
Concept explainers
PRACTICE PROBLEM
If we examine Table 21.1, we find that the methylphenols (cresols) are less acidic than phenol itself. For example,
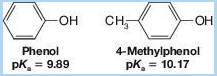
This behavior is characteristic of phenols bearing electron-releasing groups. Provide an explanation.
Interpretation:
Methyl phenols are less acidic than phenols, due to the presence of an electron releasing group on them. The statement is to be explained.
Concept introduction:
Phenols are compounds of benzene, bearing a hydroxyl group. They are alcohol derivatives but have higher acidities than alkyl alcohols.
Methyl phenols are phenol derivatives, in which a hydrogen atom attached to the carbon ring is replaced by a methyl
Answer to Problem 1PP
Solution: The
Explanation of Solution
According to table
Phenol is more acidic, as the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
- drawing, no aiarrow_forwardIf CH3COCH2CH(OCH3)2 (4,4-dimethoxy-2-butanone) and hydrazine react, two isomeric products are formed. State their structure and which will be the majority.arrow_forward+ Reset Provide the correct IUPAC name for the compound shown here. 4-methylhept-2-ene (Z)- (E)- 1-6-5-2-3-4- cyclo iso tert- sec- di tri hept hex oct meth eth pent ane yne ene ylarrow_forward
- Draw the major organic product when each of the bellow reagents is added to 3,3-dimethylbutere. ✓ 3rd attempt Part 1 (0.3 point) H.C CH CH + 1. BHG THF 210 NaOH NJ 10000 Part 2 (0.3 point) HC- CH HC 2741 OH a Search 1. He|DA HO 2. NIBH さ 士 Ju See Periodic Table See Hint j = uz C H F F boxarrow_forwardSynthesis of 2-metilbenzimidazol from 1,2-diaminobenceno y propanona.arrow_forwardPredict the product of the following reaction. 1st attempt HI 1 product 50300 Jul See Periodic Table See Hint P Br 石尚 Iarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

