
Concept explainers
What products would you expect from the reaction of 1-bromopropane with each of the following?
(a) NaNH2
(b) KOC(CH3)3
(c) NaI
(d) NaCN
(e) NaC≡CH
(f) Mg, then H2O
a)
Interpretation:
The product has to be identified when 1-bromopropane reacts with the given reagents.
Concept introduction:
SN1 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid which yield the corresponding carbocation intermediate, this carbocation intermediate undergoes substitution reaction which yields the corresponding substitution product.
Tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation.
Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergo SN1 substitution reaction.
SN2 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid, the bromine atom attacks back side of the carbon atoms in simultaneous manner and which is bearing alcohol group which yield the corresponding product.
Elimination reaction: An elimination reaction is removal of two substituents in a molecule and forms alkene. An elimination reaction is one or two-step process which based on the mechanism when two substituents removed from the molecule in single step is called E2 reaction. When two substituents are removed from the molecule in two steps is called E1 reaction.
The Grignard reaction:
Alkyl, vinyl, or aryl-magnesium halides (RMgX) is called as Grignard reagent.
Answer to Problem 50AP
The product of the reaction is given below,
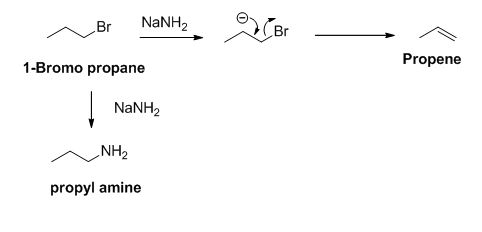
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The reactant of the reaction is given below,
The product of the reaction is given below,
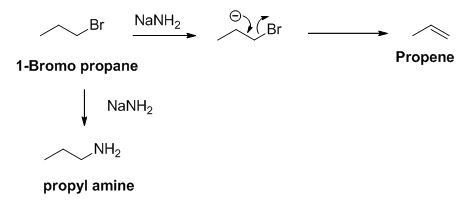
The sodium amide is acts as a base and it abstract the acidic proton from 1-bromo propane gives carbanion, this carbanion under goes elimination reaction gives propene as a major product.
1-bromo propane undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction gives propyl amine as a minor product.
The product of the reaction is given when 1-bromopropane reacts with the given reagents.
b)
Interpretation:
The product has to be identified when 1-bromopropane reacts with the given reagents.
Concept introduction:
SN1 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid which yield the corresponding carbocation intermediate, this carbocation intermediate undergoes substitution reaction which yields the corresponding substitution product.
Tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation.
Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergo SN1 substitution reaction.
SN2 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid, the bromine atom attacks back side of the carbon atoms in simultaneous manner and which is bearing alcohol group which yield the corresponding product.
Elimination reaction: An elimination reaction is removal of two substituents in a molecule and forms alkene. An elimination reaction is one or two-step process which based on the mechanism when two substituents removed from the molecule in single step is called E2 reaction. When two substituents are removed from the molecule in two steps is called E1 reaction.
The Grignard reaction:
Alkyl, vinyl, or aryl-magnesium halides (RMgX) is called as Grignard reagent.
Answer to Problem 50AP
The product of the reaction is given below,
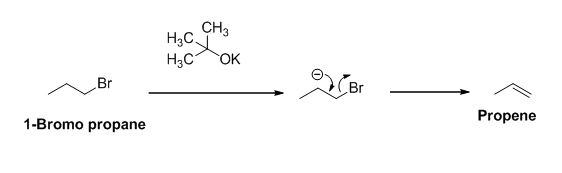
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The reactant of the reaction is given below,
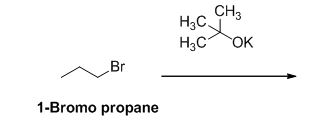
The product of the reaction is given below,
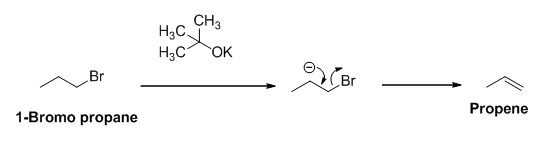
The potassium tertiary butoxide is acts as a base and it abstract the acidic proton from 1-bromo propane gives carbanion, this carbanion under goes elimination reaction gives propene as a major product.
The product of the reaction is given when 1-bromopropane reacts with the given reagents.
c)
Interpretation:
The product has to be identified when 1-bromopropane reacts with the given reagents.
Concept introduction:
SN1 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid which yield the corresponding carbocation intermediate, this carbocation intermediate undergoes substitution reaction which yields the corresponding substitution product.
Tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation.
Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergo SN1 substitution reaction.
SN2 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid, the bromine atom attacks back side of the carbon atoms in simultaneous manner and which is bearing alcohol group which yield the corresponding product.
Elimination reaction: An elimination reaction is removal of two substituents in a molecule and forms alkene. An elimination reaction is one or two-step process which based on the mechanism when two substituents removed from the molecule in single step is called E2 reaction. When two substituents are removed from the molecule in two steps is called E1 reaction.
The Grignard reaction:
Alkyl, vinyl, or aryl-magnesium halides (RMgX) is called as Grignard reagent.
Answer to Problem 50AP
The product of the reaction is given below,
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
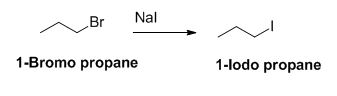
The reactant of the reaction is given below,
The product of the reaction is given below,
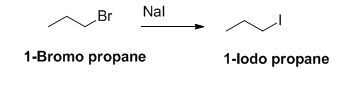
The sodium iodide is acts as nucleophile, 1-bromo propane undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction with sodium iodide gives 1-iodo propane.
The product of the reaction is given when 1-bromopropane reacts with the given reagents.
d)
Interpretation:
The product has to be identified when 1-bromopropane reacts with the given reagents.
Concept introduction:
SN1 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid which yield the corresponding carbocation intermediate, this carbocation intermediate undergoes substitution reaction which yields the corresponding substitution product.
Tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation.
Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergo SN1 substitution reaction.
SN2 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid, the bromine atom attacks back side of the carbon atoms in simultaneous manner and which is bearing alcohol group which yield the corresponding product.
Elimination reaction: An elimination reaction is removal of two substituents in a molecule and forms alkene. An elimination reaction is one or two-step process which based on the mechanism when two substituents removed from the molecule in single step is called E2 reaction. When two substituents are removed from the molecule in two steps is called E1 reaction.
The Grignard reaction:
Alkyl, vinyl, or aryl-magnesium halides (RMgX) is called as Grignard reagent.
Answer to Problem 50AP
The product of the reaction is given below,
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
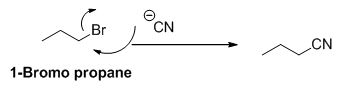
The reactant of the reaction is given below,
The product of the reaction is given below,
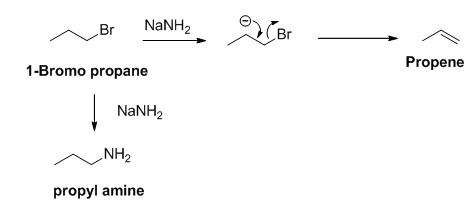
The sodium amide is acts as a base and it abstract the acidic proton from 1-bromo propane gives carbanion, this carbanion under goes elimination reaction gives propene as a major product.
1-bromo propane undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction gives propyl amine as a minor product.
The product of the reaction is given when 1-bromopropane reacts with the given reagents.
e)
Interpretation:
The product has to be identified when 1-bromopropane reacts with the given reagents.
Concept introduction:
SN1 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid which yield the corresponding carbocation intermediate, this carbocation intermediate undergoes substitution reaction which yields the corresponding substitution product.
Tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation.
Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergo SN1 substitution reaction.
SN2 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid, the bromine atom attacks back side of the carbon atoms in simultaneous manner and which is bearing alcohol group which yield the corresponding product.
Elimination reaction: An elimination reaction is removal of two substituents in a molecule and forms alkene. An elimination reaction is one or two-step process which based on the mechanism when two substituents removed from the molecule in single step is called E2 reaction. When two substituents are removed from the molecule in two steps is called E1 reaction.
The Grignard reaction:
Alkyl, vinyl, or aryl-magnesium halides (RMgX) is called as Grignard reagent.
Answer to Problem 50AP
The product of the reaction is given below,
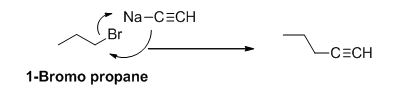
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The reactant of the reaction is given below,
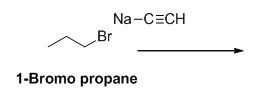
The product of the reaction is given below,
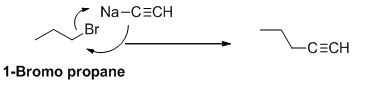
1-bromo propane undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction with given alkyne compound gives the corresponding alkyne product.
The product of the reaction is given when 1-bromopropane reacts with the given reagents.
f)
Interpretation:
The product has to be identified when 1-bromopropane reacts with the given reagents.
Concept introduction:
SN1 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid which yield the corresponding carbocation intermediate, this carbocation intermediate undergoes substitution reaction which yields the corresponding substitution product.
Tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation.
Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergo SN1 substitution reaction.
SN2 reaction:
The alcohol is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid, the bromine atom attacks back side of the carbon atoms in simultaneous manner and which is bearing alcohol group which yield the corresponding product.
Elimination reaction: An elimination reaction is removal of two substituents in a molecule and forms alkene. An elimination reaction is one or two-step process which based on the mechanism when two substituents removed from the molecule in single step is called E2 reaction. When two substituents are removed from the molecule in two steps is called E1 reaction.
The Grignard reaction:
Alkyl, vinyl, or aryl-magnesium halides (RMgX) is called as Grignard reagent.
Answer to Problem 50AP
The product of the reaction is given below,
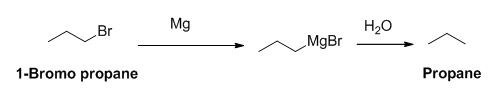
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The reactant of the reaction is given below,
The product of the reaction is given below,
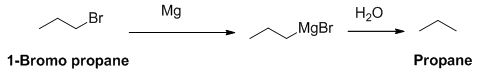
1-bromo propane reaction with magnesium gives Grignard reagent and it undergoes hydrolysis gives propane.
The product of the reaction is given when 1-bromopropane reacts with the given reagents.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- An electrode process takes place at a metal-solution interface. Indicate the current condition that must be met for Faradaic rectification to occur.arrow_forwardAt a metal-solution interface, an electron is exchanged, and the symmetry factor beta < 0.5 is found in the Butler-Volmer equation. What does this indicate?arrow_forwardTopic: Photochemistry and Photophysics of Supramoleculesarrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

