
Connect 1-Semester Online Access for Principles of General, Organic & Biochemistry
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780077633707
Author: Janice Smith
Publisher: Mcgraw-hill Higher Education (us)
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 12, Problem 12.35UKC
Consider the following ball-and-stick model of an alcohol.
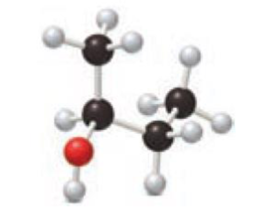
- a. Locate the chirality center.
- b. Classify the alcohol as 1°, 2°, or 3°.
- c. Name the alcohol.
- d. Draw the structure of the product formed when the alcohol is oxidized.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
1.
Which compounds contain chiral centers? Show your solution for each
ww ww w w
item.
a. 2-Chloropentane
b. 3-Chloro-1-pentene
c. 3-Chloropentane
d. 1,2-Dichloropropane
58. Which of the following statements incorrectly describes alcohols?
A. The solubility of an alcohol is affected by the length of its carbon chain.
B. The boiling point of an alcohol is affected by the length of its carbon chain.
C. The solubility of an alcohol is affected by the shape of the molecule.
D. Straight chain isomers will have a higher boiling point than the branched molecule.
59. Why do phenols have a higher boiling point than toluene despite having similar shape?
A. The higher boiling point of phenol is attributed to the electronegativity of the oxygen.
B. The higher boiling point of phenol is attributed to the hydrogen bonding.
C. Both
D. Neither
60. Which of the following statements incorrectly describes ethers?
A. Ethers react easily with acids.
B. Ethers are miscible with water.
C. Ether serves as an electron acceptor group.
D. None of the above
Refer to the reaction to answer items 61 to 63.
CH₂
OH KMnO4 H₂C
61. What type of reaction is catalyzed based on the…
Identify which type of isomerism is described by each statement.
A. Isomerism based on a single difference on the location of OH
B. Isomerism based on functional group of the monosaccharides
C. Isomerism based on configuration of hemiketal or hemiacetal carbon
D. Isomerism based on ability to rotate plane of polarized light
E. Isomerism based on OH position in the carbon atoms of the linear structure
F. Isomerism based on aromatic ring structure derivation
Chapter 12 Solutions
Connect 1-Semester Online Access for Principles of General, Organic & Biochemistry
Ch. 12.1 - a. Label the hydroxyl groups, thiols, halogens,...Ch. 12.1 - Draw out each compound to clearly show what groups...Ch. 12.2 - Classify each alcohol as 1, 2, or 3.Ch. 12.2 - Classify each hydroxyl group in sorbitol as 1, 2,...Ch. 12.2 - Which compound in each pair has the higher boiling...Ch. 12.2 - Label each compound as water soluble or water...Ch. 12.2 - Give the IUPAC name for each compound.Ch. 12.2 - Give the structure corresponding to each name. a....Ch. 12.3 - Name each ether. a. CH3OCH2CH2CH2CH3 b....Ch. 12.3 - Prob. 12.10P
Ch. 12.3 - Which compound in each pair has the higher boiling...Ch. 12.5 - Prob. 12.12PCh. 12.5 - Prob. 12.13PCh. 12.6 - Prob. 12.14PCh. 12.6 - Prob. 12.15PCh. 12.6 - Give the structure corresponding to each name. a....Ch. 12.7 - Prob. 12.17PCh. 12.8 - Give the IUPAC name for each aldehyde. a....Ch. 12.8 - Prob. 12.19PCh. 12.8 - Give the IUPAC name for each aldehyde depicted in...Ch. 12.8 - Prob. 12.21PCh. 12.8 - Prob. 12.22PCh. 12.8 - Acetone and progesterone are two ketones that...Ch. 12.9 - Prob. 12.24PCh. 12.10 - Prob. 12.25PCh. 12.11 - Prob. 12.26PCh. 12.11 - Prob. 12.27PCh. 12.11 - Prob. 12.28PCh. 12.11 - Prob. 12.29PCh. 12.11 - Prob. 12.30PCh. 12.11 - Prob. 12.31PCh. 12.11 - Prob. 12.32PCh. 12 - Prob. 12.33UKCCh. 12 - Prob. 12.34UKCCh. 12 - Consider the following ball-and-stick model of an...Ch. 12 - Consider the following ball-and-stick model. a....Ch. 12 - Name each compound. a. CH3CH2OCH2CH2CH2CH3Ch. 12 - Name each compound. a. CH3OCH2CH2CH3 b....Ch. 12 - Answer the following questions about alcohol A. a....Ch. 12 - Answer the following questions about alcohol B. a....Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.41UKCCh. 12 - Prob. 12.42UKCCh. 12 - Prob. 12.43UKCCh. 12 - Prob. 12.44UKCCh. 12 - Prob. 12.45APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.46APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.47APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.48APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.49APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.50APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.51APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.52APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.53APCh. 12 - Give the structure corresponding to each name. a....Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.55APCh. 12 - Draw structures for the four constitutional...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.57APCh. 12 - Rank the following compounds in order of...Ch. 12 - Explain why two four-carbon organic molecules have...Ch. 12 - Explain why the boiling point of CH3CH2CH2CH2OH...Ch. 12 - Which compound in each pair has the higher boiling...Ch. 12 - Which compound in each pair is more water soluble?...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.63APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.64APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.65APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.66APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.67APCh. 12 - Xylitol is a nontoxic compound as sweet as table...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.69APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.70APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.71APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.72APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.73APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.74APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.75APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.76APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.77APCh. 12 - Draw the structure corresponding to each name. a....Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.79APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.80APCh. 12 - What product is formed when each compound is...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.82APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.83APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.84APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.85APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.86APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.87APCh. 12 - Label each of the following objects as chiral or...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.89APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.90APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.91APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.92APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.93APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.94APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.95APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.96APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.97APCh. 12 - How are the compounds in each pair related? Are...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.99APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.100APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.101APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.102APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.103APCh. 12 - Lactic acid [CH3CH(OH)CO2H] gives sour milk its...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.105APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.106APCh. 12 - Prob. 12.107CPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.108CPCh. 12 - Prob. 12.109BTCCh. 12 - Prob. 12.110BTC
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 7. Considering the following chemical, which statement is true? CHO H-C-OH HO-C-H HO-C-H H-C-OH CH₂OH A. It needs to form the ring form first before it can interact with methanol to form an intramolecular hemiketal B. When the molecule forms the ring form, the carbon atom #5 becomes the anomeric carbon C. Both A and B D. Neither A nor Barrow_forwardof the product. Name the reactant and the product. a) Cy-CH-C-OH b) CHy-CH-CH-CHy c) 4. Complete the following intermolecular dehydration reactions for alcohols. Draw the structure of the product. Name the reactant and the product. a) CH3-CHS-OH b) CH-CH-CH_-OH 5. Complete the following oxidation reactions for alcohols. Draw the structure of the product. Name the reactant and identify the type of compound formed in the product. a) CHっ-CHュ-CH-Cs OH b) c) Co] Ho--cgCらarrow_forwardIdentify the organic functional groups and reaction type for the following reaction.The reactant is a(n)a. ketopentoseb. aldopentosec. ketotriosed. alcohol pentosee. carboxylic acid tetroseThe product is a(n)a. aldohexosesb. alcohol pentosesc. carboxylic acid pentosesd. deoxypentosee. ketopentosesThe reaction type is:a. hemiacetal formationb. reduction (hydrogenation)c. hydrolysisd. acetal formatione. mutarotationf. oxidation (benedict's)arrow_forward
- Alcohols with two or more - OH groups have higher boiling point.I. Alcohols with more than two -OH groups are more water soluble than similar alcohols with only one -OH group.A.BOTH statements are CORRECTB. BOTH statements are INCORRECTC. FIRST statement is CORRECT. SECOND is INCORRECT D.FIRST statement is INCORRECT, SECOND is CORRECT 2. l. An alcohol is an organic compound with at least one hydroxyl (-OH) group bound to unsaturated carbon atom. II. Alcohols have higher boiling points than corresponding alkynes.A.FIRST statement is CORRECT. SECOND is INCORRECTO FIRST statement is INCORRECT SECOND Is CORRECTAre INCORKI© bUlk statements are CORRECTIarrow_forward1. What functional group is produced when an aldehyde reacts with H2/Pt? A.secondary alcohol B. carboxylic acid C.hemiacetal D. primary alcohol E.alkane F.tertiary alcohol G. alkene 2. What reaction occurs when an aldehyde reacts with H2/Pt to form a primary alcohol? A. Hydration B. Hydration C. Dehydration D. Oxidation E. Reduction( hydrogentation) 3. What reaction occurs when an Ester react with H+/H2O to from a carboxylic acid and alcohol? A. Dehydration B. Reduction ( Hydrogenation) C.Hydrolysis D. Hydration E.oxidationarrow_forwardHow many isopropene units in this structure?arrow_forward
- 1. When an aldehyde is reduced with hydrogen (H2) gas in the presence of a transition metal catalyst, what type of product is formed? A. primary alcohol B. secondary alcohol C. tertiary alcohol D. carboxylic acidarrow_forward33. Determine whether or not each molecule is a fatty acid. If it is a fatty acid, classify it as saturated, monounsaturated, or polyun- saturated. a. CH HO, b. CH, CH CH, . CH CH;-C-OH d. CH, CH=CHarrow_forwardA primary alcohol has a hydroxyl group bonded to a(n) a. aromatic carbon. b. trisubstituted carbon. c. disubstituted carbon. d. singly substituted or unsubstituted carbon.arrow_forward
- An example of a primary alcohol is shown by the structure CH3CH2CH(OH)CH3. A. true B. falsearrow_forwardSome alkenes have cis-trans isomers because a. the carbon atoms in the double bond are free to rotate. b. one of the carbon atoms in the double bond has two identical groups attached to it. c. all of the carbon atoms in the compound are rigid and cannot rotate. d. each of the carbon atoms in the double bond has four different groups attached to it. e. the carbon atoms in the double bond cannot rotate.arrow_forwardDraw the reaction of the following 1. Reaction of alcohols to sodium metal a. isopropyl alcohol b. Ethyl alcohol c. Tertiary butyl alcoholarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133109655
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Cengage Learning

07 Physical Properties of Organic Compounds; Author: Mindset;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UjlSgwq4w6U;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY