
Concept explainers
a)
Interpretation:
The carbocation has to be arranged in increasing order.
Concept introduction:
Carbocation: carbon atom bears positive charged species with three bonds is called Carbocation and it plays vital intermediate in
Carbocation’s are classified in to three types as primary, secondary and tertiary depending on the number of carbon atoms which is attached to the ionized carbon. Tertiary carbocation is more stable than secondary carbocation, secondary carbocation is more stable than the primary carbocation as shown below.
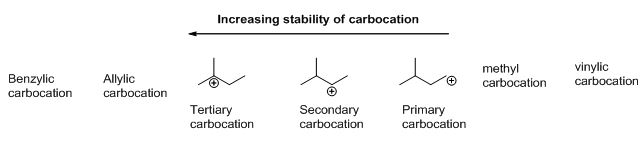
b)
Interpretation:
The carbocation has to be arranged in increasing order.
Concept introduction:
Carbocation: carbon atom bears positive charged species with three bonds is called Carbocation and it plays vital intermediate in organic synthesis. Carbocation migratory aptitude is mainly depending on the stability of the carbocation. This type of carbocation undergoes inter or intra molecule reactions and it form more stable product this type of rearrangement called carbocation rearrangement.
Carbocation’s are classified in to three types as primary, secondary and tertiary depending on the number of carbon atoms which is attached to the ionized carbon. Tertiary carbocation is more stable than secondary carbocation, secondary carbocation is more stable than the primary carbocation as shown below.
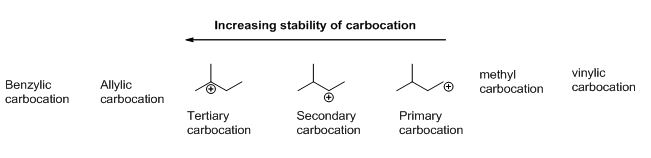
c)
Interpretation:
The carbocation has to be arranged in increasing order.
Concept introduction:
Carbocation: carbon atom bears positive charged species with three bonds is called Carbocation and it plays vital intermediate in organic synthesis. Carbocation migratory aptitude is mainly depending on the stability of the carbocation. This type of carbocation undergoes inter or intra molecule reactions and it form more stable product this type of rearrangement called carbocation rearrangement.
Carbocation’s are classified in to three types as primary, secondary and tertiary depending on the number of carbon atoms which is attached to the ionized carbon. Tertiary carbocation is more stable than secondary carbocation, secondary carbocation is more stable than the primary carbocation as shown below.
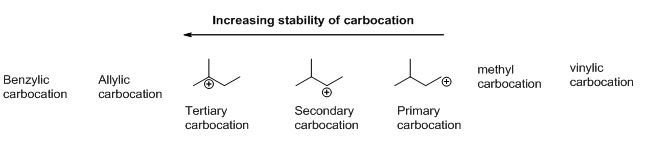
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 11 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- 1. Identify the following alkenes as E or Z NH₂ Br 2. Draw the structures based on the IUPAC names (3R,4R)-3-bromo-4-fluoro- 1-hexene (Z)-4-bromo-2-iodo-3-ethyl- 3-heptene تر 3. For the following, predict all possible elimination product(s) and circle the major product. HO H₂SO4 Heat 80 F4 OH H2SO4 Heat 어요 F5 F6 1 A DII 4 F7 F8 F9 % & 5 6 7 * ∞ 8 BAB 3 E R T Y U 9 F D G H J K O A F11 F10arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. ○ O 1. H₂O, pyridine 2. neutralizing work-up a N W X 人 Parrow_forward✓ Check the box under each molecule that has a total of five ẞ hydrogens. If none of the molecules fit this description, check the box underneath the table. tab OH CI 0 Br xx Br None of these molecules have a total of five ẞ hydrogens. esc Explanation Check caps lock shift 1 fn control 02 F2 W Q A N #3 S 80 F3 E $ t 01 205 % 5 F5 & 7 © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility FT * 8 R T Y U כ F6 9 FIG F11 F D G H J K L C X V B < N M H option command P H + F12 commandarrow_forward
- Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts and the carboxylic acid side product. O 1. CHзMgBr (excess) 2. H₂O ✓ W X 人arrow_forwardIf cyclopentyl acetaldehyde reacts with NaOH, state the product (formula).arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. N S S HgCl2, H2SO4 く 8 W X Parrow_forward
- tab esc く Drawing the After running various experiments, you determine that the mechanism for the following reaction occurs in a step-wise fashion. Br + OH + Using this information, draw the correct mechanism in the space below. 1 Explanation Check F2 F1 @2 Q W A os lock control option T S # 3 80 F3 Br $ 4 0105 % OH2 + Br Add/Remove step X C F5 F6 6 R E T Y 29 & 7 F D G H Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Ce A F7 DII F8 C Ո 8 * 9 4 F10 F C J K L C V Z X B N M H command P ge Coarrow_forwardIndicate compound A that must react with ethylbenzene to obtain 4-ethylbenzene-1-sulfonic acid. 3-bromo-4-ethylbenzene-1-sulfonic acid.arrow_forwardPart 1 of 2 Draw the structure of A, the minor E1 product of the reaction. esc I Skip Part Check H₂O, D 2 A + Click and drag to start drawing a structure. -0- F1 F2 1 2 # 3 Q A 80 F3 W E S D F4 $ 4 % 5 F5 ㅇ F6 R T Y F G X 5 & 7 + Save 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. DII F7 F8 H * C 80 J Z X C V B N 4 F9 6arrow_forward
- File Preview The following is a total synthesis of the pheromone of the western pine beetle. Such syntheses are interesting both because of the organic chemistry, and because of the possibility of using species specific insecticides, rather than broad band insecticides. Provide the reagents for each step. There is some chemistry from our most recent chapter in this synthesis, but other steps are review from earlier chapters. (8 points) COOEt COOEt A C COOEt COOEt COOH B OH OTS CN D E See the last homework set F for assistance on this one. H+, H₂O G OH OH The last step is just nucleophilic addition reactions, taking the ketone to an acetal, intramolecularly. But it is hard to visualize the three dimensional shape as it occurs. Frontalin, pheromone of the western pine beetlearrow_forwardFor the reaction below: 1. Draw all reasonable elimination products to the right of the arrow. 2. In the box below the reaction, redraw any product you expect to be a major product. C Major Product: Check + ◎ + X ง © Cl I F2 80 F3 I σ F4 I F5 NaOH Click and drawing F6 A 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights E F7 F8 $ # % & 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Q W E R T Y U A S D F G H Jarrow_forwardCan I please get help with this graph. If you can show exactly where it needs to pass through.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
