
Organic Chemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781305080485
Author: John E. McMurry
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 11.SE, Problem 26MP
Interpretation Introduction
a)
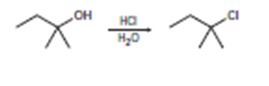
Interpretation:
The mechanisms for the reaction are given below.
Interpretation Introduction
b)
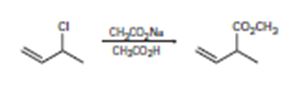
Interpretation:
The mechanisms for the reaction are given below.
Interpretation Introduction
c)
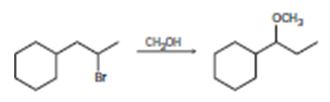
Interpretation:
The mechanisms for the reaction are given below.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Draw a stepwise mechanism for the following reaction.
OH
Help with annotating the labeled peaks in the 'H NMR (solvent CDCls) spectra and 'H NMR (solvent Acetone-D6) spectra Also help with Calculating the keto-enol tautomerization Ka constant for the product in both solvents.Two solvents and two different Ka
Draw a Haworth projection of a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide
CH₂OH
HO
H
HO
H
H
OH
CH₂OH
Chapter 11 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Ch. 11.1 - Prob. 1PCh. 11.2 - Prob. 2PCh. 11.2 - Prob. 3PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 4PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 5PCh. 11.3 - Rank the following compounds in order of their...Ch. 11.3 - Organic solvents like benzene, ether, and...Ch. 11.4 - Prob. 8PCh. 11.4 - Prob. 9PCh. 11.4 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 11.5 - Rank the following substances in order of their...Ch. 11.5 - 3-Bromo-1-butene and 1-bromo-2-butene undergo SN1...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 13PCh. 11.6 - Review the mechanism of geraniol biosynthesis...Ch. 11.7 - Prob. 15PCh. 11.7 - What alkyl halides might the following alkenes...Ch. 11.8 - Prob. 17PCh. 11.8 - Prob. 18PCh. 11.9 - Prob. 19PCh. 11.12 - Prob. 20PCh. 11.SE - Prob. 21VCCh. 11.SE - From what alkyl bromide was the following alkyl...Ch. 11.SE - Prob. 23VCCh. 11.SE - Prob. 24VCCh. 11.SE - Prob. 25MPCh. 11.SE - Prob. 26MPCh. 11.SE - Prob. 27MPCh. 11.SE - Prob. 28MPCh. 11.SE - Prob. 29MPCh. 11.SE - Prob. 30MPCh. 11.SE - Prob. 31MPCh. 11.SE - Prob. 32MPCh. 11.SE - Metabolism of S-adenosylhomocysteine (Section...Ch. 11.SE - Reaction of iodoethane with CN- yields a small...Ch. 11.SE - One step in the urea cycle for ridding the body of...Ch. 11.SE - Prob. 36MPCh. 11.SE - Prob. 37MPCh. 11.SE - Propose a mechanism for the following reaction, an...Ch. 11.SE - Prob. 39APCh. 11.SE - The following Walden cycle has been carried out....Ch. 11.SE - Prob. 41APCh. 11.SE - Which reactant in each of the following pairs is...Ch. 11.SE - Prob. 43APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 44APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 45APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 46APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 47APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 48APCh. 11.SE - Propose structures for compounds that fit the...Ch. 11.SE - What products would you expect from the reaction...Ch. 11.SE - Prob. 51APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 52APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 53APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 54APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 55APCh. 11.SE - Order each of the following sets of compounds with...Ch. 11.SE - Order each of the following sets of compounds with...Ch. 11.SE - Prob. 58APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 59APCh. 11.SE - Ethers can often be prepared by SN2 reaction of...Ch. 11.SE - Show the stereochemistry of the epoxide (see...Ch. 11.SE - Prob. 62APCh. 11.SE - In addition to not undergoing substitution...Ch. 11.SE - The tosylate of (2R, 3S)-3-phenyl-2-butanol...Ch. 11.SE - Prob. 65APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 66APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 67APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 68APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 69APCh. 11.SE - (S)-2-Butanol slowly racemizes on standing in...Ch. 11.SE - Reaction of HBr with (R)-3-methyl-3-hexanol leads...Ch. 11.SE - Treatment of 1-bromo-2-deuterio-2-phenylethane...Ch. 11.SE - Prob. 73APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 74APCh. 11.SE - In light of your answer to Problem 11-74, explain...Ch. 11.SE - Prob. 76APCh. 11.SE - Compound X is optically inactive and has the...Ch. 11.SE - When a primary alcohol is treated with...Ch. 11.SE - Prob. 79APCh. 11.SE - Amines are converted into alkenes by a two-step...Ch. 11.SE - The antipsychotic drug flupentixol is prepared by...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Can you explain how I get these here and show the steps plz?arrow_forwardGive the IUPAC name for this compound Hydrocarbon Condensed Formulas Hint C2H5 CH2CH3 expand that in all the formula Part A: (CH3)2CHCH(C2H5)CH2CH2CH3 Give the IUPAC name for this compound. Part B: CH2=C(C2H5)CH2CH2CH3 Give the IUPAC name for this compound. Part C: (CH3)2C=CHC(C2H5)=CH2 Give the IUPAC name for this compound. Part D: CH3C=CCH(C2H5)2 Give the IUPAC name for this compound. Part E: (CH3)3CC=CCH2CH=C(CH3)2arrow_forwardSelect/ Match the correct letter from the image below for the IUPAC names given below: A B C D 3 E F G H K L Part 1. 4-methylheptane For example.mmmm Answer Letter H _for part 1 Part 2. 2,4-dimethylhexane Part 3. 2,3-dimethylpentane Part 4. 2,2-dimethylhexane Part 5. 2-ethyl-1,1,3,3-tetramethylcyclopentane Part 6. 3-ethyl-2-methylpentanearrow_forward
- Can u show the process as to how to get these?arrow_forwardSketch the expected 'H NMR spectra for the following compound. Label all of the H's in the structure and the corresponding signal for the spectra you sketch. Make sure you include the integration value and the splitting pattern for each signal Indicate how many signals you would expect in the 13C NMRarrow_forwardUse IUPAC naming rules to name the following hydrocarbon compounds: CH2-CH3 | a) CH-CH-CH2-CH-CH-CH3 b) | CH2 CH3 | CH3 CH3 \ / C=C H 1 H CH2-CH3 c) d) CH=C-CH3 e) CH3-CH2-CH2-CH=CH-CH3 f) CH2=CH-CH2-CH=CH-CH3 g) CH3-CH2-C = C-CH2-CH3 h)arrow_forward
- Q5 Name the following : a. b. C. d. e.arrow_forward25. Predict the major product of the following reaction. 1 equivalent of each of the starting materials was used. H₂C CH3 CH3 H3C H3C H3C. CH2 + H3C. heat CH3 CH H.C. CH3 H.C H.C CH3 CH CH3 CH3 A B C Earrow_forwardFind chemical structures based on the below information. a) Chemical formula C6H8O Compound is aromatic plus has two 1H NMR peaks that integrated for 3 each that are singlets (it could have more peaks in the 1H NMR b) Chemical Formula: C6H100 Compounds is conjugated 'H NMR has a signal that integrates for 6 and is a doublet IR spectra has a signal at 1730 cm-1arrow_forward
- Jaslev Propose a synthesis of the following starting from benzene and any other reagents and chemicals. No mechanisms are required. Indicate the condition for each step plus the major product for each step. More than two steps are required. Step 1 Step 2 مہد Brarrow_forwardPart C: The line formula for another branched alkane is shown below. i. In the IUPAC system what is the root or base name of this compound? ii. How many alkyl substituents are attached to the longest chain? iii. Give the IUPAC name for this compound.arrow_forwardPart D: Draw the Structural Formula for 4-ethyl-2-methylhexane Part E. Draw the Structural Formula for 1-chloro-3,3-diethylpentane (Chloro = Cl)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning
