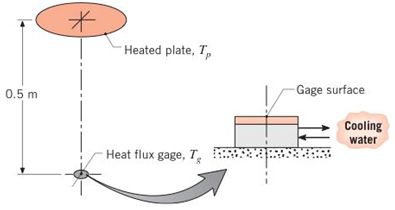
Problem 13.1P: Determine F12 and F21 for the following configurations using the reciprocity theorem and other basic... Problem 13.3P: Drive expressions for the view factor F12 associated with the following arrangements. Express your... Problem 13.4P: A right-circular cone and a right-circular cylinder of the same diameter and length (A2) are... Problem 13.5P: Consider the two parallel, coaxial, ringshaped disks shown schematically. Show that F12 can be... Problem 13.6P: The “crossed-strings” method of Hottel [13] provides a simple means to calculate view factors... Problem 13.7P: Consider the rightcircular cylinder of diameter D, length L, and the areas A1 , A2 , and A3... Problem 13.8P: Consider the parallel rectangles shown schematically. Show that the view factor F12 can be expressed... Problem 13.9P: Consider the perpendicular rectangles shown schematically. (a) Determine the shape factor F12 . (b)... Problem 13.10P: The reciprocity relation, the summation rule, and Equations 13.5 to 13.7 can be used to develop view... Problem 13.11P: Determine the shape factor, F12, for the rectangles shown. Perpendicular rectangles without edge.... Problem 13.12P: Consider parallel planes of infinite extent normal to the page as shown in the sketch. (a) Determine... Problem 13.13P: Consider the parallel planes of infinite extent normal to the page having opposite edges aligned as... Problem 13.14P: Consider two diffuse surfaces A1 and A2 on the inside of a spherical enclosure of radius R. Using... Problem 13.15P: As shown in the sketch, consider the disk A1 located coaxially 1m distant, but titled 30 off the... Problem 13.16P: A heat flux gage of 4mm diameter is positioned normal to and 1m from the 5mmdiameter aperture of a... Problem 13.17P: A circular ice rink 25 m in diameter is enclosed by a hemispherical dome 35m in diameter. If the ice... Problem 13.18P: A drying oven consists of a long semicircular duct of diameter D=1m Materials to be dried cover the... Problem 13.19P: Consider the arrangement of the three black surfaces shown, where A1 is small compared to A2 or A3 .... Problem 13.20P: A long, Vshaped pan is heat treated by suspending it in a tubular furnace with a diameter of 2m and... Problem 13.21P: Consider coaxial, parallel, black disks separated a distance of 0.20m. The lower disk of diameter... Problem 13.23P: A tubular healer with a black inner surface of uniform temperature Ts=1000K irradiates a coaxial... Problem 13.24P: A circular plate of 500-mm diameter is maintained at T1=600K and is positioned coaxial to a conical... Problem 13.27P: To enhance heat rejection from a spacecraft, an engineer proposes to attach an array of rectangular... Problem 13.28P: Determine the temperatures of surfaces 1 through 4 ofthe furnace cavity of Example 13.3 if the... Problem 13.29P: A cylindrical cavity of diameter D and depth L is machined in a metal block, and conditions are such... Problem 13.30P: In the arrangement shown, the tower disk has a diameter of 30 mm and a temperature of 500 K. The... Problem 13.31P: Two plane coaxial disks are separated by a distance L=0.20m . The lower disk (A1) is solid with a... Problem 13.32P: A radiometer views a small target (1) that is being heated by a ring-shaped disk heater (2). The... Problem 13.33P: A meter to measure the power of a laser beam is constructed with a thin-walled, black conical cavity... Problem 13.35P: The arrangement shown is to be used to calibrate a heat flux gage. The gage has a black surface that... Problem 13.36P: A long, cylindrical heating element of 20-mm diameter operating at 700 K in vacuum is located 40mm... Problem 13.37P: Water flowing through a large number of long, circular, thin-walled tubes is heated by means of ho... Problem 13.38P: A row of regularly spaced, cylindrical heating elements is used to maintain an insulated furnace... Problem 13.39P: A manufacturing process calls for heating long copper rods, which are coated with a thin film having... Problem 13.40P: Consider the very long, inclined black surfaces (A1,A2) maintained at uniform temperatures of... Problem 13.41P: Many products are processed in a manner that requires a specified product temperature as a function... Problem 13.42P: Consider two very large parallel plates with diffuse, gray surfaces. Determine the irradiation and... Problem 13.43P: A flat-bottomed hole 6 mm in diameter is bored to a depth of 24 mm in a diffuse, gray material... Problem 13.46P: In Problems 12.20 and 12.25, we estimated the earth’s surface temperature, assuming the earth is... Problem 13.47P: Consider the cavities formed by a cone, cylinder, and sphere having the same opening size (d) and... Problem 13.48P: Consider the attic of a home located in a hot climate. The floor of the attic is characterized by a... Problem 13.49P: A long, thin-walled horizontal tube 100 mm in diameter is maintained at 120°C by the passage of... Problem 13.50P: A t=5-mm -thick sheet of anodized aluminum is used to reject heat in a space power application. The... Problem 13.51P: Consider the spacecraft heat rejection scheme of Problem 13.27, but under conditions for which... Problem 13.53P: A very long electrical conductor 10 mm in diameter is concentric with a cooled cylindrical tube 50... Problem 13.54P: Liquid oxygen is stored in a thin-walled, spherical container 0.8 m in diameter, which is enclosed... Problem 13.55P: Two concentric spheres of diameter D1=0.8m and D2=1.2m are separated by an air space and have... Problem 13.56P: Determine the steady-stale temperatures of two radiation shields placed in the evacuated space... Problem 13.57P: Consider two large (infinite) parallel planes that are diffuse-gray with temperatures and... Problem 13.58P: Consider two large, diffuse, gray, parallel surfaces separated by a small distance. If the surface... Problem 13.59P: Heat transfer by radiation occurs between two large parallel plates, which are maintained at... Problem 13.60P: The end of a cylindrical liquid cryogenic propellant tank in free space is to be protected from... Problem 13.61P: At the bottom of a very large vacuum chamber whose walls are at 300 K, a black panel 0.1 m in... Problem 13.62P: A furnace is located next to a dense array of cryogenic fluid piping. The ice-covered piping... Problem 13.63P: A cryogenic fluid flows through a tube 20 mm in diameter, the outer surface of which is diffuse and... Problem 13.64P: A diffuse, gray radiation shield of 60mm diameter and emissivities of 2,i=0.01 and 2,o=0.1 on the... Problem 13.65P: Consider the three-surface enclosure shown. The lower plate (A1) is a black disk of 200-mm diameter... Problem 13.67P: Two parallel, aligned disks, 0.4 m in diameter and separated by 0.1 m, are located in a large room... Problem 13.68P: Coatings applied to long metallic strips are cured by installing the strips along the walls of a... Problem 13.70P: A molten aluminum alloy at 900 K is poured into a cylindrical container that is well insulated from... Problem 13.71P: A long, hemicylindrical (1-m radius) shaped furnace used to heat treat sheet metal products is... Problem 13.72P: The bottom of a steam-producing still of 200-mm diameter is heated by radiation. The heater,... Problem 13.73P: A long cylindrical healer element of diameter D=10mm , temperature T1=1500K and emissivity 1=1 is... Problem 13.74P: A radiative heater consists of a bank of ceramic tubes with internal heating elements. The tubes art... Problem 13.75P: Consider a long duct constructed with diffuse, gray walls 1 m wide. (a) Determine the net radiation... Problem 13.79P: A solar collector consists of a long duct through which air is blown; its cross section forms an... Problem 13.81P: The cylindrical peephole in a furnace wall of thickness L=250mm has a diameter of D=125mm . The... Problem 13.82P: A composite wall is comprised of two large plates separated by sheets of refractory insulation, as... Problem 13.83P: A small disk of diameter D1=50mm and emissivity 1=0.6 is maintained at a temperature of T1=900K .... Problem 13.84P: Consider a cylindrical cavity of diameter D=100mm turn and depth L=50mm whose sidewall and bottom... Problem 13.85P: Consider a circular furnace that is 0.3 m long and 0.3 in in diameter. The two ends have diffuse,... Problem 13.86P: Consider two very large metal parallel plates. The top plate is at a temperature Tt=400K while the... Problem 13.87P: Two convex objects are inside a large vacuum enclosure whose walls are maintained at T3=300K . The... Problem 13.88P: the diffuse, gray, four-surface enclosure with all sides equal as shown. The temperatures of three... Problem 13.90P: A cylindrical furnace for heal-treating materials in a spacecraft environment has a 90-mm diameter... Problem 13.91P: A laboratory oven bas a cubical interior chamber 1 m on a side with interior surfaces that are of... Problem 13.93P: A small oven consists of a cubical box of dimension L=0.1m , as shown. The floor of the box consists... Problem 13.94P: An opaque, diffuse, gray (200mm200mm) plate with an emissivity of 0.8 is placed over the opening of... Problem 13.95P: A tool for processing silicon waters is housed within a vacuum chamber whose walls are black and... Problem 13.96P: Consider Problem 6.17. The stationary plate, ambient air, and surroundings are at T=Tsur=20C the... Problem 13.97P: Most architects know that the ailing of an ice-skating rink must have a high reflectivity.... Problem 13.98P: Boiler tubes exposed to the products of coal combustion in a power plant are subject to fouling by... Problem 13.99P: Consider two very large parallel plates. The bottom plate is warmer than the top plate, which is... Problem 13.100P: Coated metallic disks are cured by placing them at the top of a cylindrical furnace whose bottom... Problem 13.101P: A double-glazed window consists of two panes of glass, each of thickness t=6mm . The inside room... Problem 13.102P: Electrical conductors, in the form of parallel plates of length L=40mm , have one edge mounted to a... Problem 13.103P: The spectral absorptivity of a large diffuse surface is =0.9 for 1m and =0.3 for 1m . The bottom of... Problem 13.105P: The cross section of a long circular tube, which is divided mw two semicylindrical ducts by a thin... Problem 13.106P: Cylindrical pillars similar to those of Problem 4.22 are positioned between the glass sheets with a... Problem 13.107P: A row of regularly spaced, cylindrical healing elements (1) is used to cure a surface coating that... Problem 13.110P: The composite insulation shown, which was described in Chapter 1 (Problem 1.86e), is being... Problem 13.111P: Hot coffee is contained in a cylindrical thermos bottle that is of length L=0.3m and is lying on its... Problem 13.112P: Consider a vertical, double-pane window for the conditions prescribed in Problem 9.94. That is,... Problem 13.113P: Consider the double-pane window of Problem 9.95, for which 1m1m panes are separated by a 25-mm gap... Problem 13.114P: A flat-plate solar collector, consisting of an absorber plate and single cover plate, is inclined at... Problem 13.115P: Consider the tube and radiation shield of Problem 13.49, hut now account for free convection in the... Problem 13.116P: Consider the tube and radiation shield of Problem 13.49, but now account for free convection in the... Problem 13.117P: Consider the flatplate solar collector of Problem 9.98. The absorber plate has a coating for which... Problem 13.118P: The lower side of a 400-mm-diameter disk is heated by an electric furnace, while the upper side is... Problem 13.119P: The surface of a radiation shield facing a black hot wall at 400 K has a reflectivity of 0.95.... Problem 13.120P: The fire tube of a hot water heater consists of a long circular duct of diameter D=0.07m and... Problem 13.122P: Consider the conditions of Problem 9.107. Accounting for radiation, as well as convection, across... Problem 13.123P: A special surface coating on a square panel that is 5m5m on a side is cured by placing the panel... Problem 13.124P: A long rod heater of diameter D1=10mm and emissivity 1=1.0 is coaxial with a well-insulated,... Problem 13.125P: A radiant heater, which is used for surface treatment processes, consists of a long cylindrical... Problem 13.126P: A steam generator consists of an in-line array of tubes, each of outer diameter D=10mm and length... Problem 13.129P: A furnace having a spherical cavity of 0.5-m diameter contains a gas mixture at 1 atm and 1400 K.... Problem 13.130P: A gas turbine combustion chamber may be approximated as a long tube of 0.4-m diameter. The... Problem 13.131P: A flue gas at 1-atm total pressure and a temperature of 1400 K Contains CO2 and water vapor at... Problem 13.132P: A furnace consists of two large parallel plates separated by 0.75 m. A gas mixture comprised of O2 ,... Problem 13.133P: In an industrial process, products of combustion at a temperature and pressure of 2000 K and 1 atm,... Problem 13.137P: A grain dryer consists of a long semicircular duct of radius R=1m . One-half of the base surface... Problem 13.138P: A novel infrared recycler has been proposed for reclaiming the millions of kilograms of waste... format_list_bulleted


 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning