
Organic Chemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781305080485
Author: John E. McMurry
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 11.SE, Problem 75AP
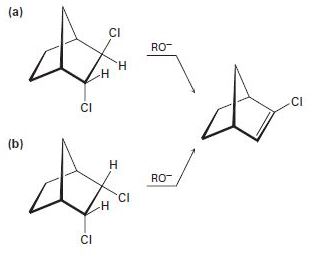
In light of your answer to Problem 11-74, explain why one of the following isomers undergoes E2 reaction approximately 100 times as fast as the other. Which isomer is more reactive, and why?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Write the amididation reaction mechanism of a-aminophenol and acetic acid to produce acetaminophen
For the condensation reaction between Alamine and histamine, please help me write the amididation reaction mechanism. Then write the three letter code for the product of the reaction, then write the one letter code for the product of the reaction. 
How to draw the reaction mechasnism below
Chapter 11 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Ch. 11.1 - Prob. 1PCh. 11.2 - Prob. 2PCh. 11.2 - Prob. 3PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 4PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 5PCh. 11.3 - Rank the following compounds in order of their...Ch. 11.3 - Organic solvents like benzene, ether, and...Ch. 11.4 - Prob. 8PCh. 11.4 - Prob. 9PCh. 11.4 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 11.5 - Rank the following substances in order of their...Ch. 11.5 - 3-Bromo-1-butene and 1-bromo-2-butene undergo SN1...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 13PCh. 11.6 - Review the mechanism of geraniol biosynthesis...Ch. 11.7 - Prob. 15PCh. 11.7 - What alkyl halides might the following alkenes...Ch. 11.8 - Prob. 17PCh. 11.8 - Prob. 18PCh. 11.9 - Prob. 19PCh. 11.12 - Prob. 20PCh. 11.SE - Prob. 21VCCh. 11.SE - From what alkyl bromide was the following alkyl...Ch. 11.SE - Prob. 23VCCh. 11.SE - Prob. 24VCCh. 11.SE - Prob. 25MPCh. 11.SE - Prob. 26MPCh. 11.SE - Prob. 27MPCh. 11.SE - Prob. 28MPCh. 11.SE - Prob. 29MPCh. 11.SE - Prob. 30MPCh. 11.SE - Prob. 31MPCh. 11.SE - Prob. 32MPCh. 11.SE - Metabolism of S-adenosylhomocysteine (Section...Ch. 11.SE - Reaction of iodoethane with CN- yields a small...Ch. 11.SE - One step in the urea cycle for ridding the body of...Ch. 11.SE - Prob. 36MPCh. 11.SE - Prob. 37MPCh. 11.SE - Propose a mechanism for the following reaction, an...Ch. 11.SE - Prob. 39APCh. 11.SE - The following Walden cycle has been carried out....Ch. 11.SE - Prob. 41APCh. 11.SE - Which reactant in each of the following pairs is...Ch. 11.SE - Prob. 43APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 44APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 45APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 46APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 47APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 48APCh. 11.SE - Propose structures for compounds that fit the...Ch. 11.SE - What products would you expect from the reaction...Ch. 11.SE - Prob. 51APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 52APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 53APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 54APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 55APCh. 11.SE - Order each of the following sets of compounds with...Ch. 11.SE - Order each of the following sets of compounds with...Ch. 11.SE - Prob. 58APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 59APCh. 11.SE - Ethers can often be prepared by SN2 reaction of...Ch. 11.SE - Show the stereochemistry of the epoxide (see...Ch. 11.SE - Prob. 62APCh. 11.SE - In addition to not undergoing substitution...Ch. 11.SE - The tosylate of (2R, 3S)-3-phenyl-2-butanol...Ch. 11.SE - Prob. 65APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 66APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 67APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 68APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 69APCh. 11.SE - (S)-2-Butanol slowly racemizes on standing in...Ch. 11.SE - Reaction of HBr with (R)-3-methyl-3-hexanol leads...Ch. 11.SE - Treatment of 1-bromo-2-deuterio-2-phenylethane...Ch. 11.SE - Prob. 73APCh. 11.SE - Prob. 74APCh. 11.SE - In light of your answer to Problem 11-74, explain...Ch. 11.SE - Prob. 76APCh. 11.SE - Compound X is optically inactive and has the...Ch. 11.SE - When a primary alcohol is treated with...Ch. 11.SE - Prob. 79APCh. 11.SE - Amines are converted into alkenes by a two-step...Ch. 11.SE - The antipsychotic drug flupentixol is prepared by...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Name the following molecules with IUpacarrow_forwardWhat is the molecular orbital for cyclopropenyl anion and is it aromatic, antiaromatic or nonaromatic?arrow_forwardUsing the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid and its impact on the protein.arrow_forward
- How to get the predicted product of this reaction belowarrow_forwardPlease help me fill out the chart then using the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Then using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid.arrow_forwardWrite the Esterification reaction mechanism for acetic acid, and one propanol to make propanol ethanoate (molecule that gives peas its odor in flavor)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

Alcohols, Ethers, and Epoxides: Crash Course Organic Chemistry #24; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j04zMFwDeDU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY