
a)
Interpretation:
The given molecule has to be prepared by using nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Concept introduction:
SN1 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid which yield the corresponding carbocation intermediate, this carbocation intermediate undergoes substitution reaction which yields the corresponding substitution product.
Tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation.
Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergo SN1substitution reaction.
SN2 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid, the bromine atom attacks back side of the carbon atoms in simultaneous manner and which is bearing alcohol group which yield the corresponding product.
Example:
Alcohol is reaction with tosyl chloride in pyridine which provides retention of configuration of tosylated compound. This tosylated compound is further reaction with sodium methoxide which undergoes again SN2 type of reaction, the methoxide ion attacks the carbon atom through the back side and provides Inverse configuration of methoxy compound. This is shown below,
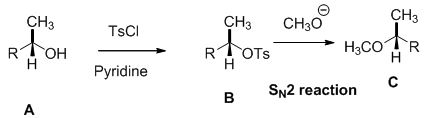
SN2 reaction is second order
Answer to Problem 45AP
The reaction is given below,
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
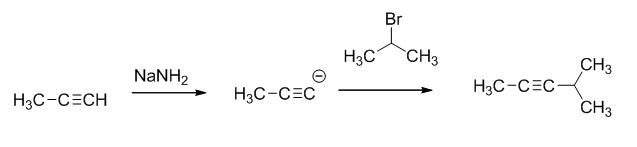
The product of the reaction is given below,
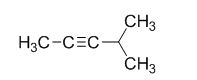
The reaction is given below,
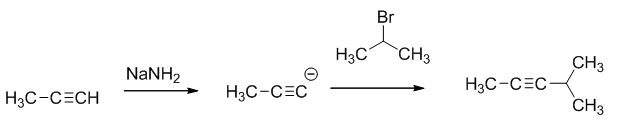
The sodium amide is acts as a base and it abstract the highly acidic proton from propylene gives carbanion, this carbanion react with 2-bromo propane gives the corresponding product.
The given molecule is prepared by using nucleophilic substitution reaction.
b)
Interpretation:
The given molecule has to be prepared by using nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Concept introduction:
SN1 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid which yield the corresponding carbocation intermediate, this carbocation intermediate undergoes substitution reaction which yields the corresponding substitution product.
Tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation.
Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergo SN1substitution reaction.
SN2 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid, the bromine atom attacks back side of the carbon atoms in simultaneous manner and which is bearing alcohol group which yield the corresponding product.
Example:
Alcohol is reaction with tosyl chloride in pyridine which provides retention of configuration of tosylated compound. This tosylated compound is further reaction with sodium methoxide which undergoes again SN2 type of reaction, the methoxide ion attacks the carbon atom through the back side and provides Inverse configuration of methoxy compound. This is shown below,

SN2 reaction is second order reaction, the rate of the reaction is depending on the both substrate and nucleophiles.
Answer to Problem 45AP
The reaction is given below,
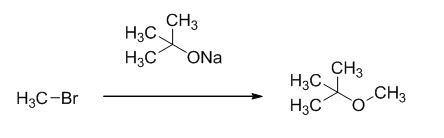
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
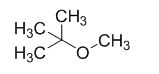
The product of the reaction is given below,
The reaction is given below,
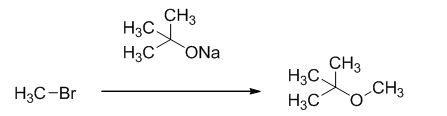
The sodium tertiary butoxide is acts as a base and it react with methyl bromide gives the corresponding ether product.
The given molecule is prepared by using nucleophilic substitution reaction.
c)
Interpretation:
The given molecule has to be prepared by using nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Concept introduction:
SN1 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid which yield the corresponding carbocation intermediate, this carbocation intermediate undergoes substitution reaction which yields the corresponding substitution product.
Tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation.
Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergo SN1substitution reaction.
SN2 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid, the bromine atom attacks back side of the carbon atoms in simultaneous manner and which is bearing alcohol group which yield the corresponding product.
Example:
Alcohol is reaction with tosyl chloride in pyridine which provides retention of configuration of tosylated compound. This tosylated compound is further reaction with sodium methoxide which undergoes again SN2 type of reaction, the methoxide ion attacks the carbon atom through the back side and provides Inverse configuration of methoxy compound. This is shown below,

SN2 reaction is second order reaction, the rate of the reaction is depending on the both substrate and nucleophiles.
Answer to Problem 45AP
The reaction is given below,
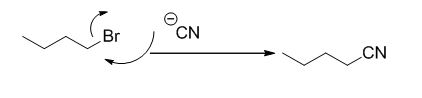
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The product of the reaction is given below,
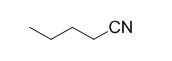
The reaction is given below,
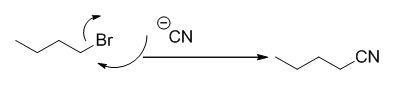
n-butyl bromide undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction with cyanide (sodium cyanide) gives the corresponding cyanide product.
The given molecule is prepared by using nucleophilic substitution reaction.
d)
Interpretation:
The given molecule has to be prepared by using nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Concept introduction:
SN1 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid which yield the corresponding carbocation intermediate, this carbocation intermediate undergoes substitution reaction which yields the corresponding substitution product.
Tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation.
Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergo SN1substitution reaction.
SN2 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid, the bromine atom attacks back side of the carbon atoms in simultaneous manner and which is bearing alcohol group which yield the corresponding product.
Example:
Alcohol is reaction with tosyl chloride in pyridine which provides retention of configuration of tosylated compound. This tosylated compound is further reaction with sodium methoxide which undergoes again SN2 type of reaction, the methoxide ion attacks the carbon atom through the back side and provides Inverse configuration of methoxy compound. This is shown below,

SN2 reaction is second order reaction, the rate of the reaction is depending on the both substrate and nucleophiles.
Answer to Problem 45AP
The reaction is given below,
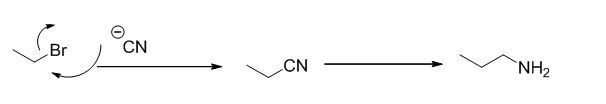
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The reaction is given below,
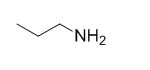
The reaction is given below,
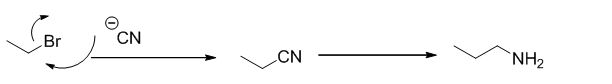
Ethyl bromide undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction with cyanide (sodium cyanide) gives the corresponding cyanide product, this cyanide undergoes catalytic reduction using Pt (metal reduction) gives
The given molecule is prepared by using nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- . M 1- MATCH each of the following terms to a structure from the list below. There is only one correct structure for each term and structures may be used more than once. Place the letter of the structure in the blank to the left of the corresponding term. A. Sanger dideoxy method C. Watson-Crick B. GAUCGUAAA D. translation E. HOH2C OH OH G. transcription I. AUGGCUGAG 0 K. OPOH2C 0- OH N- H NH2 F. -OPOH2C 0- OH OH H. Maxam-Gilbert method J. replication N L. HOH2C a. b. C. d. e. f. g. B M. AGATCGCTC a pyrimidine nucleoside RNA base sequence with guanine at the 3' end. DNA base sequence with cytosine at the 3' end. a purine nucleoside DNA sequencing method for the human genome 2'-deoxyadenosine 5'-phosphate process by which mRNA directs protein synthesis OH NH2arrow_forwardPlease use hand drawn structures when neededarrow_forwardB. Classify the following amino acid. Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled. a. acidic b. basic C. neutral C. Consider the following image. Which level of protein structure is shown here? a. primary b. secondary c. tertiary d. quaternary D. Consider the following image. H RH H HR H R HR HR RH Which level of protein structure is shown in the box? a. primary b. secondary R c. tertiary d. quaternary コー Rarrow_forward
- Briefly answer three from the followings: a. What are the four structures of the protein? b. Why is the side chain (R) attached to the alpha carbon in the amino acids is important for the function? c. What are the types of amino acids? And how is it depend on the (R) structure? d. Write a reaction to prepare an amino acid. prodarrow_forwardAnswe Answer A and B pleasearrow_forward3. Refer to the data below to answer the following questions: Isoelectric point Amino Acid Arginine 10.76 Glutamic Acid 3.22 Tryptophan 5.89 A. Define isoelectric point. B. The most basic amino acid is C. The most acidic amino acid is sidizo zoarrow_forward
- 3. A gas mixture contains 50 mol% H2 and 50 mol% He. 1.00-L samples of this gas mixture are mixed with variable volumes of O2 (at 0 °C and 1 atm). A spark is introduced to allow the mixture to undergo complete combustion. The final volume is measured at 0 °C and 1 atm. Which graph best depicts the final volume as a function of the volume of added O2? (A) 2.00 1.75 Final Volume, L 1.50 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.25 0.00 0.00 0.25 0.50 2.00 (B) 1.75 1.50 Final Volume, L 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50- 0.25 0.00 0.75 1.00 0.00 0.25 Volume O₂ added, L 2 0.50 0.75 1.00 Volume O₂ added, L 2 2.00 2.00 (C) (D) 1.75 1.75 1.50 1.50 Final Volume, L 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50 Final Volume, L 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.25 0.25 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.25 0.50 0.75 1.00 0.00 0.25 Volume O₂ added, L 0.50 0.75 1.00 Volume O₂ added, L 2arrow_forwardLeucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid. It has pai 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60. H2N-C(R)H-COOH and R is -CH2-CH(CH3)2 A. Draw the condensed structure for leucine, and label all chirality centers with an asterisk. B. How many possible stereoisomers of leucine are there? C. Draw a Fischer projection of L-leucine and label the chirality center(s) as R or S. D. What is the p/ of leucine? E. Draw the structure of the predominant form of leucine at 10.00. F. Draw the structure of the predominant form of leucine at pH = 1.50. G. Leucine is described as an essential amino acid. What does this mean? H. Show the alkyl halide you would use to prepare leucine by the amidomalonate method. =arrow_forwarda) Write out 6 completely different reactions of acetophenone (reagent, product). b) Write out 3 preparations of 1-methylcyclohexanol, using a different starting material for each one. You may use preps where you just change the functional group, and/or preps where you construct the carbon chain. c) Write out 3 preparations of 2-ethoxybenzoic acid, a different starting material for each one. You may use preps where you just change the functional group, and/or preps where you construct the carbon chain.arrow_forward
- 12. CH3 OH OH H&C CH3 H₂C N OH H₂C CH3 H&C CH3 H₂C' CH3 H.C CH3OH H.C CH2CH3OH CH3CEN Which one of these 17 compounds is represented by this IR and this 'H NMR spectrum? IR Spectrum 3000 4000 3000 NMR Spectrum 2000 £500 RAVENUMBER 2000 1500 9 8 6 5 10 HP-00-290 ppm m 1000 500 1000 4 °arrow_forwardDraw the structure of (E,6R) 6-methoxy-4-hepten-2-one. Give the IUPAC name of this compound, including stereochemistry. Draw the most stable chair conformation of (cis) 1,3-isobutylcyclohexane. H HC=CCH₂ CH2CH3 EN(CH3)2 -CN(CH3)2arrow_forward10. Write out the mechanism (intermediate/transition state) for this reaction; indicate stereochemistry in product. H3C CH₂OH CH3 SN1 Harrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

