
(a)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for
Concept Introduction:
In
In organic chemistry, reduction reaction is referred to the number
Alcohols undergo
Aldehyde undergoes oxidation to give carboxylic acid as the product while ketone does not undergo oxidation reaction.
(a)
Answer to Problem 5.46EP
The structural formula of the expected product is,
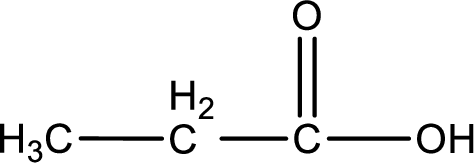
Explanation of Solution
Aldehyde on oxidation gives carboxylic acid as the product. The general scheme can be represented as shown below,

Given substance is,
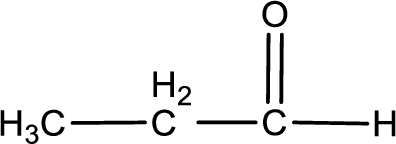
The given compound is propanal and it is an aldehyde. Propanal on oxidation gives propanoic acid as the product. The complete scheme can be represented as shown below,

The carboxylic acid that is formed on oxidation of the given substance is propanoic acid. The structural formula of propanoic acid is given below,
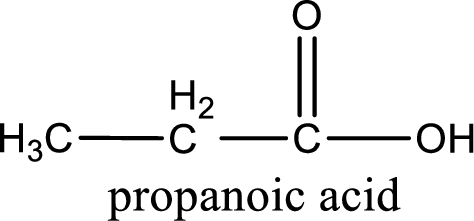
Structural formula of the carboxylic acid formed by the oxidation of given substance is drawn.
(b)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for carboxylic acid that is expected to be formed on oxidation of the given substance has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
In organic chemistry, oxidation reaction is referred to the number
In organic chemistry, reduction reaction is referred to the number
Alcohols undergo oxidation reaction and reduction reaction. This depends upon the number of hydrogen atoms that is bonded to the alpha carbon atom. Primary and secondary alcohol undergoes oxidation reaction while tertiary alcohol does not undergo oxidation reaction. Primary alcohols undergo oxidation to give aldehyde and carboxylic acid as product. Secondary alcohol undergoes oxidation to give ketone as the product.
Aldehyde undergoes oxidation to give carboxylic acid as the product while ketone does not undergo oxidation reaction.
Aromatic carboxylic acids are prepared from alkyl substituted benzenes.
(b)
Answer to Problem 5.46EP
The structural formula of the expected product is,
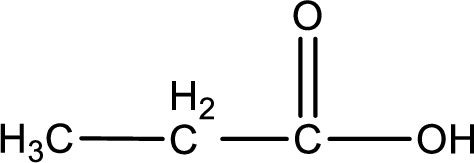
Explanation of Solution
Primary alcohol on oxidation gives aldehyde as intermediate product. This on further oxidation gives carboxylic acid as the product. The general scheme can be represented as shown below,
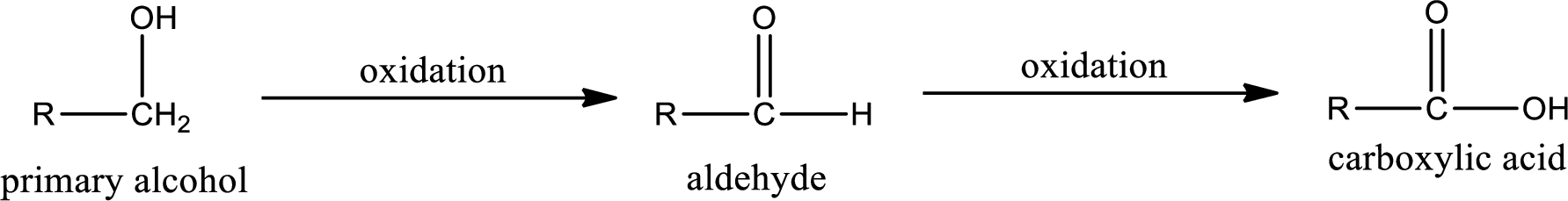
Given substance is,
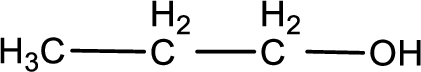
This is a primary alcohol. The given compound is propanol. Propanol on oxidation gives propanal as the intermediate product. The formed propanal on oxidation gives propanoic acid as the product. The complete scheme can be represented as shown below,
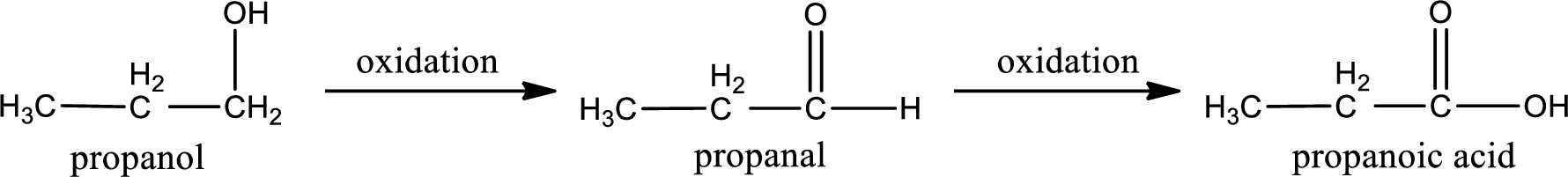
The carboxylic acid that is formed on oxidation of the given substance is propanoic acid. The structural formula of propanoic acid is given below,
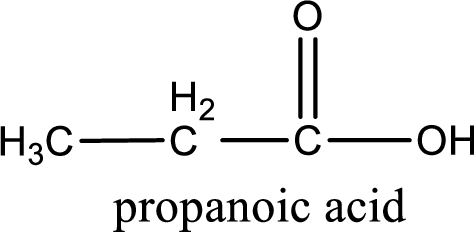
Structural formula of the carboxylic acid formed by the oxidation of given substance is drawn.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for carboxylic acid that is expected to be formed on oxidation of the given substance has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
In organic chemistry, oxidation reaction is referred to the number
In organic chemistry, reduction reaction is referred to the number
Alcohols undergo oxidation reaction and reduction reaction. This depends upon the number of hydrogen atoms that is bonded to the alpha carbon atom. Primary and secondary alcohol undergoes oxidation reaction while tertiary alcohol does not undergo oxidation reaction. Primary alcohols undergo oxidation to give aldehyde and carboxylic acid as product. Secondary alcohol undergoes oxidation to give ketone as the product.
Aldehyde undergoes oxidation to give carboxylic acid as the product while ketone does not undergo oxidation reaction.
Aromatic carboxylic acids are prepared from alkyl substituted benzenes.
(c)
Answer to Problem 5.46EP
The structural formula of the expected product is,
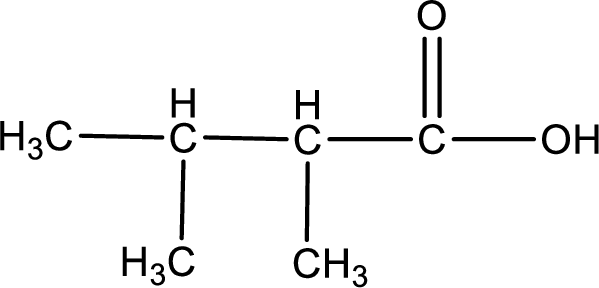
Explanation of Solution
Aldehyde on oxidation gives carboxylic acid as the product. The general scheme can be represented as shown below,

Given substance is,
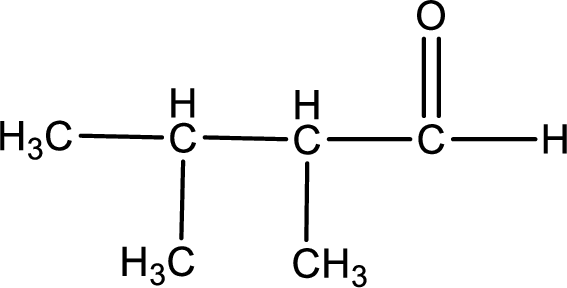
The given compound is 2,3-dimethylbutanal and it is an aldehyde. 2,3-dimethylbutanal on oxidation gives 2,3-dimethylbutanoic acid as the product. The complete scheme can be represented as shown below,
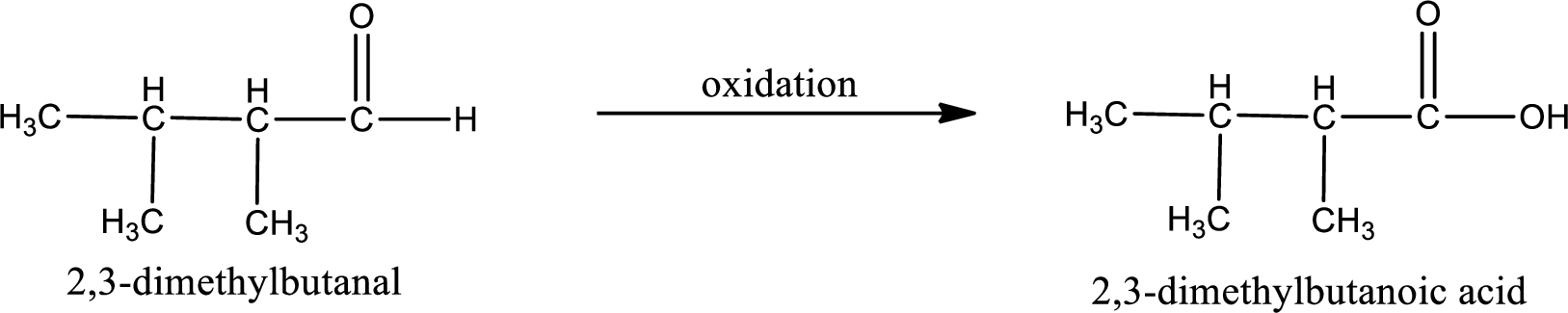
The carboxylic acid that is formed on oxidation of the given substance is 2,3-dimethylbutanoic acid. The structural formula of 2,3-dimethylbutanoic acid is given below,
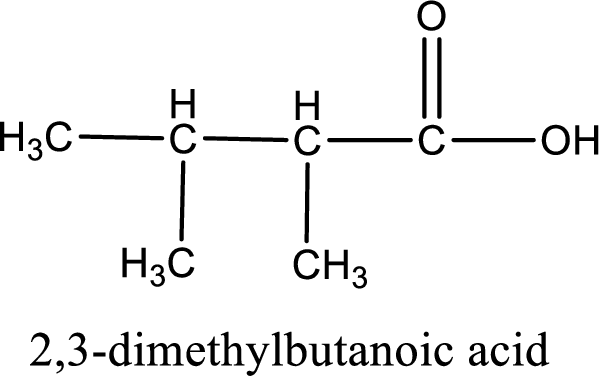
Structural formula of the carboxylic acid formed by the oxidation of given substance is drawn.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for carboxylic acid that is expected to be formed on oxidation of the given substance has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
In organic chemistry, oxidation reaction is referred to the number
In organic chemistry, reduction reaction is referred to the number
Alcohols undergo oxidation reaction and reduction reaction. This depends upon the number of hydrogen atoms that is bonded to the alpha carbon atom. Primary and secondary alcohol undergoes oxidation reaction while tertiary alcohol does not undergo oxidation reaction. Primary alcohols undergo oxidation to give aldehyde and carboxylic acid as product. Secondary alcohol undergoes oxidation to give ketone as the product.
Aldehyde undergoes oxidation to give carboxylic acid as the product while ketone does not undergo oxidation reaction.
Aromatic carboxylic acids are prepared from alkyl substituted benzenes.
(d)
Answer to Problem 5.46EP
The structural formula of the expected product is,
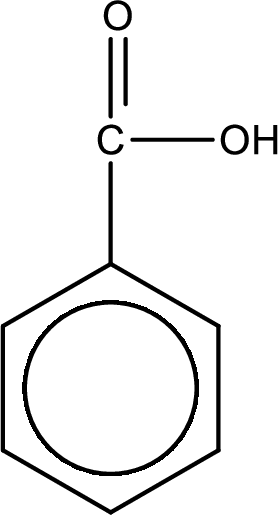
Explanation of Solution
Given substance is,
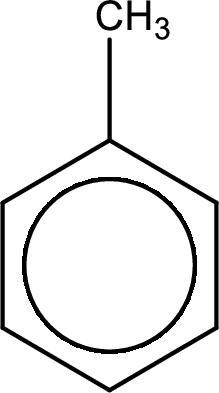
Oxidation of the alkyl side chain in a benzene derivative leads to the formation of aromatic acids. All the carbon atoms in alkyl group are lost except the one that is attached to the ring. The one carbon that is attached to the ring becomes a part of carboxyl
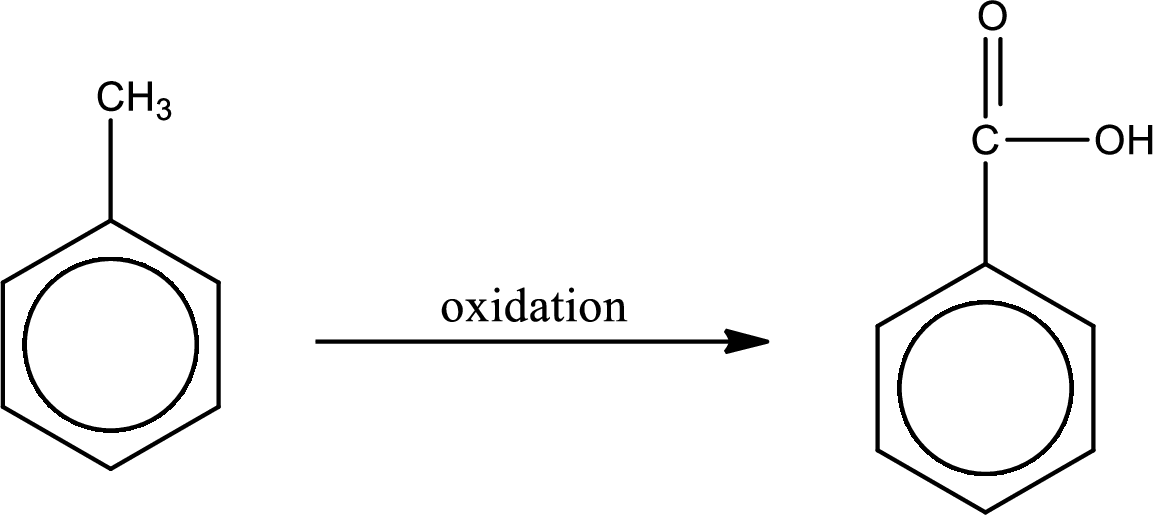
The product formed is benzoic acid.
Structural formula of the carboxylic acid formed by the oxidation of given substance is drawn.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Organic And Biological Chemistry
- Indicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting D-Galactose with hydroxylamine.arrow_forward
- helparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning




