
Concept explainers
The antipsychotic drug flupentixol is prepared by the following scheme:
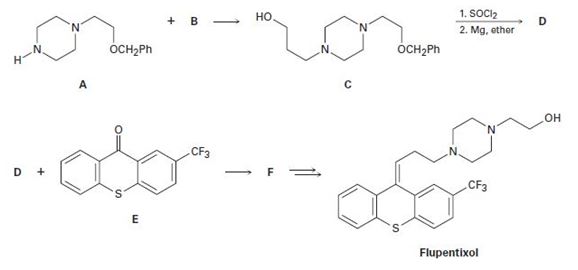
a)
The alkyl chloride, structure of D has to be identified and R and S configuration has to be assigned for the products.
Concept introduction:
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
Chiral: A molecule is non superimposable on its mirror image is called chiral molecule.
Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Isomer: A molecule having the same molecular formula but with different chemical structure is called isomer.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-superimposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-superimposable and non-mirror image is called diastereomers.
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer.
Achiral: A molecule is superimposable on its mirror image is called achiral molecule.
Answer to Problem 81AP
The reaction is given below,
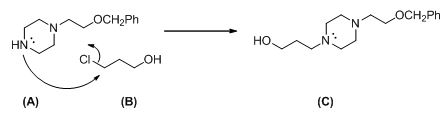
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
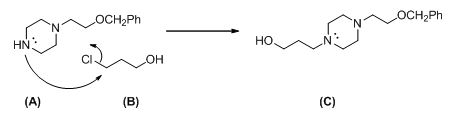
The given reactant shown below,
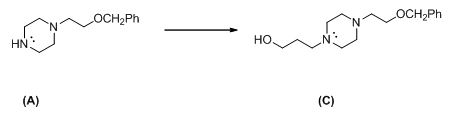
The given compound (A) reacts with chloro propanol gives the compound (C).
The reaction is given below,
The alkyl chloride, structure of D is given and R and S configuration is assigned for the products.
b)
Interpretation:
The alkyl chloride, structure of D has to be identified and R and S configuration has to be assigned for the products.
Concept introduction:
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
Chiral: A molecule is non superimposable on its mirror image is called chiral molecule.
Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Isomer: A molecule having the same molecular formula but with different chemical structure is called isomer.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-superimposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-superimposable and non-mirror image is called diastereomers.
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer.
Achiral: A molecule is superimposable on its mirror image is called achiral molecule.
Answer to Problem 81AP
The Grignard reagent is given below,
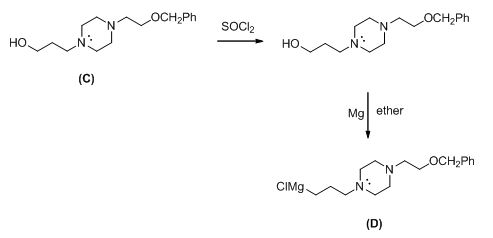
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The given reactant shown below,
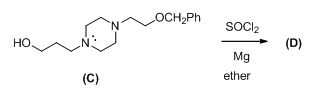
The Grignard reagent is given below,
The compound (c) reaction with thionyl chloride gives chlorinated compound, then it is reacting with magnesium gives the Grignard reagent (D).
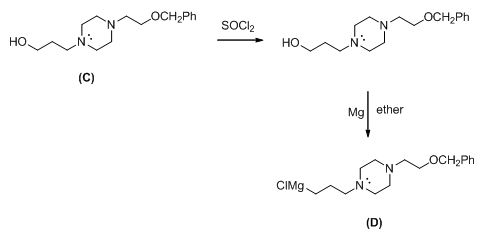
The alkyl chloride, structure of D is given and R and S configuration is assigned for the products.
c)
Interpretation
The alkyl chloride, structure of D has to be identified and R and S configuration has to be assigned for the products.
Concept introduction:
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
Chiral: A molecule is non superimposable on its mirror image is called chiral molecule.
Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Isomer: A molecule having the same molecular formula but with different chemical structure is called isomer.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-superimposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-superimposable and non-mirror image is called diastereomers.
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer.
Achiral: A molecule is superimposable on its mirror image is called achiral molecule.
Answer to Problem 81AP
The pair of enantiomers is given below,
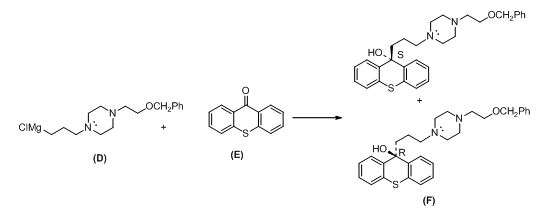
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The given reactant shown below,
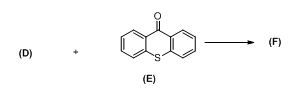
The pair of enantiomers is given below,
The compound (D) reaction with compound (E) gives enantiomer of corresponding products.
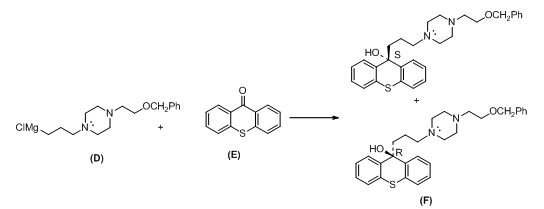
The alkyl chloride, structure of D is given and R and S configuration is assigned for the products.
d)
Interpretation:
The alkyl chloride, structure of D has to be identified and R and S configuration has to be assigned for the products.
Concept introduction:
R and S nomenclature: it is used to assign the molecule using CIP rules.
The CIP rules are as follows:
Select the chiral carbon and assign the numbers according to the decreasing atomic mass of atoms attached to it.
If the numbering follows clockwise direction then the molecule is termed as R and if it follows anti-clockwise direction then molecule is termed as S.
Chiral: A molecule is non superimposable on its mirror image is called chiral molecule.
Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Isomer: A molecule having the same molecular formula but with different chemical structure is called isomer.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-superimposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-superimposable and non-mirror image is called diastereomers.
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer.
Achiral: A molecule is superimposable on its mirror image is called achiral molecule.
Answer to Problem 81AP
The compound (F) undergoes hydrolysis reaction gives E and Z isomers of corresponding products.
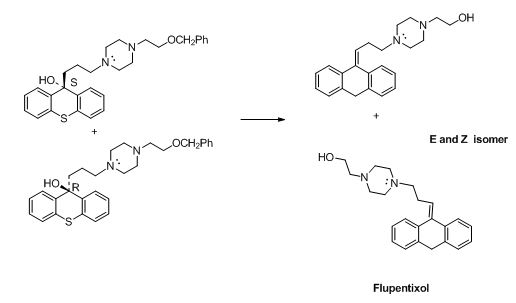
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The given reactant shown below,
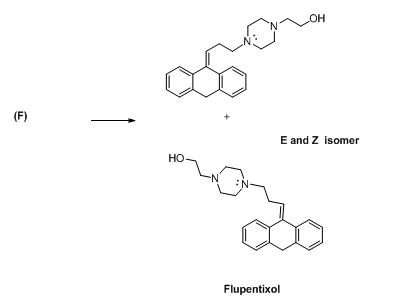
The compound (F) undergoes hydrolysis reaction gives E and Z isomers of corresponding products.
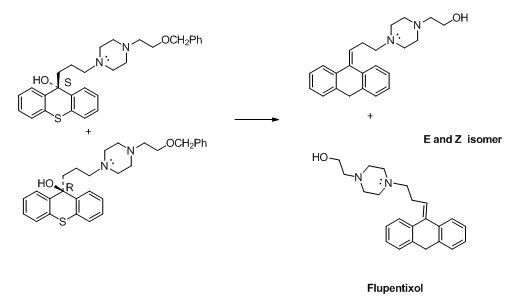
The alkyl chloride, structure of D is given and R and S configuration is assigned for the products.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- V Biological Macromolecules Drawing the Haworth projection of an aldose from its Fischer projection Draw a Haworth projection of a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: H C=O HO H HO H H OH CH₂OH Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Xarrow_forwardComplete the mechanismarrow_forwardComplete the mechanismarrow_forward
- 8 00 6 = 10 10 Decide whether each of the molecules in the table below is stable, in the exact form in which it is drawn, at pH = 11. If you decide at least one molecule is not stable, then redraw one of the unstable molecules in its stable form below the table. (If more than unstable, you can pick any of them to redraw.) Check OH stable HO stable Ounstable unstable O OH stable unstable OH 80 F6 F5 stable Ounstable X Save For Later Sub 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy C ཀྭ་ A F7 매 F8 F9 4 F10arrow_forwardJust try completing it and it should be straightforward according to the professor and TAs.arrow_forwardThe grading is not on correctness, so if you can just get to the correct answers without perfectionism that would be great. They care about the steps and reasoning and that you did something. I asked for an extension, but was denied the extension.arrow_forward
- Show your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers. Something that looks reasonable or correct would be sufficient. If you can get many of them correct that would be great!arrow_forwardShow your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers. Something that looks reasonable or correct would be sufficient. If you can get many of them correct that would be great!arrow_forwardTake a look at the following molecule, and then answer the questions in the table below it. (You can click the other tab to see the molecule without the colored regions.) with colored region plain 0= CH2-0-C-(CH2)16-CH3 =0 CH-O-C (CH2)7-CH=CH-(CH2)5-CH3 D CH3 | + OMPLO CH3-N-CH2-CH2-0-P-O-CH2 B CH3 A Try again * 000 Ar 8 0 ?arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

