
Concept explainers
3-38 Complete the chart by writing formulas for the compounds formed:
| Br- | MnO4- | O2- | NO3- | SO42- | PO43- | OH- | |
| Li+ | |||||||
| Ca2+ | |||||||
| Co3+ | |||||||
| K+ | |||||||
| Cu2+ |
Interpretation:
Complete the chart by writing formulas.
Concept Introduction:
The compounds which contain ionic bond, which is a type of bond which formed between positive metal ion and negative, non-metal ions.
Answer to Problem 3.38P
The complete chart is as follows:
Explanation of Solution
Polyatomic ion is a group of covalently bonded nonmetal atoms which has an overall electrical charge.
In general, there are two types of ions: positive metal ions and negative non −metal ions.
When a neutral element gain electrons, the negative charge increases on it and it convert into negative ion. This negative ion is always greater than its parent atom.
Similarly, when a neutral element loss electrons, the negative charge decreases on it and it convert into positive ion. This positive ion is always smaller than its parent atom.
The general rules for writing formula of binary compound are as follows:
- To write the formula of positive ion first.
- The write the formula of negative ions after positive ion.
- Using criss-cross method, the charges of both the ions are interchanged.
- The formula shows the lowest whole-number ratio of both the ions.
For example: the symbols of the magnesium and chloride ions are as follows:
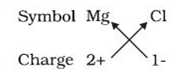
The formula of the ionic compound of these ions is as follows:
The complete chart is as follows:
The chart was completed using the criss-cross method, in which the respective ions are written with their formulas and charge and are then cross multiplied.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- Nonearrow_forward3. A molecular form of "dicarbon", C2, can be generated in gas phase. Its bond dissociation energy has been determined at 599 kJ/mol. Use molecular orbital theory to explain why energy of dissociation for C₂+ is 513 kJ/mol, and that for C2² is 818 kJ/mol. (10 points)arrow_forward9.73 g of lead(IV) chloride contains enough Cl- ions to make ____ g of magnesium chloride.arrow_forward
- 6. a) C2's. Phosphorus pentafluoride PF5 belongs to D3h symmetry group. Draw the structure of the molecule, identify principal axis of rotation and perpendicular (4 points) b) assume that the principal axis of rotation is aligned with z axis, assign symmetry labels (such as a1, b2, etc.) to the following atomic orbitals of the P atom. (character table for this group is included in the Supplemental material). 3s 3pz (6 points) 3dz²arrow_forward2. Construct Lewis-dot structures, and draw VESPR models for the ions listed below. a) SiF5 (4 points) b) IOF4 (4 points)arrow_forward5. Complex anion [AuCl2]¯ belongs to Doh symmetry point group. What is the shape of this ion? (4 points)arrow_forward
- 4. Assign the following molecules to proper point groups: Pyridine N 1,3,5-triazine N Narrow_forward7. a) Under normal conditions (room temperature & atmospheric pressure) potassium assumes bcc lattice. Atomic radius for 12-coordinate K atom is listed as 235 pm. What is the radius of potassium atom under normal conditions? (3 points) b) Titanium metal crystallyzes in hcp lattice. Under proper conditions nitrogen can be absorbed into the lattice of titanium resulting in an alloy of stoichiometry TiNo.2. Is this compound likely to be a substitutional or an interstitial alloy? (Radius of Ti (12-coordinate) is 147 pm; radius of N atom is 75 pm. (3 points)arrow_forwardcan someone answer the questions and draw out the complete mechanismarrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning

