
Concept explainers
Compound W was isolated from a marine annelid commonly used in Japan as a fish bait, and it was shown to be the substance that gives this organism its observed toxicity to some insects that contact it.
MS (m/z): 151 (relative abundance 0.09), 149 (

IR (cm−1): 2960, 2850, 2775
1H NMR (δ): 2.3 (s, 6H), 2.6 (d, 4H), and 3.2 (pentet, 1H)
13C NMR (δ): 38 (CH3), 43 (CH2), and 75 (CH)
These reactions were used to obtain further information about the structure ofW:
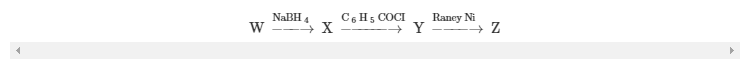
Compound X had a new infrared band at 2570 cm−1and these NMR data:
1H NMR(δ): 1.6 (t, 2H), 2.3 (s, 6H), 2.6 (m, 4H), and 3.2 (pentet, 1H)
13C NMR(δ): 28 (CH2), 38 (CH3), and 70 (CH)
Compound Y had these data:
IR (cm−1): 3050, 2960, 2850, 1700, 1610, 1500, 760, 690
1H NMR (δ): 2.3 (s, 6H), 2.9 (d, 4H), 3.0 (pentet, 1H), 7.4 (m, 4H), 7.6 (m, 2H), and 8.0 (m, 4H)
13C NMR (δ): 34 (CH2), 39 (CH3), 61 (CH), 128 (CH), 129 (CH), 134 (CH), 135 (C), and 187 (C)
Compound Z had
MS (m/z): 87 (

IR (cm−1): 2960, 2850, 1385, 1370, 1170
1H NMR (δ): 1.0 (d, 6H), 2.3 (s, 6H), and 3.0 (heptet, 1H)
13C NMR (δ): 21 (CH3), 39 (CH3), and 55 (CH)
What are the structures of W and of each of its reaction products X, Y, and Z?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 21 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
- What is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- please help me with my homeworkarrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forward
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
