboxylic acid that is formed on oxidation of the given substance is ethanoic acid. The structural formula of ethanoic acid is given below,
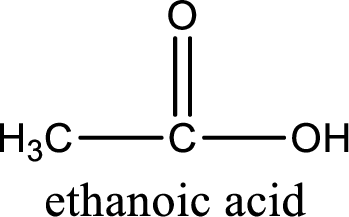
Structural formula of the carboxylic acid formed by the oxidation of given substance is drawn.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for carboxylic acid that is expected to be formed on oxidation of the given substance has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
In organic chemistry, oxidation reaction is referred to the number
In organic chemistry, reduction reaction is referred to the number
Alcohols undergo oxidation reaction and reduction reaction. This depends upon the number of hydrogen atoms that is bonded to the alpha carbon atom. Primary and secondary alcohol undergoes oxidation reaction while tertiary alcohol does not undergo oxidation reaction. Primary alcohols undergo oxidation to give aldehyde and carboxylic acid as product. Secondary alcohol undergoes oxidation to give ketone as the product.
Aldehyde undergoes oxidation to give carboxylic acid as the product while ketone does not undergo oxidation reaction.
Aromatic carboxylic acids are prepared from alkyl substituted benzenes.
(c)
Answer to Problem 5.45EP
The structural formula of the expected product is,
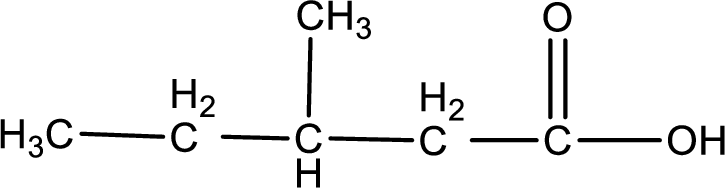
Explanation of Solution
Aldehyde on oxidation gives carboxylic acid as the product. The general scheme can be represented as shown below,

Given substance is,
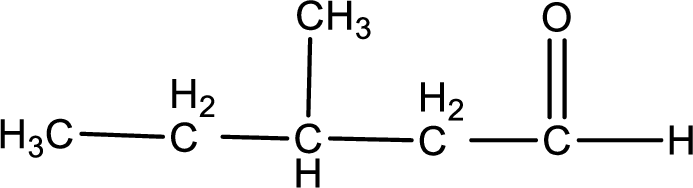
The given compound is 3-methylpentanal and it is an aldehyde. 3-methylpentanal on oxidation gives 3-methylpentanoic acid as the product. The complete scheme can be represented as shown below,

The carboxylic acid that is formed on oxidation of the given substance is 3-methylpentanoic acid. The structural formula of 3-methylpentanoic acid is given below,
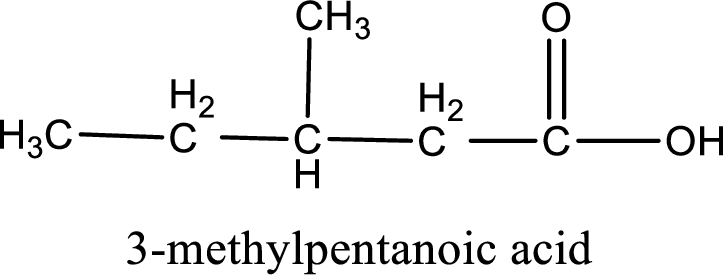
Structural formula of the carboxylic acid formed by the oxidation of given substance is drawn.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for carboxylic acid that is expected to be formed on oxidation of the given substance has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
In organic chemistry, oxidation reaction is referred to the number
In organic chemistry, reduction reaction is referred to the number
Alcohols undergo oxidation reaction and reduction reaction. This depends upon the number of hydrogen atoms that is bonded to the alpha carbon atom. Primary and secondary alcohol undergoes oxidation reaction while tertiary alcohol does not undergo oxidation reaction. Primary alcohols undergo oxidation to give aldehyde and carboxylic acid as product. Secondary alcohol undergoes oxidation to give ketone as the product.
Aldehyde undergoes oxidation to give carboxylic acid as the product while ketone does not undergo oxidation reaction.
Aromatic carboxylic acids are prepared from alkyl substituted benzenes.
(d)
Answer to Problem 5.45EP
The structural formula of the expected product is,
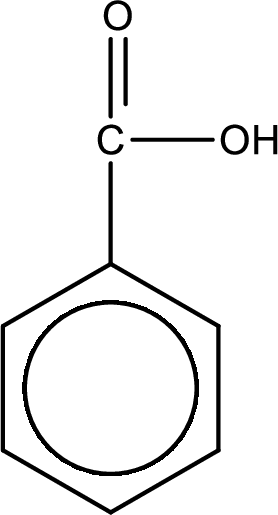
Explanation of Solution
Given substance is,
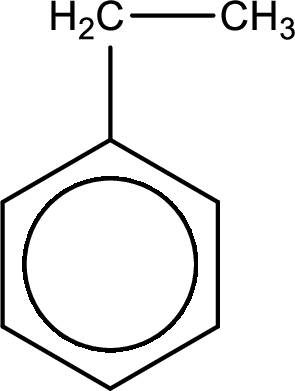
Oxidation of the alkyl side chain in a benzene derivative leads to the formation of aromatic acids. All the carbon atoms in alkyl group are lost except the one that is attached to the ring. The one carbon that is attached to the ring becomes a part of carboxyl
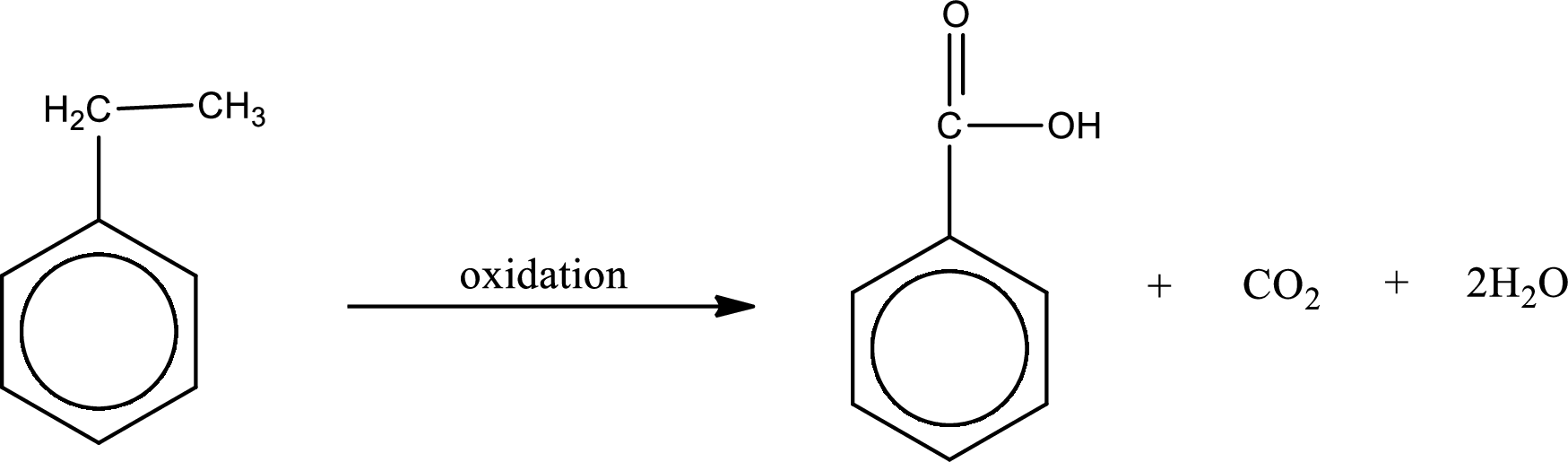
The product formed is benzoic acid.
Structural formula of the carboxylic acid formed by the oxidation of given substance is drawn.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- Provide the semi-developed formula of isooxazole obtained by reacting acetylacetone and hydroxylamine.arrow_forwardGiven a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound (R1-CO-CH2-CO-R2), indicate the formula of the compound obtaineda) if I add hydroxylamine (NH2OH) to give an isooxazole.b) if I add thiosemicarbazide (NH2-CO-NH-NH2) to give an isothiazole.arrow_forwardAn orange laser has a wavelength of 610 nm. What is the energy of this light?arrow_forward
- The molar absorptivity of a protein in water at 280 nm can be estimated within ~5-10% from its content of the amino acids tyrosine and tryptophan and from the number of disulfide linkages (R-S-S-R) between cysteine residues: Ε280 nm (M-1 cm-1) ≈ 5500 nTrp + 1490 nTyr + 125 nS-S where nTrp is the number of tryptophans, nTyr is the number of tyrosines, and nS-S is the number of disulfide linkages. The protein human serum transferrin has 678 amino acids including 8 tryptophans, 26 tyrosines, and 19 disulfide linkages. The molecular mass of the most dominant for is 79550. Predict the molar absorptivity of transferrin. Predict the absorbance of a solution that’s 1.000 g/L transferrin in a 1.000-cm-pathlength cuvet. Estimate the g/L of a transferrin solution with an absorbance of 1.50 at 280 nm.arrow_forwardIn GC, what order will the following molecules elute from the column? CH3OCH3, CH3CH2OH, C3H8, C4H10arrow_forwardBeer’s Law is A = εbc, where A is absorbance, ε is the molar absorptivity (which is specific to the compound and wavelength in the measurement), and c is concentration. The absorbance of a 2.31 × 10-5 M solution of a compound is 0.822 at a wavelength of 266 nm in a 1.00-cm cell. Calculate the molar absorptivity at 266 nm.arrow_forward
- How to calculate % of unknown solution using line of best fit y=0.1227x + 0.0292 (y=2.244)arrow_forwardGiven a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound, state the (condensed) formula of the compound obtaineda) if I add hydroxylamine (NH2OH) to give an isooxazole.b) if I add thiosemicarbazide (NH2-CO-NH-NH2) to give an isothiazole.arrow_forwardComplete the following acid-base reactions and predict the direction of equilibrium for each. Justify your prediction by citing pK values for the acid and conjugate acid in each equilibrium. (a) (b) NHs (c) O₂N NH NH OH H₁PO₁arrow_forward
- 23.34 Show how to convert each starting material into isobutylamine in good yield. ཅ ནད ཀྱི (b) Br OEt (c) (d) (e) (f) Harrow_forwardPlease help me Please use https://app.molview.com/ to draw this. I tried, but I couldn't figure out how to do it.arrow_forwardPropose a synthesis of 1-butanamine from the following: (a) a chloroalkane of three carbons (b) a chloroalkane of four carbonsarrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning





